Cellulose nano-fiber/polymethyl methacrylate composite film preparation method
A polymethyl methacrylate and nanofiber technology, applied in the direction of pulping with organic solvents, can solve the problems of multi-energy, low aspect ratio, fiber interruption, etc., and achieve excellent mechanical properties and rich sources of raw materials , The effect of thermal performance improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
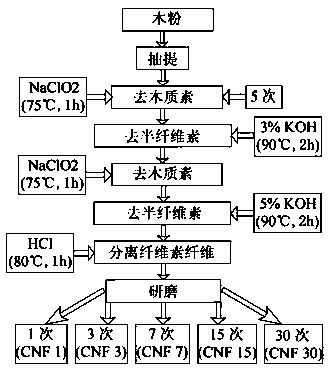
[0026] Preparation of cellulose nanofiber / polymethyl methacrylate composite membrane: step 1) raw material treatment, take poplar wood powder, and use a combination of sieves with apertures of 60 mesh and 70 mesh to screen to obtain wood powder with a fineness of 60 to 70 mesh, and then Take by weighing 15g wherein for subsequent use, measure the toluene of 220ml and the ethanol of 110ml with measuring cylinder, mix the two and pour in the flask of Soxhlet extractor, put into Soxhlet extractor to 15g wood powder, carry out benzene Alcohol extraction treatment, the temperature is controlled at 120 °C, and the time is 6 h. After extraction, the wood powder is taken out, placed in a petri dish, and dried naturally in a fume hood for 24 h.
[0027]Step 2) Chemical treatment: Weigh 10 g of extracted wood flour, add appropriate amount of distilled water to filter several times, then put it into a beaker and add 500 ml of distilled water, 3 ml of glacial acetic acid and 3 g of sodiu...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Weigh 10 g of extracted wood powder, add appropriate amount of distilled water and filter several times. After the last pass of filtration is completed, put it into a beaker and add 500 ml of distilled water, 3 ml of glacial acetic acid and 3 g of sodium chlorite. Then heat treatment in a water bath in a collector type magnetic heating stirrer for 1 h at a temperature of 75°C. After the reaction was completed, 3 ml of glacial acetic acid and 3 g of sodium chlorite were added, and the reaction was continued under the same conditions for 1 h. This step was repeated 5 times in total. After the reaction is complete, use distilled water to filter and wash repeatedly until the pH value of the aqueous suspension is close to 7.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Prepare 500 ml of potassium hydroxide solution with a mass concentration of 3%, put the sample prepared in Example 1 into a beaker and pour it into the prepared solution, and then heat it in a water bath for 2 hours at a temperature of 90°C. After the reaction was finished, it was repeatedly filtered and washed with distilled water until the pH value of the aqueous suspension was close to 7.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fineness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thermal expansion coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thermal expansion coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com