Method for producing cellulose ester acetate by using plant cellulose
A technology of cellulose acetate and plant cellulose, applied in the field of preparation of cellulose acetate, can solve the problem of high cost of raw materials, and achieve the effects of improving reaction rate, expanding application scope and abundant raw material sources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
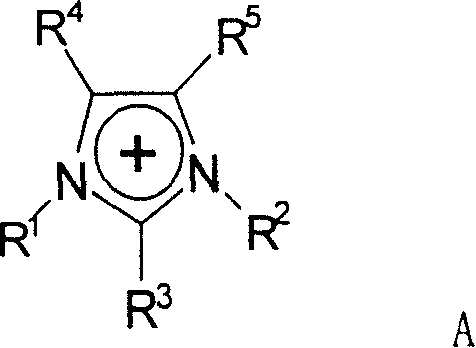
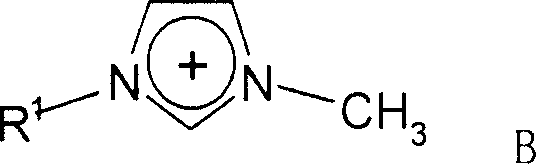
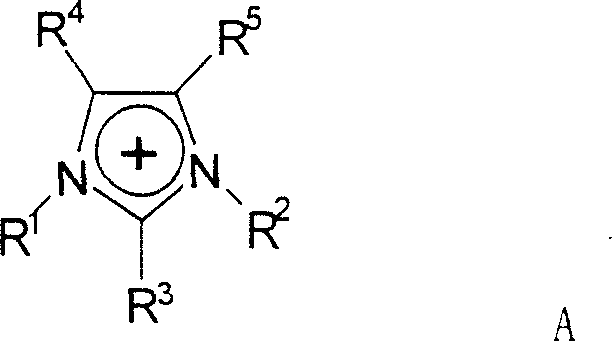
[0031] Weigh about 0.6g of corn cob cellulose and 59.4g of ionic liquid 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (AMIMCl), put them into a round bottom flask, heat in an oil bath to 80°C, seal and stir vigorously 2h. A clear and transparent cellulose solution was obtained, and the concentration of the cellulose solution was 1% (mass fraction). At the same time, acetic anhydride (about 1.05 ml) was added to the solution so that the molar ratio of acetic anhydride to cellulose glucose unit was 3:1, and the reaction was carried out for 1 h. After the reaction was completed, the product was repeatedly washed with water, then placed in a vacuum drying oven, and dried at 60°C for 24 hours; at the same time, the water in the washing liquid was removed by rotary evaporation to realize the recovery of the ionic liquid.
[0032] Weigh 0.1 g of the intermediate product, dissolve in 3 ml of dichloromethane-methanol mixed solvent (volume ratio 9:1), dissolve at room temperature for 2 h, and t...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Weigh about 0.6g of corn stalk cellulose and 9.6g of ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate (EMIMAc), put them into a round bottom flask, heat to 60°C in an oil bath, seal and stir vigorously for 4h . A clear and transparent cellulose solution was obtained, and the concentration of the cellulose solution was 4% (mass fraction). The temperature of the oil bath was raised to 90°C, and acetic anhydride (about 1.58 ml) was added to the solution at the same time, so that the molar ratio of acetic anhydride to cellulose glucose unit was 4.5:1, and the reaction was carried out for 8 hours.
[0035] Ionic liquid recovery and product separation are the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0037] Weigh about 0.6g of peanut shell cellulose and 9.6g of ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (BMIMCl), put them into a round bottom flask, heat to 90°C in an oil bath, seal and vigorously stir mechanically for 6h. A clear and transparent cellulose solution was obtained, and the concentration of the cellulose solution was 4% (mass fraction). The temperature of the oil bath was raised to 120° C., and acetic anhydride (about 2.45 ml) was added to the solution at the same time, so that the molar ratio of acetic anhydride to cellulose glucose unit was 7:1, and the reaction was carried out for 12 hours.
[0038] Weigh 0.1 g of the intermediate product, dissolve it in 5 ml of dichloromethane-methanol mixed solvent (volume ratio 9:1), dissolve at room temperature for 4 h, and then filter with suction to obtain a clear and transparent filtrate. Settling and filtering the filtrate in n-hexane, and collecting the filter residue, the filter residue is cellulose acetate....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com