Oxidation resistant treatment for metallic medical devices
a technology for metallic medical devices and treatment methods, applied in the direction of prosthesis, furnaces, impression caps, etc., can solve the problems of residual chemical impurities on the treated device, and achieve the effect of efficient passivating a metallic medical device, reducing or eliminating the possibility of residual chemical impurities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
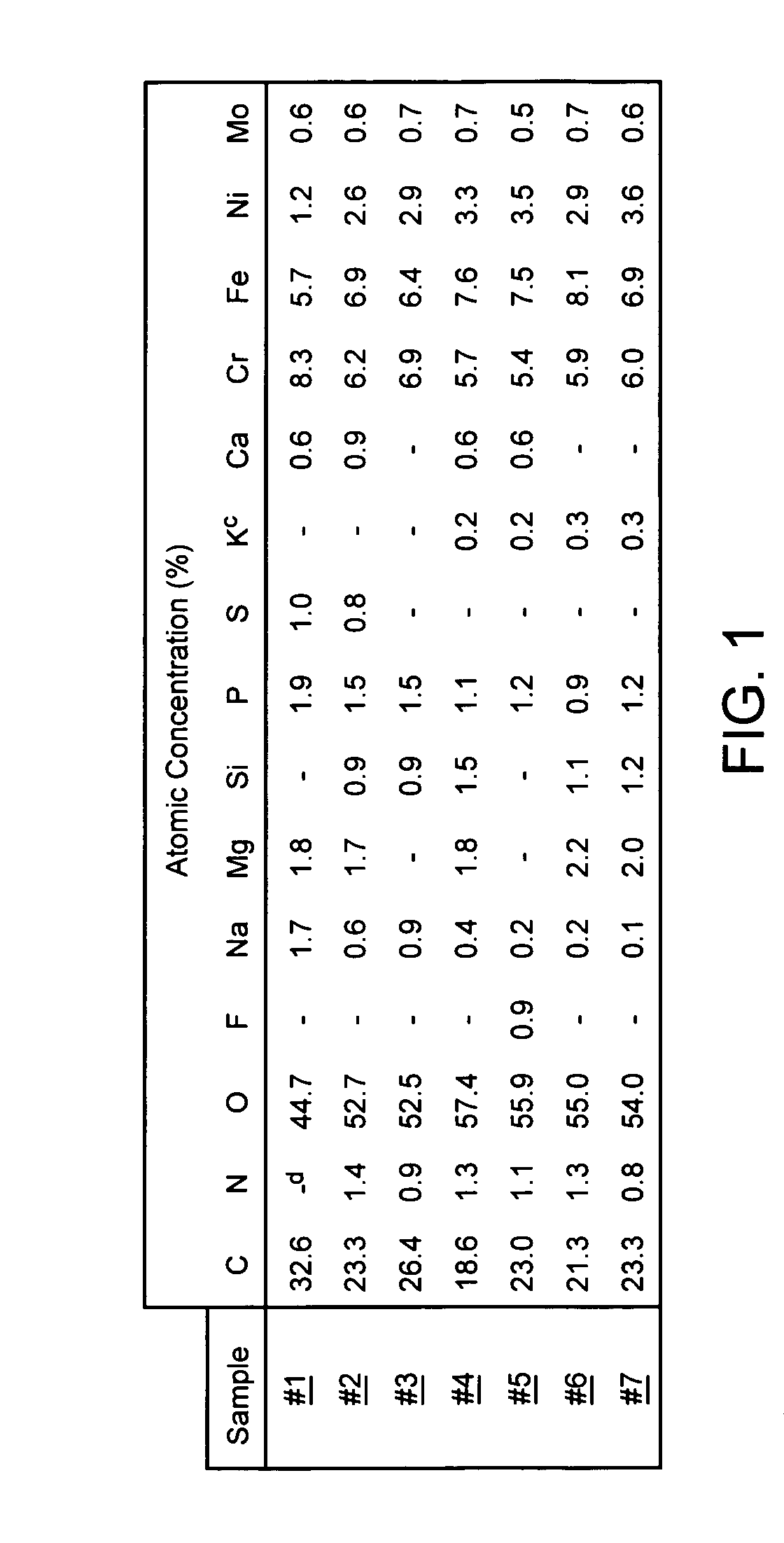
[0024] Seven stainless steel S670 stents manufactured by Medtronic AVE were washed for three minutes within an ultrasound bath containing 99% isopropyl alcohol (IPA). Thereafter, the seven stents were removed from the IPA bath and dried within a gaseous flow of nitrogen.
[0025] Once dried, the scents were number 1 through 7. Sample number 1 was left untreated. Sample numbers 2 through 7 underwent passivation using the oxidation treatment disclosed herein. A corona discharge device included an electrode was positioned within an oxygen environment. Approximately 18 kV of direct current electrical energy was applied to the electrode, thereby ionizing the oxygen proximate to the electrode and resulting in the creation of a ionizing plasma. As Table 1 shows, sample numbers 2-7 were exposed to a plasma created from a corona discharge device for varying lengths of times.
TABLE 1SAMPLE NO.CORONA EXPOSURE TIME1 0 sec (control)2 5 sec.310 sec.420 sec.520 sec. (Dwell)660 mm. (Dwell)795 mm. (D...
example 2
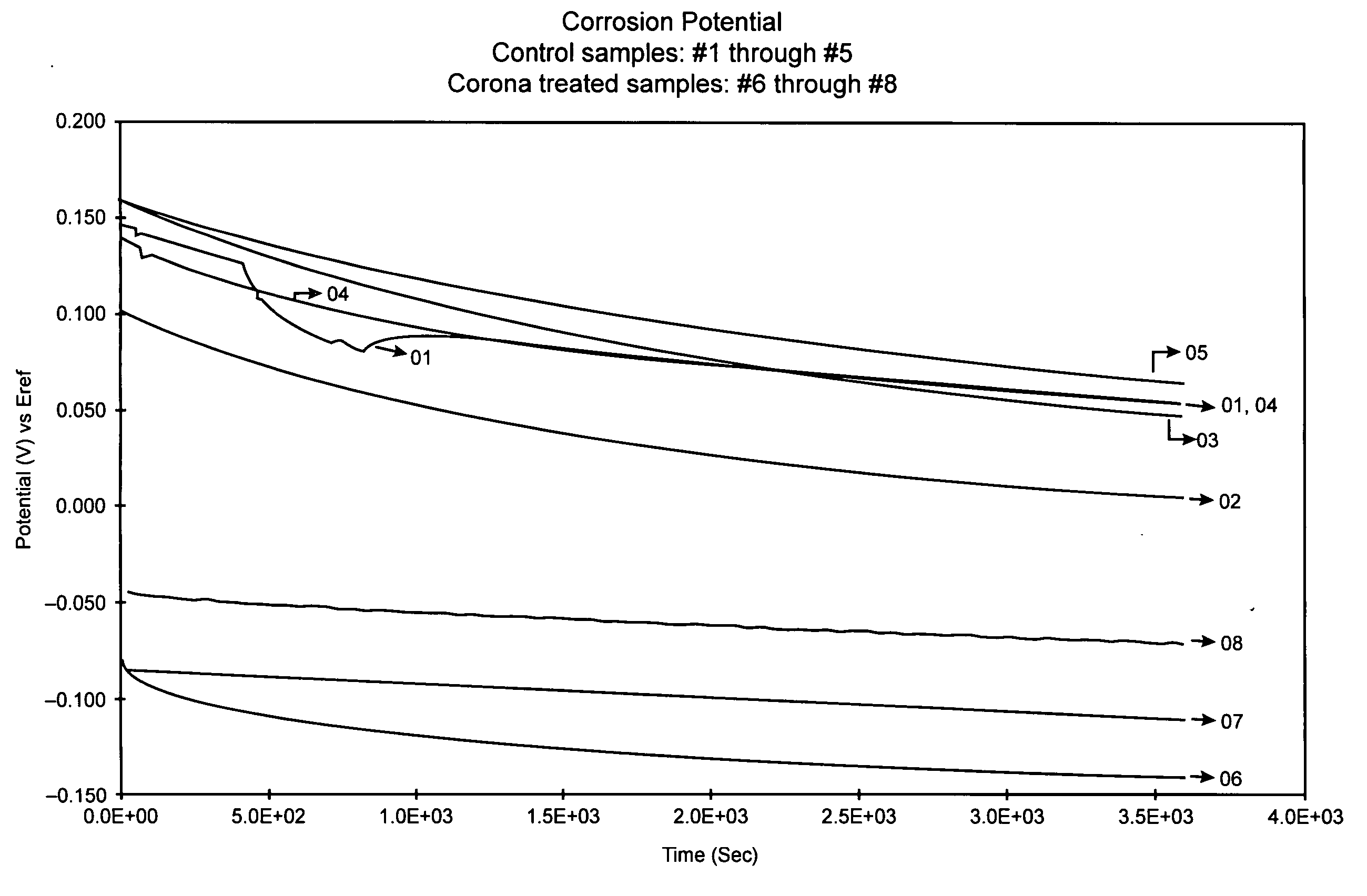
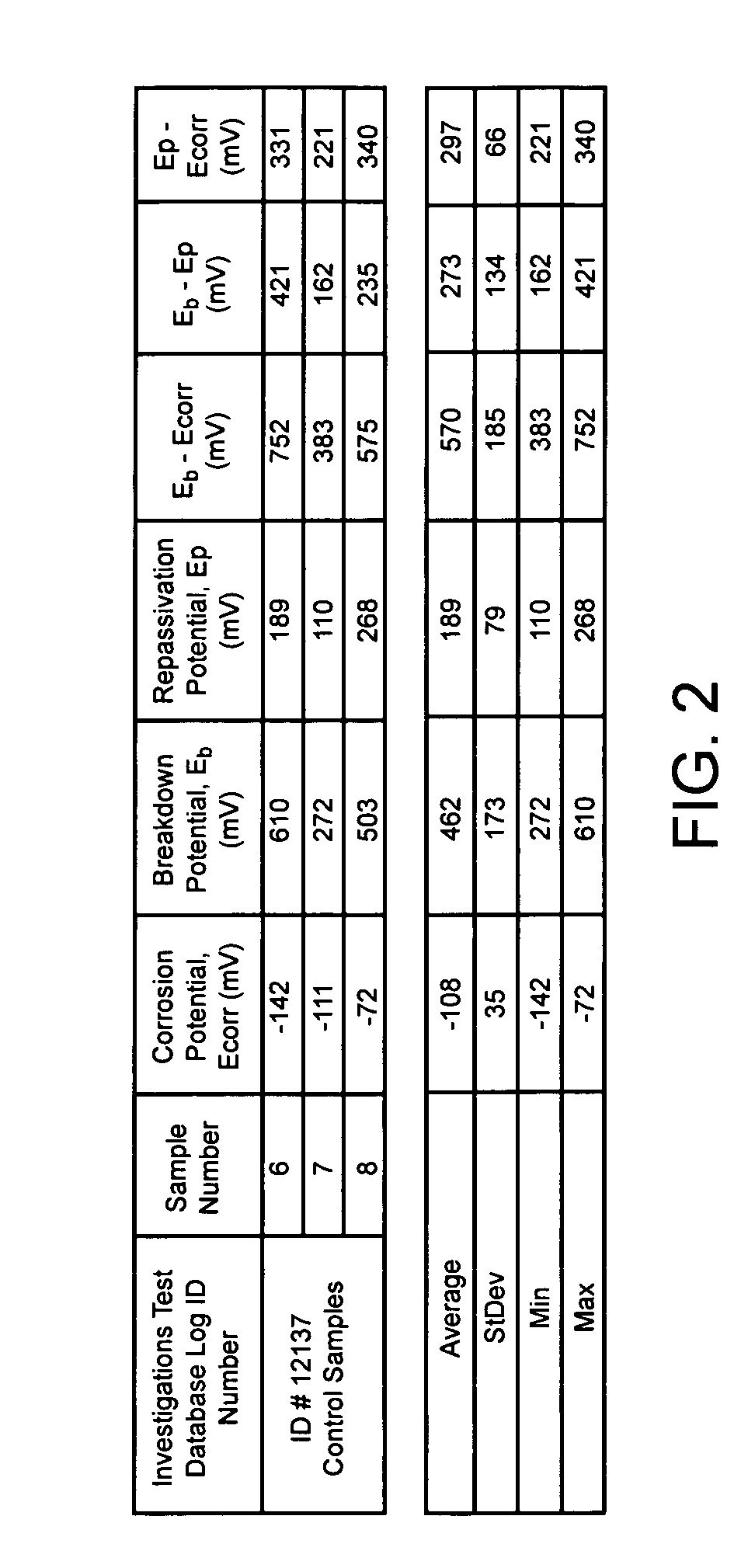
[0028] Eight stainless steel S670 stents manufactured by Medtronic AVE were washed for three minutes within an ultrasound bath containing 99% isopropyl alcohol (IPA). Thereafter, the eight stents were removed from the IPA bath and dried within a gaseous flow of Nitrogen.
[0029] Once dried, the stents were number 1 through 8. Sample numbers 6-8 were left untreated. Sample numbers 1 through 5 underwent passivation using the oxidation treatment disclosed within. A corona discharge device included an electrode was positioned within an oxygen environment. Approximately 18 kV of direct current electrical energy was applied to the electrode, thereby ionizing the oxygen proximate to the electrode and resulting in the creation of a ionizing plasma. As Table 1 shows, sample numbers 1-5 were exposed to the plasma created from a corona discharge device for varying lengths of times between 5 seconds and 10 seconds.
TABLE 3SAMPLE NO.CORONA EXPOSURE TIME15-10 sec.25-10 sec.35-10 sec.45-10 sec.55-...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Metallic bond | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Corrosion resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com