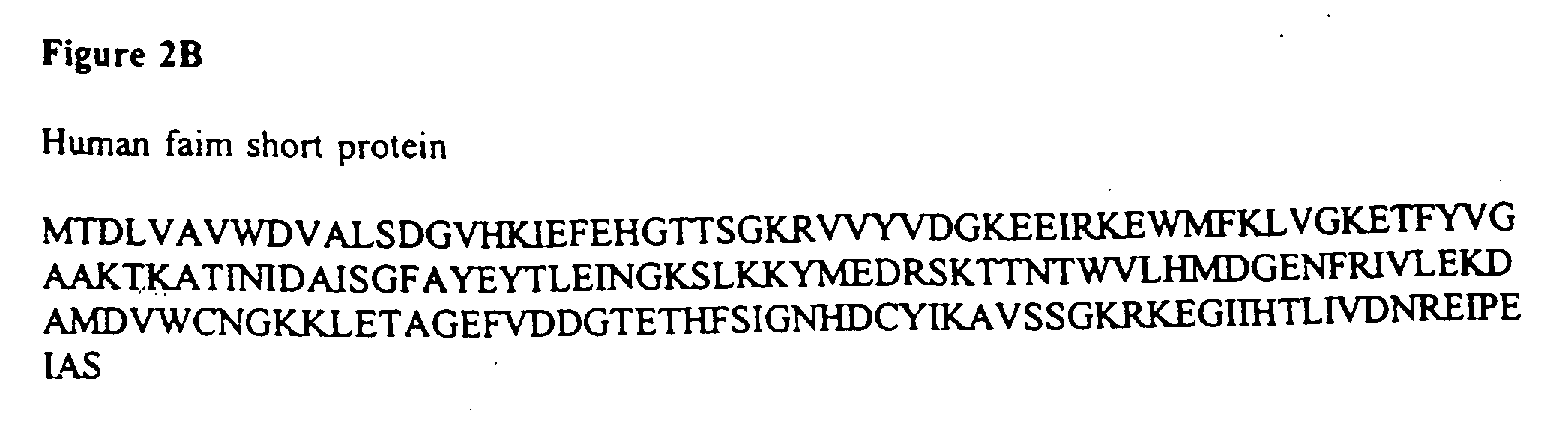Novel genes and methods that modulate apoptosis
a technology of apoptosis and genes, applied in the field of new genes and methods that modulate apoptosis, can solve the problems of hindering the screening of potential therapeutics, lack of understanding, and negatively interfering with the host process, and achieve the effect of reducing the number of cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment i
[0119] In previous work we showed that B cell treatment with anti-Ig for only the final 1-12 hours of a 48 hour culture with CD40L produced a time-dependent increase in Fas-resistance that was abrogated by cycloheximide (Foote et al. "Intracellular signaling for inducible antigen receptor-mediated Fas resistance in B cells" J. Immunol. 157:1878-1885, 1996). Additional experiments demonstrated that the induction of Fas-resistance in CD40L-stimulated B cells by anti-Ig treatment for 6 hours was completely blocked by the addition of actinomycin D (data not shown). These results strongly suggest that transcriptional activation and gene expression are required for the receptor-specific induction of the Fas-resistant state. For this reason, genes that oppose Fas-mediated apoptosis might be captured by identifying transcripts expressed uniquely in Fas-resistant B cells.
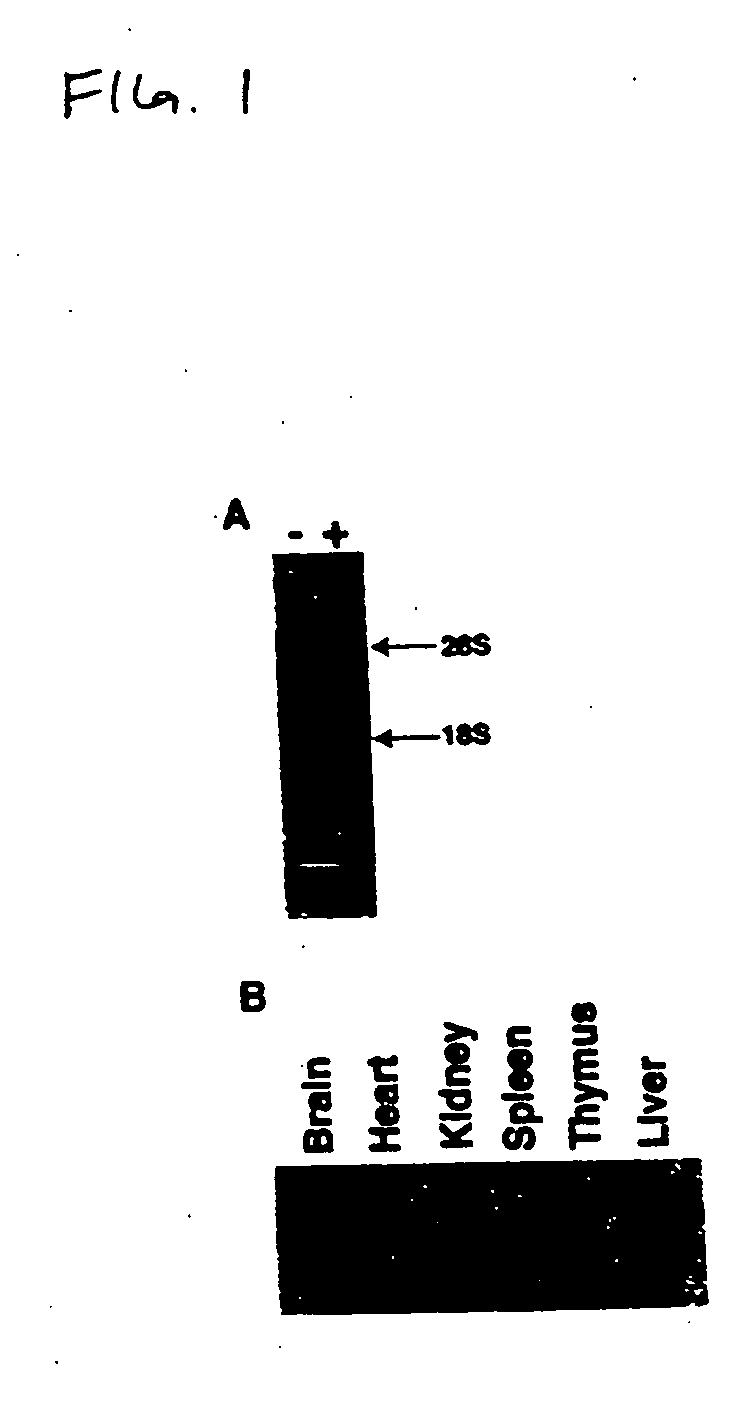
[0120] To identify genes expressed coordinately with the induction of Fas-resistance we employed a differential display st...
experiment ii
[0121] Using a radiolabeled probe generated by PCR, a murine thymic cDNA library was screened and the DNA from positive plaques sequenced. A number of overlapping clones were identified whose consensus sequence was approximately 1.2 kb, consistent with the expression data described above. Subsequently a full-length clone was identified that contained an in-frame STOP codon upstream of the START methionine, and possessed, in the 3' UTR, an RNA instability motif, polyA+ consensus motifs and a polyA+ tail (Malter "Identification of an AUUUA-specific messenger RNA binding protein" Science 246:664-666, 1989). This cDNA appeared to encode a novel 179 amino acid open reading frame (FIG. 2). Structural analysis predicted a b-strand-rich, stable, soluble protein with a slightly acidic p1 (pH 5.4). No substantial regions of homology with any other sequence are present.
experiment iii
[0122] To determine the capacity of the isolated cDNA clone to produce resistance to Fas-mediated apoptosis, BAL-17 murine B lymphoma cells were transfected with the pBKCMV expression vector. BAL-17 cells were chosen because their activation responses mimic primary B cells in a variety of ways and they are readily transfectable (Chiles et al. "Cross-linking of surface Ig receptors on murine B lymphocytes stimulates the expression of nuclear tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate-response element binding-proteins" J. Immunol. 146:1730-1735, 1991; Mizuguchi et al. "Protein kinase C activation blocks anti-IgM-mediated signaling in BAL-17 B lymphoma cells" J. Immunol. 139:1054-1059, 1987; Seyfert et al. "Egr-1 expression in surface Ig-mediated B cell activation:kinetics and association with protein kinase C activation" J. Immunol. 145:3547-3553, 1990). Like primary B cells, unstimulated BAL-17 B cells express little Fas, but treatment with CD40L induces Fas expression and sensitivity to Fas-medi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com