Insulin resistance improving agent
A technology of insulin resistance and improving agent, applied in the direction of organic active ingredients, metabolic diseases, drug combination, etc., to achieve the effect of improving insulin resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] 1. Test method
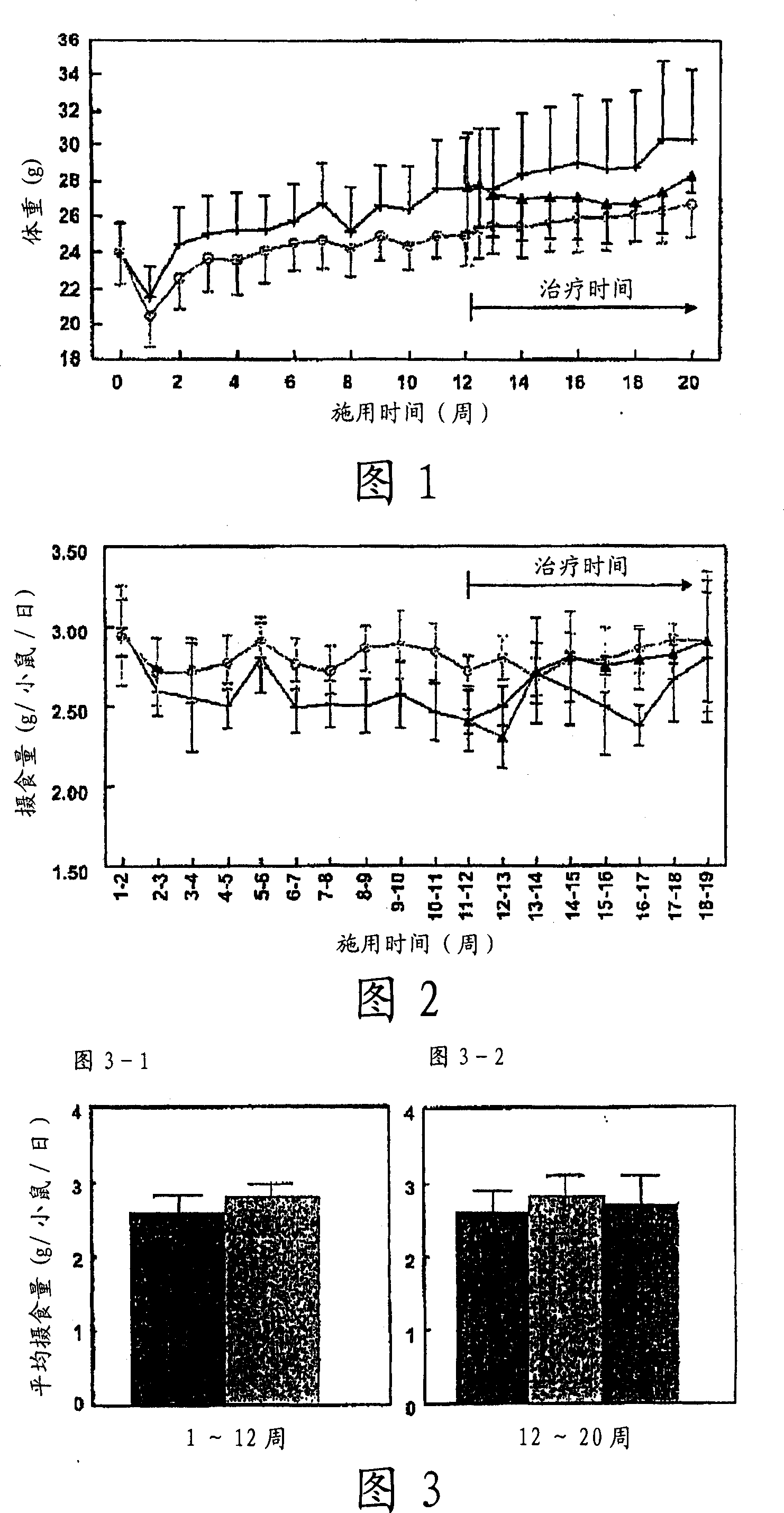
[0080]ApoE3 Leiden mice (male, TNO Pharma, Leiden, The Netherlands) (n=45) were fed a high-fat diet (45.4% fat) for three weeks, according to body weight and serum parameters (total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride Value (TG), blood glucose level (Glc)) were divided into two groups, one group (n=30) continued to be fed with high-fat food (high-fat food group) as it was, and the other group (n=15) was given high-fat food Foods containing 1.5 (w / w)% cholemide in (cholemide prevention group).
[0081] After 12 weeks, the high-fat food group was further divided into two groups according to the aforementioned body weight and serum parameters (TC, TG, Glc), one group was the high-fat food group (control group, n=15), and the other group was given high-fat food group. Diets containing 1.5 (w / w) % cholemide in fatty food (cholemide treatment group, n=15).
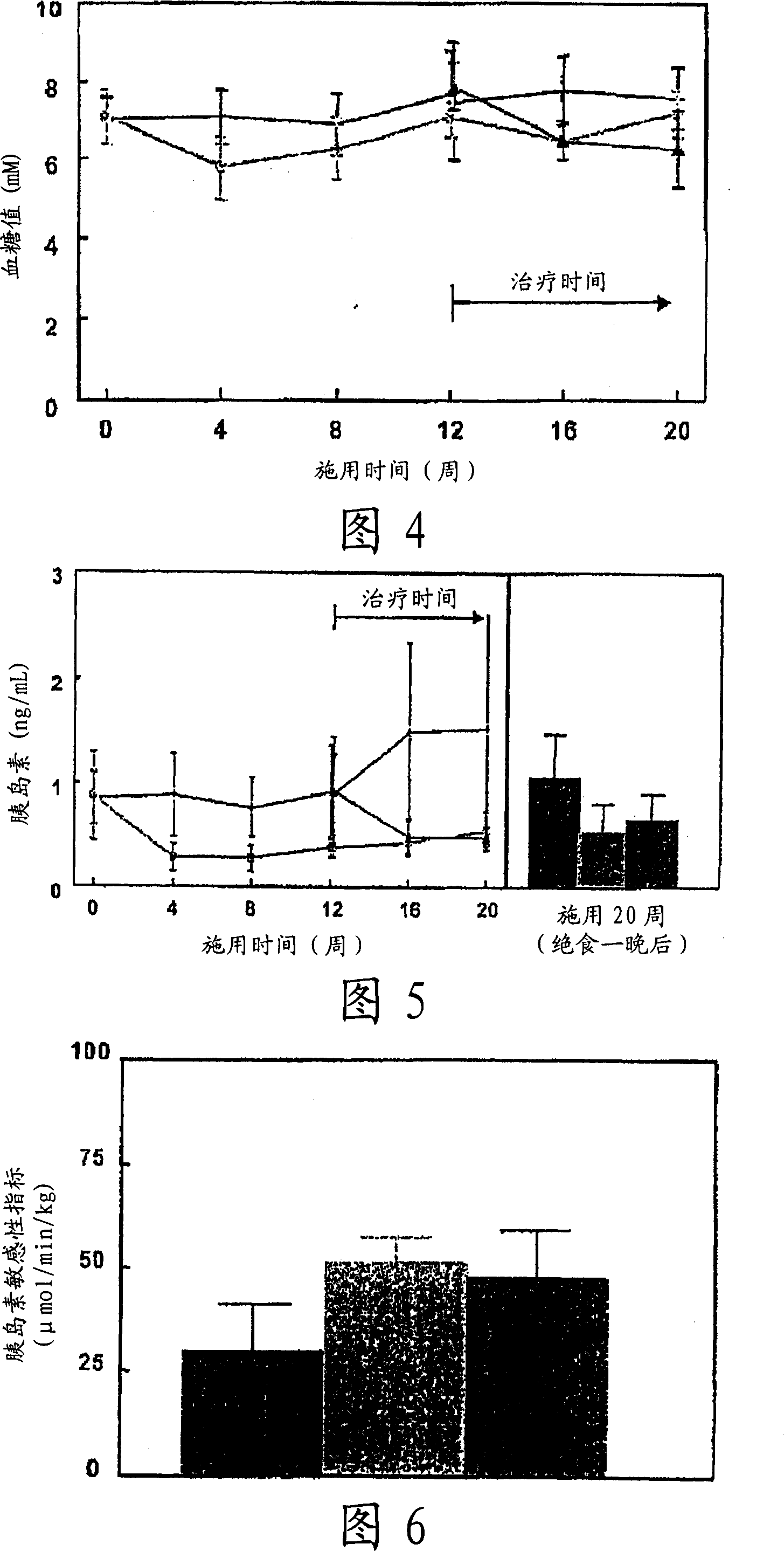
[0082] Eight weeks later, insulin resistance was determined using a hyperinsulinemic clamp. The animal w...
Embodiment 2
[0102] 1. Test method
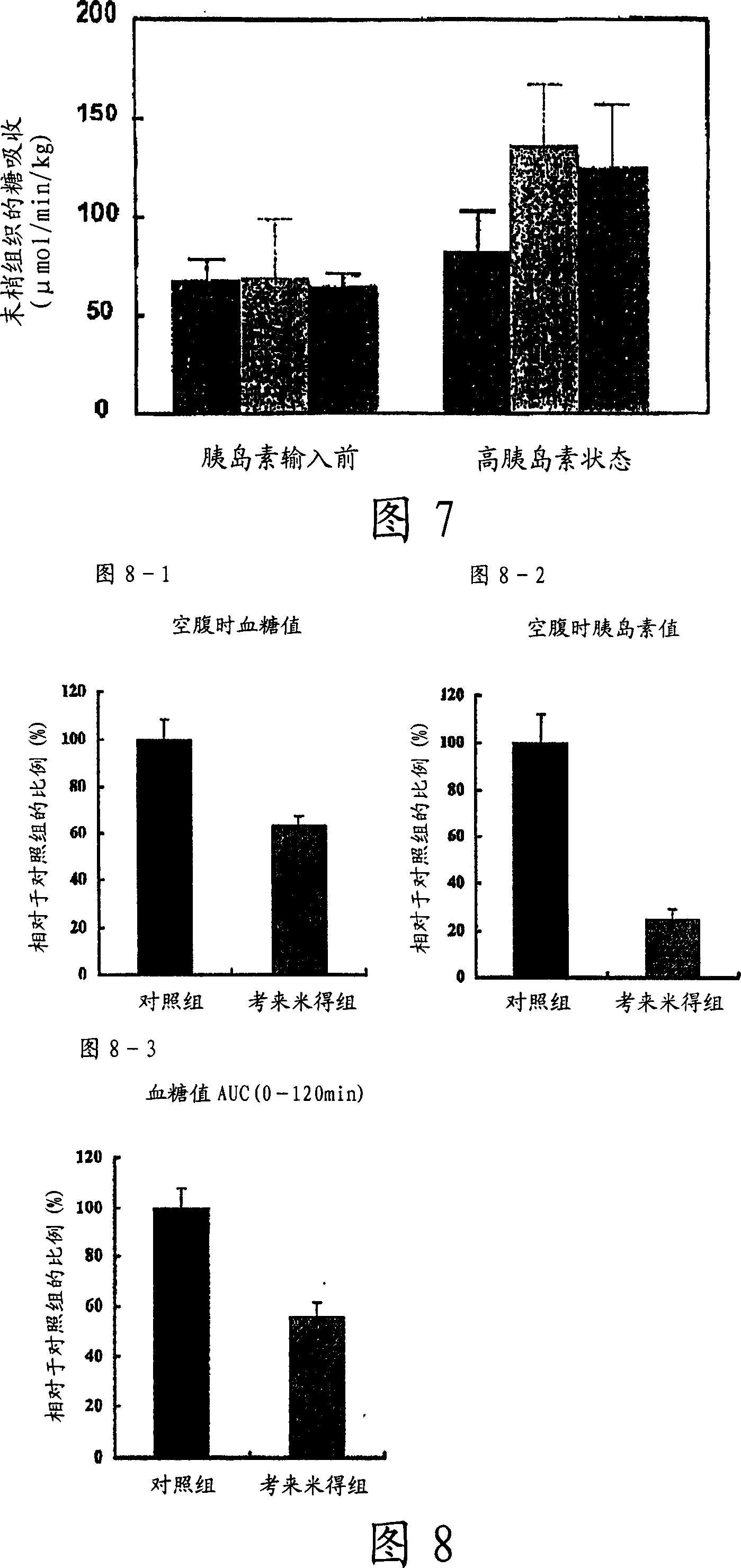
[0103] KKAy mice (male, Nippon CLEA, n=8) were used. The control group was fed a high-fat diet (23.6% fat), and the cholemide group was fed a high-fat diet containing 2% cholemide. In the second week after the administration, the glucose tolerance test was carried out according to the conventional method. The mice were fasted overnight, blood was collected before glucose tolerance, and then glucose solution was orally administered, and blood glucose levels were measured 30, 60, 90, and 120 minutes later. The blood glucose value AUC (0-120 minutes) was calculated by using the obtained blood glucose value. Fasting blood glucose and fasting insulin values were measured using blood samples before glucose tolerance.
[0104] 2. Results
[0105] (1) fasting blood sugar level
[0106] Figure 8-1 shows the fasting blood glucose values of the control group and the colemide group. The fasting blood glucose level of the colemide group was significantly l...
Embodiment 3
[0113] 1. Test method
[0114] KKAy mice (male, Nippon CLEA, n=8) were used. The control group was fed with high-fat diet (23.6% fat), and the colesevelam hydrochloride group was fed with high-fat diet containing 2% colesevelam hydrochloride. In the second week after the administration, the glucose tolerance test was carried out according to the conventional method. The mice were fasted overnight, blood was collected before glucose tolerance, and then glucose solution was orally administered, and blood glucose levels were measured 30, 60, 90, and 120 minutes later. The blood glucose value AUC (0-120 minutes) was calculated by using the obtained blood glucose value. Fasting blood glucose and fasting insulin values were measured using blood samples before glucose tolerance.
[0115] 2. Results
[0116] (1) fasting blood sugar level
[0117] Figure 9-1 shows the fasting blood glucose values of the control group and colesevelam hydrochloride group. The fasting blood gluc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com