Anti-static, wet absorption and dyeable core-skin composite fiber and its preparing method
A composite fiber, skin-core technology, used in fiber processing, filament/thread forming, conjugated synthetic polymer rayon, etc., can solve problems such as loss of antistatic properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
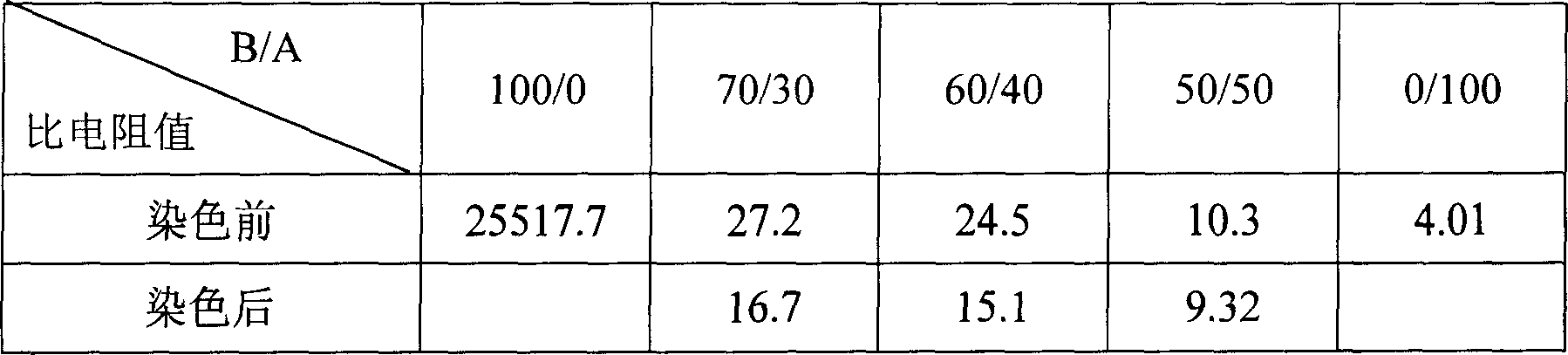
[0015] The sheath-core composite fiber uses two screws to control their respective temperatures to melt the high-temperature and high-pressure cationic dyeable polyester (CDP) (A) and PBT-PEG copolyether ester (B) to form the sheath-core respectively. , transported to the spinning box through their respective melt pipelines, and then the melt is quantitatively sent to the sheath-core composite spinning assembly by the metering pump according to the regulations, extruded, cooled, oiled, and wound to obtain the sheath-core Precursors of fiber-type composite fibers, which can then be stretched and shaped to obtain finished sheath-core fibers. The spinning temperature is 275°C, the winding speed can be adjusted within the range of 2200m / min, the stretching temperature is 80°C, the setting temperature is 156°C, and the stretching ratio is 2.5 times. The equilibrium moisture regain of this fiber is 2.5%, and it can be dyed in any color. Table 1 is a comparison of the specific resis...
Embodiment 2
[0020] The sheath-core composite fiber uses two screws to control their respective temperatures to melt the sheath-core atmospheric pressure boiling dyeable cationic dyeable polyester (ECDP) (B) and PET-PEG copolyether ester (A) respectively. Raw materials, B / A=70 / 30 (mass ratio), are transported to the spinning box through their respective melt pipelines, and then the melts are quantitatively sent to the sheath-core composite spinning assembly by the metering pump for extrusion. out, cooling, oiling, hot roller stretching, and winding to obtain the finished sheath-core composite fiber yarn. The spinning temperature is 270°C, the winding speed is adjusted within the range of 1800m / min, the stretching temperature is 80°C, the setting temperature is 160°C, and the stretching ratio is 2.7 times. The equilibrium moisture regain of the fiber is 2.6%, and it can be dyed in any color. The specific resistance value of the fiber measured under standard conditions is 10. 7 Ω·cm.
Embodiment 3
[0022] The sheath-core composite fiber uses two screws to control their respective temperatures to melt the sheath-core atmospheric pressure boiling dyeable cationic dyeable polyester (ECDP) (B) and PBT-PEG copolyether ester (A)2 respectively. Raw materials, B / A=72 / 28 (mass ratio), are transported to the spinning box through their respective melt pipelines, and then the melts are quantitatively sent to the sheath-core composite spinning assembly by the metering pump for extrusion. After drawing, cooling, oiling and winding, the raw silk of sheath-core composite fiber is obtained, and the raw silk is stretched and shaped to obtain the finished sheath-core fiber. The spinning temperature is 270°C, the winding speed can be 1200m / min, the stretching temperature is 80°C, the setting temperature is 155°C, and the stretching ratio is 3.2 times. The sheath-core composite fiber fabric also has good antistatic performance. The initial frictional static voltage of the fabric is only 0.14...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific resistance value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Breaking strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com