Electromagnetic valve system
a technology of electromagnetic valves and valve bodies, applied in the direction of non-mechanical valves, magnetic bodies, machines/engines, etc., can solve the problems of requiring more than one crankshaft revolution to make the change, poor drivability, and slow disassembly and assembly, etc., to achieve easy movement between positions, increase or decrease the local magnetic flux, and promote the effect of valve movemen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
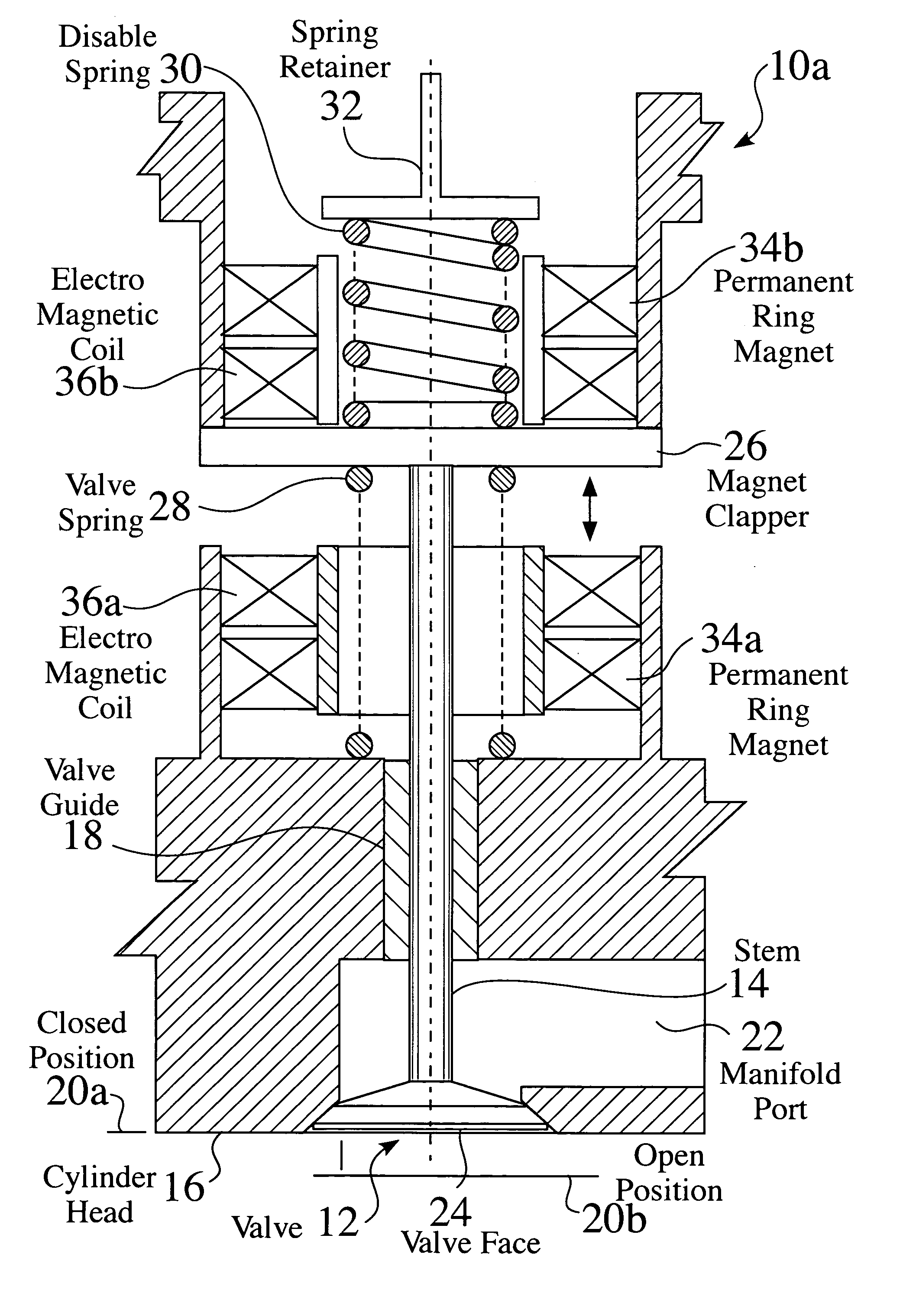
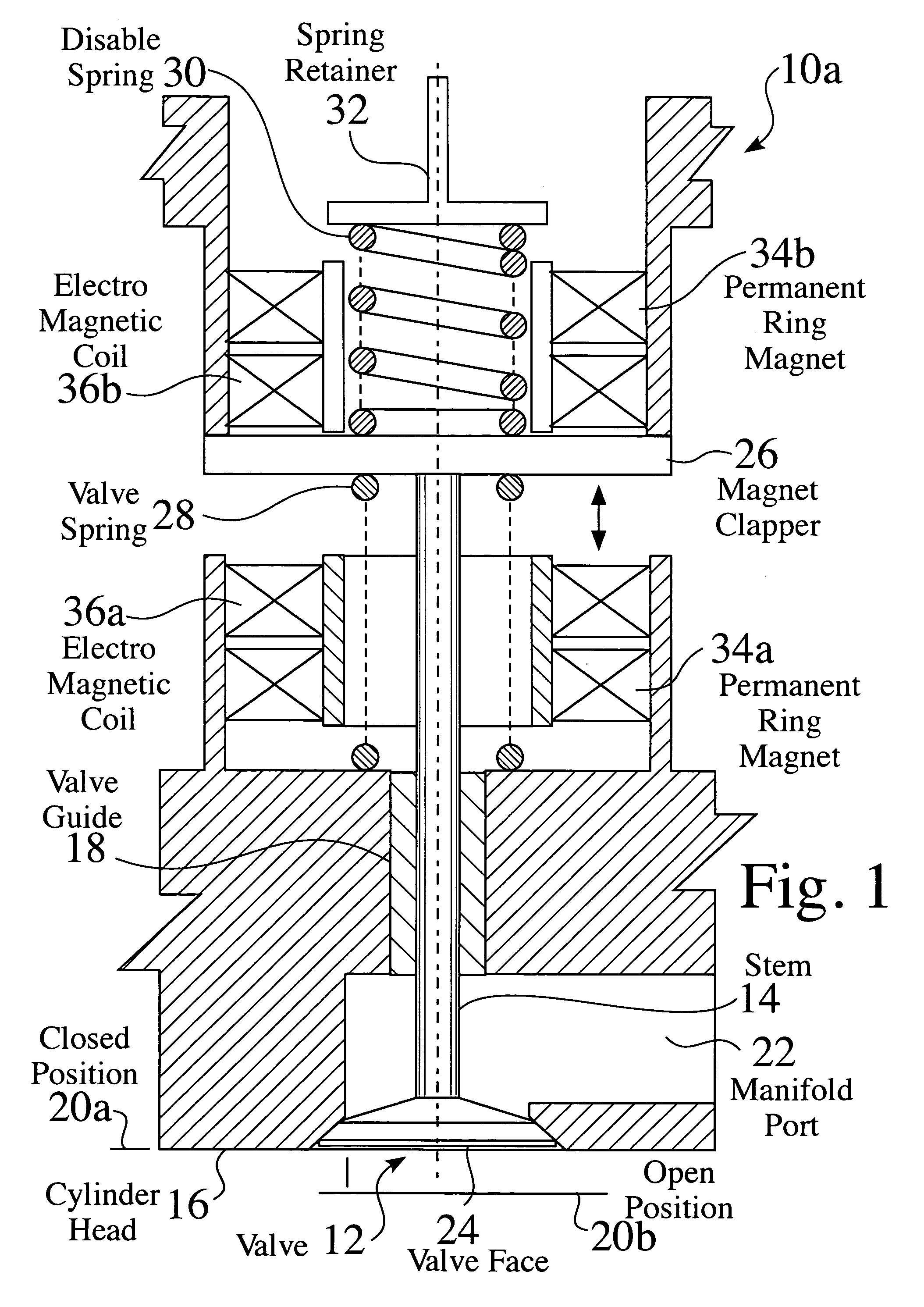
[0078]FIG. 1 is a partial cross sectional view of an electromagnetic valve system 10a. A valve 12, having a stem 14, is linearly moveable within a cylinder head 16, such as through a valve guide 18. The valve 12 is linearly moveable between a closed position 20a and an open position 20b, to allow flow into or out of a manifold port 22.
[0079] The valve 12 comprises a valve face 24 at one end of the stem 14. A clapper 26 is affixed to the stem 14, such that movement of the clapper results in movement of the valve 12. A valve spring 28 is located between the head 16 and the clapper 26, which biases the valve 12 toward a closed position 20a. A disable spring 30 is located on an opposing surface of the clapper 26, to bias the valve 12 toward an open position 20b. The disable spring 30 is typically affixed in relation to the cylinder head 16, such as by a retainer32.
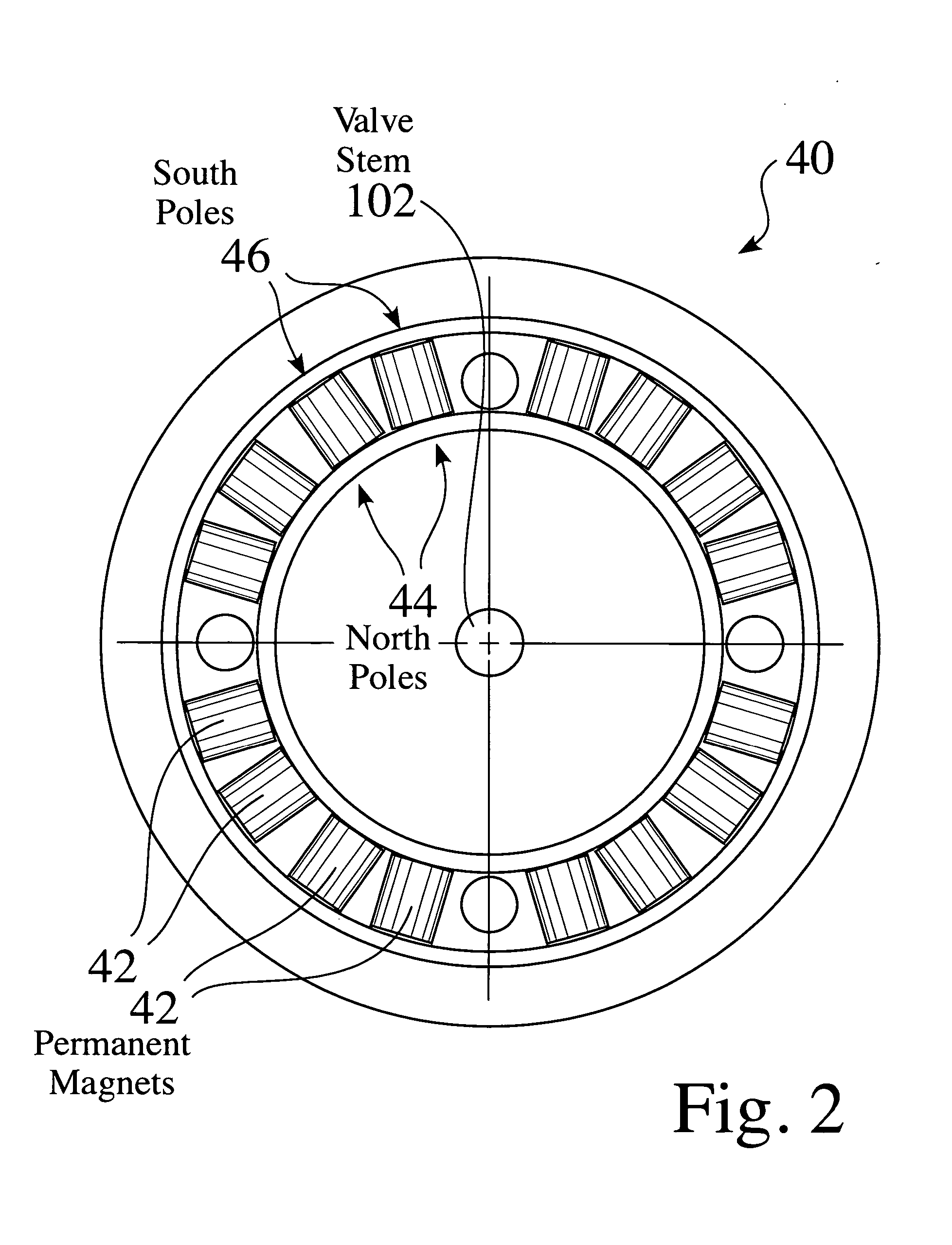
[0080] A first permanent magnet 34a and first electromagnet 36a are located on one side of the clapper 26, and a second pe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com