Fused zinc corrosion resistant intermetallic compound Ti-Al-Nb alloy
A technology of intermetallic compounds and molten zinc corrosion resistance, which is applied in the field of new high-niobium titanium-aluminum alloys and intermetallic compounds-Ti-Al-Nb alloys
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
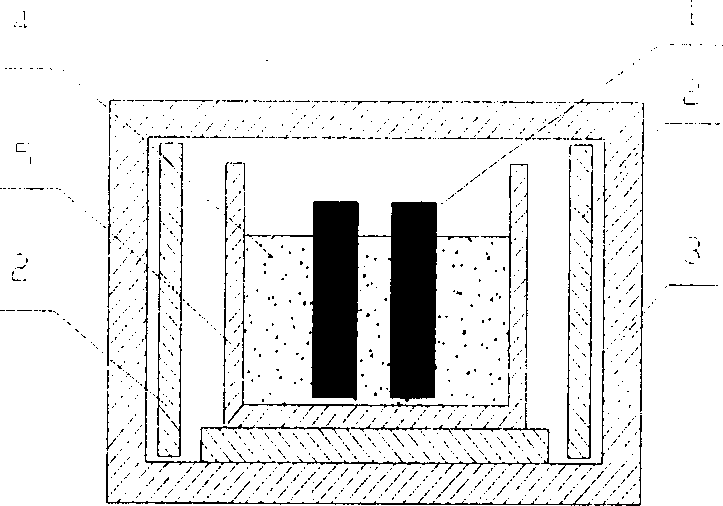
[0023] The nominal composition of the alloy used in the experiment is Ti-45Al-8Nb-0.1W-0.1B-0.1Y) (atomic percentage), and the ingot is melted by vacuum consumable solidification shell. In the experiment, the corrosion resistance of the alloy was compared with that of 316 stainless steel. The specifications of the 316 stainless steel sample and the cast high-niobium titanium-aluminum sample are both 50×20×2mm 3 , Clean the sample with ultrasonic waves before the test. Put the zinc ingot (with an aluminum content of about 0.2% by weight) into a crucible and heat it to melt it, and heat it to 450° C. to keep it warm. Then insert the sample into the zinc liquid, and do the static corrosion resistance life test at 450°C. Observe the changes of the surface topography of the samples in different experimental periods, and measure the thickness loss. figure 1 is the schematic diagram of static corrosion equipment. figure 2 It is a northern scattering photo of the as-cast high Nb-...
Embodiment 2
[0027] The nominal composition of the alloy used in the experiment is Ti-50Al-17Nb-0.5W-1B-1Y) (atomic percentage), and the ingot is smelted by vacuum consumable solidification shell. In the experiment, the corrosion resistance of the alloy was compared with that of 316 stainless steel. The specifications of the 316 stainless steel sample and the cast high-niobium titanium-aluminum sample are both 50×20×2mm 3 , Clean the sample with ultrasonic waves before the test. Put the zinc ingot (with an aluminum content of about 0.2% by weight) into a crucible and heat it to melt it, and heat it to 450° C. to keep it warm. Then insert the sample into the zinc liquid, and do the static corrosion resistance life test at 450°C. Observe the changes of the surface topography of the samples in different experimental periods, and measure the thickness loss.
[0028] The experimental results show that the zinc liquid (containing about 0.2% by weight of aluminum, 450° C.) exhibits super corro...
Embodiment 3
[0030] The nominal composition of the alloy used in the experiment is Ti-55Al-13Nb-2W-1.5B-2Y) (atomic percentage), and the ingot is melted by vacuum consumable solidification shell. In the experiment, the corrosion resistance of the alloy was compared with that of 316 stainless steel. The specifications of the 316 stainless steel sample and the cast high-niobium titanium-aluminum sample are both 50×20×2mm 3 , Clean the sample with ultrasonic waves before the test. Put the zinc ingot (with an aluminum content of about 0.2% by weight) into a crucible and heat it to melt it, and heat it to 450° C. to keep it warm. Then insert the sample into the zinc liquid, and do the static corrosion resistance life test at 450°C. Observe the changes of the surface topography of the samples in different experimental periods, and measure the thickness loss.
[0031] The experimental results show that the zinc liquid (containing about 0.2% by weight of aluminum, 450° C.) exhibits super corros...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com