Methods and compositions utilizing rad51
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Immunofluorescent Staining of Human Breast Cancer Cells
[0092] Breast tumour cells have mutated p53 and have various types of chromosomal aberrations like insertions, deletions, rearrangements, amplifications etc. Recombination proteins such as Rad51 could evidently participate in such processes. In order to better understand the role of uncontrolled recombination and its role in tumour formation and progression, the status of Rad51 protein in breast tumour cells by staining them with anti Rad51 antibodies was done.
[0093] Detailed methods of cloning and expression of HsRad51 gene in E. coli, purification of recombinant HsRad51 protein with six histidine residues at it's aminoterminal end and preparation of ployclonal antibodies against HsRad51 protein were described previously by Haaf, Golub et al. 1995, supra, which is expressly incorporated herein by reference.
[0094] Immunofluorescent staining with anti-Rad51 protein antibodies. Monolayer cultures of different cell substrates (see ...
example 2
Nuclear Foci of Human Recombination Protein Rad51 in Nucleotide Excision Repair Defective Cells
[0104] Eurkaryotic cells have several different mechanisms for repairing damaged DNA (for review see R. Wood, 1996). One of the major pathway is nucleotide excision repair (NER), which excises damage within oligomers that are 25-32 nucleotides long. Patients with recessive heredity disorder XP have defects in one of several enzymes, which participate in ER. There are seven XP groups (XP-A to XP-G), which have defects in the initial steps of the DNA excision repair.
[0105] DNA damage is removed several-fold faster from transcribed genes than from non-transcribed, mainly due to preferential NER of the transcribed strand (for review see Hanawalt, 1994). This mechanism does not function in Cockayne's syndrome (CS) patients.
[0106] NER defective cells, evidently, sustain increased amount of DNA damage. Thus we evaluated NER defective cells from XP and CS cells for an increased amount of Rad51 pro...
example 3
Higher Order Nuclear Structures of Rad51 and Its Exclusion Into Micronuclei After Cell Damage
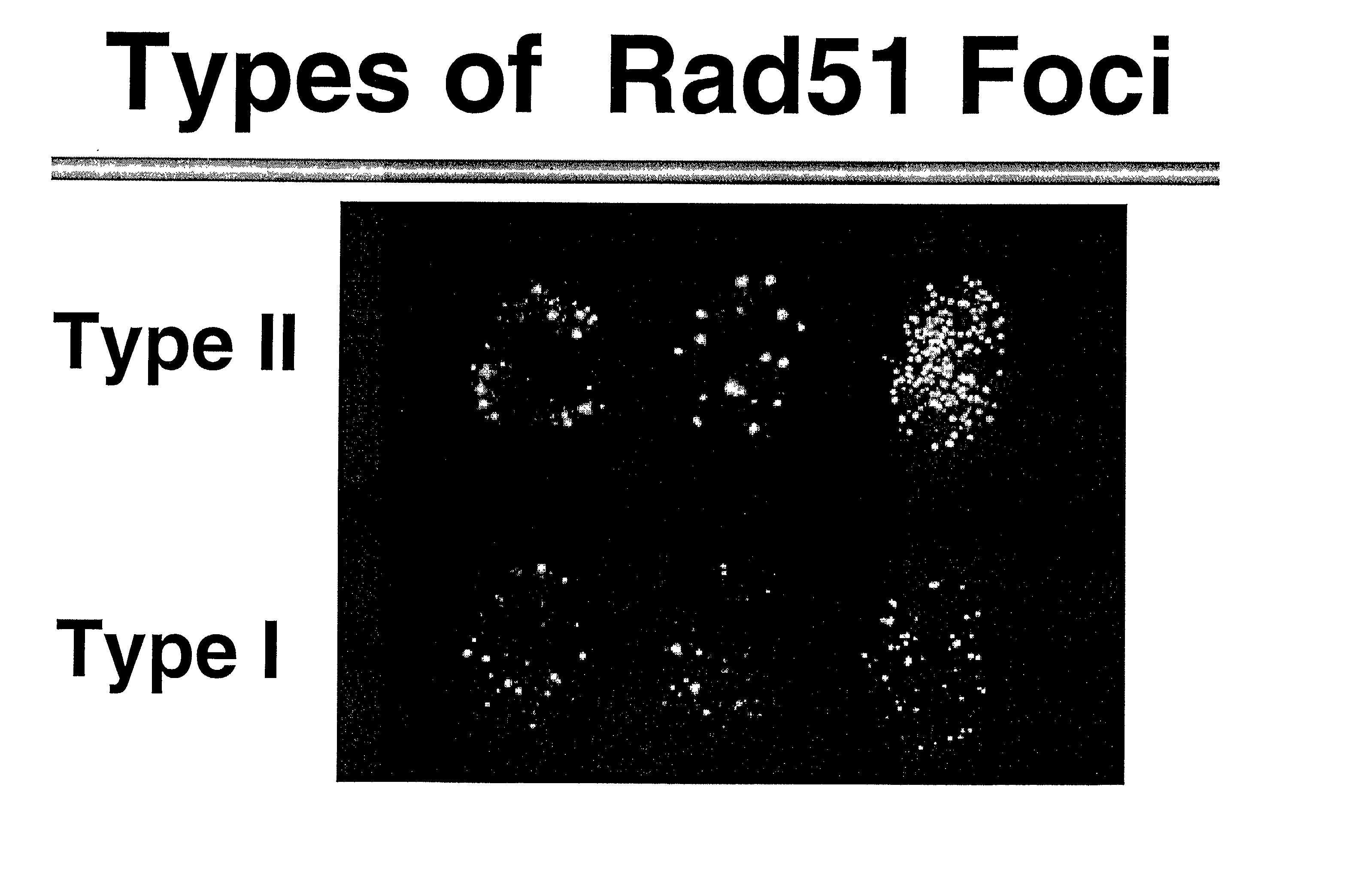
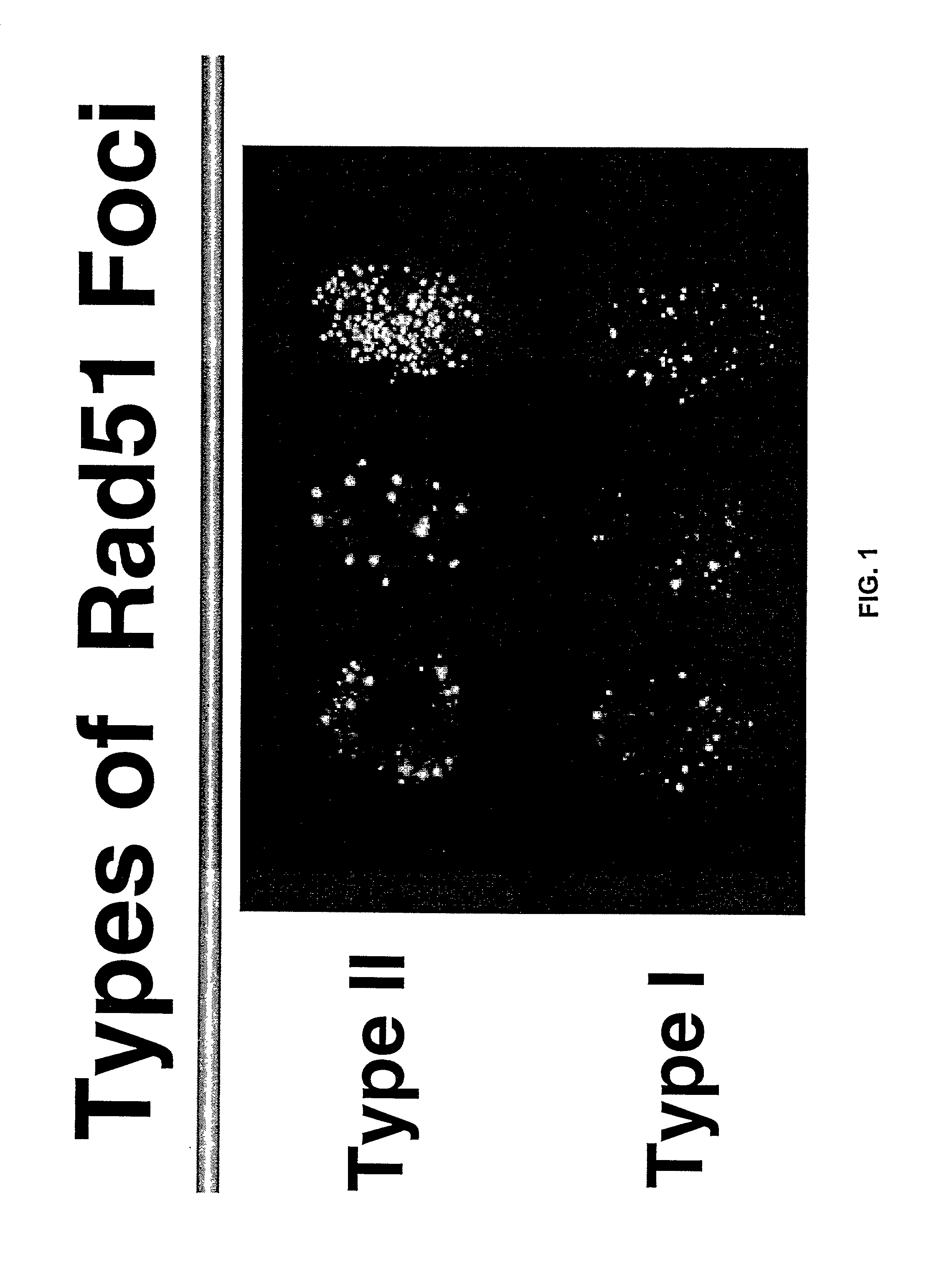
[0116] Previous studies have revealed a time- and dose-dependent increase of nuclear HsRad51 protein foci after DNA damage introduced into the genome by various agents (Haaf et al., 1995, supra). Here we show that when the damaged cells are allowed to recover, these Rad51 foci form specific higher-order nuclear structures. Finally, all the focally concentrated Rad51 protein is eliminated into micronuclei that undergo apoptotic genome fragmentation. Treatment of cells with clastogens and aneuploidogens implements a mechanism that affects the nuclear distribution of Rad51 protein and targets Rad51 foci, most likely along with irreversibly damaged DNA into micronuclei. To examine the role of Rad51 protein in DNA repair and cell proliferation, we have analyzed the intranuclear distribution of overexpressed Rad51 protein during the cell cycle and in cell populations proceeding through apoptosis.
[...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com