Method for selective electroless attachment of contacts to electrochemically-active molecules
a technology of electrochemically-active molecules and contacts, applied in the field of molecular electronics, can solve the problems of reducing the extent of metal, and reducing the efficiency of electrochemical contacts, so as to achieve the effect of reducing additional process steps, reducing the number of chemical steps, and reducing the number of electrochemical contacts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
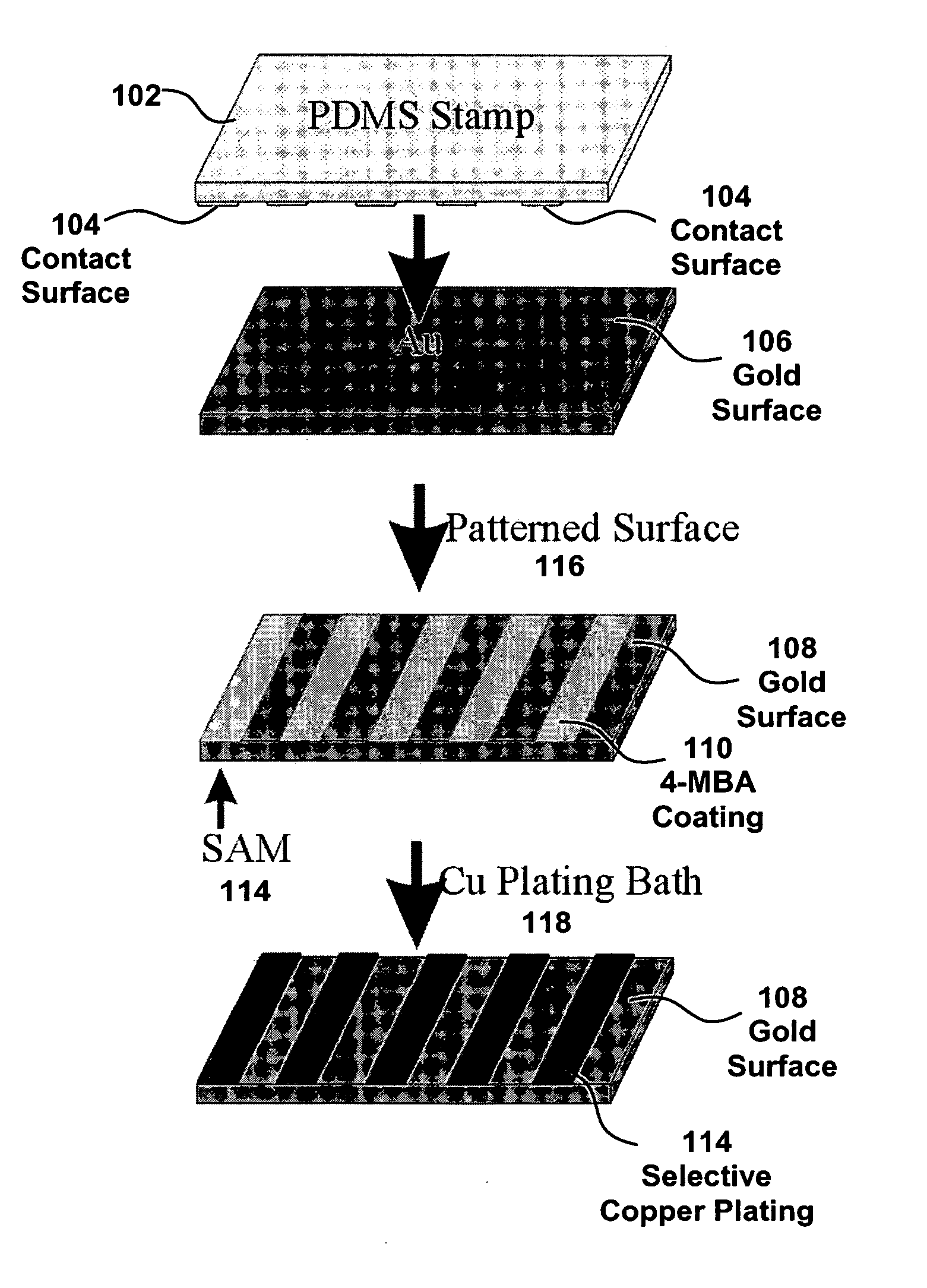
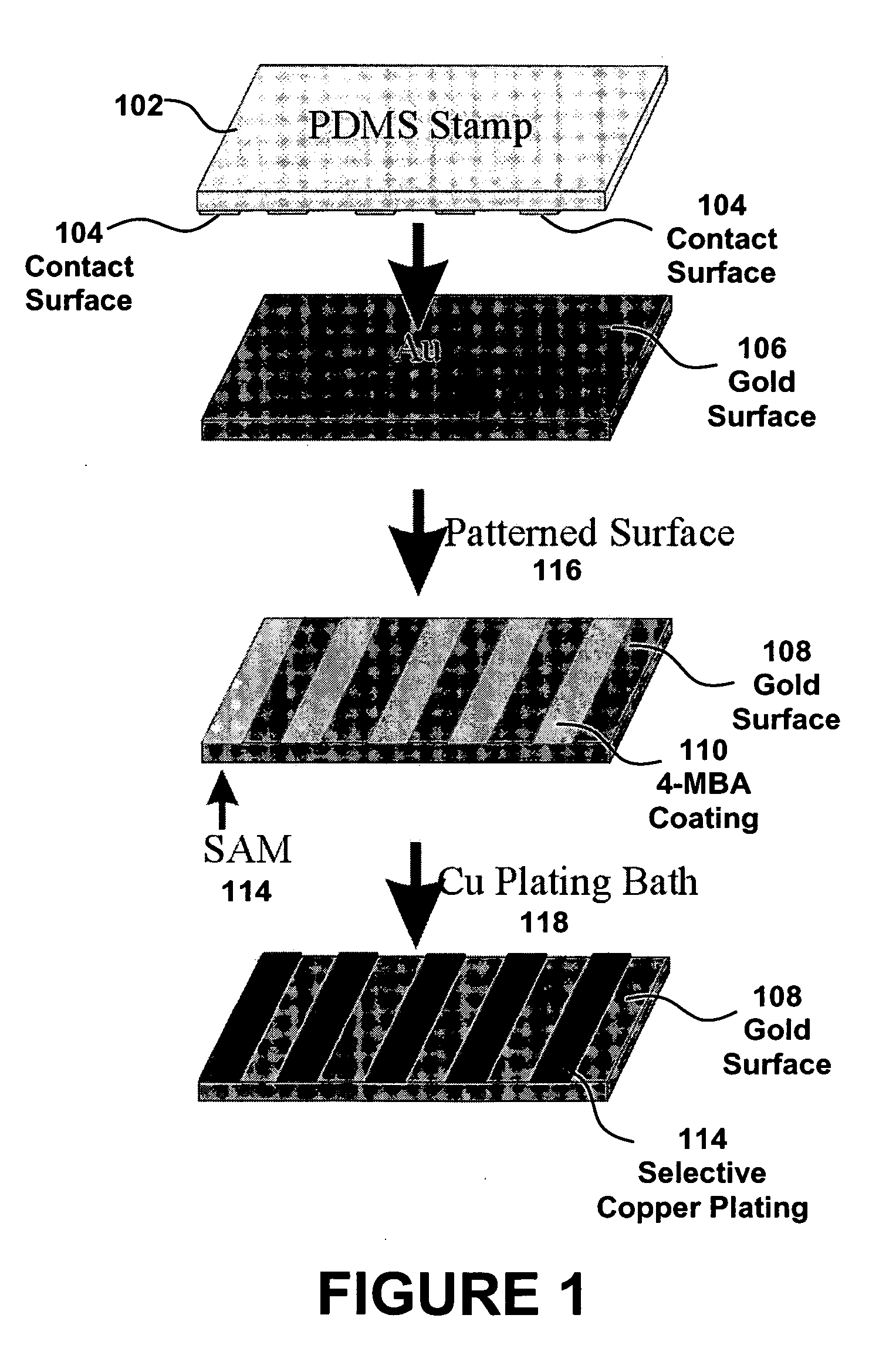
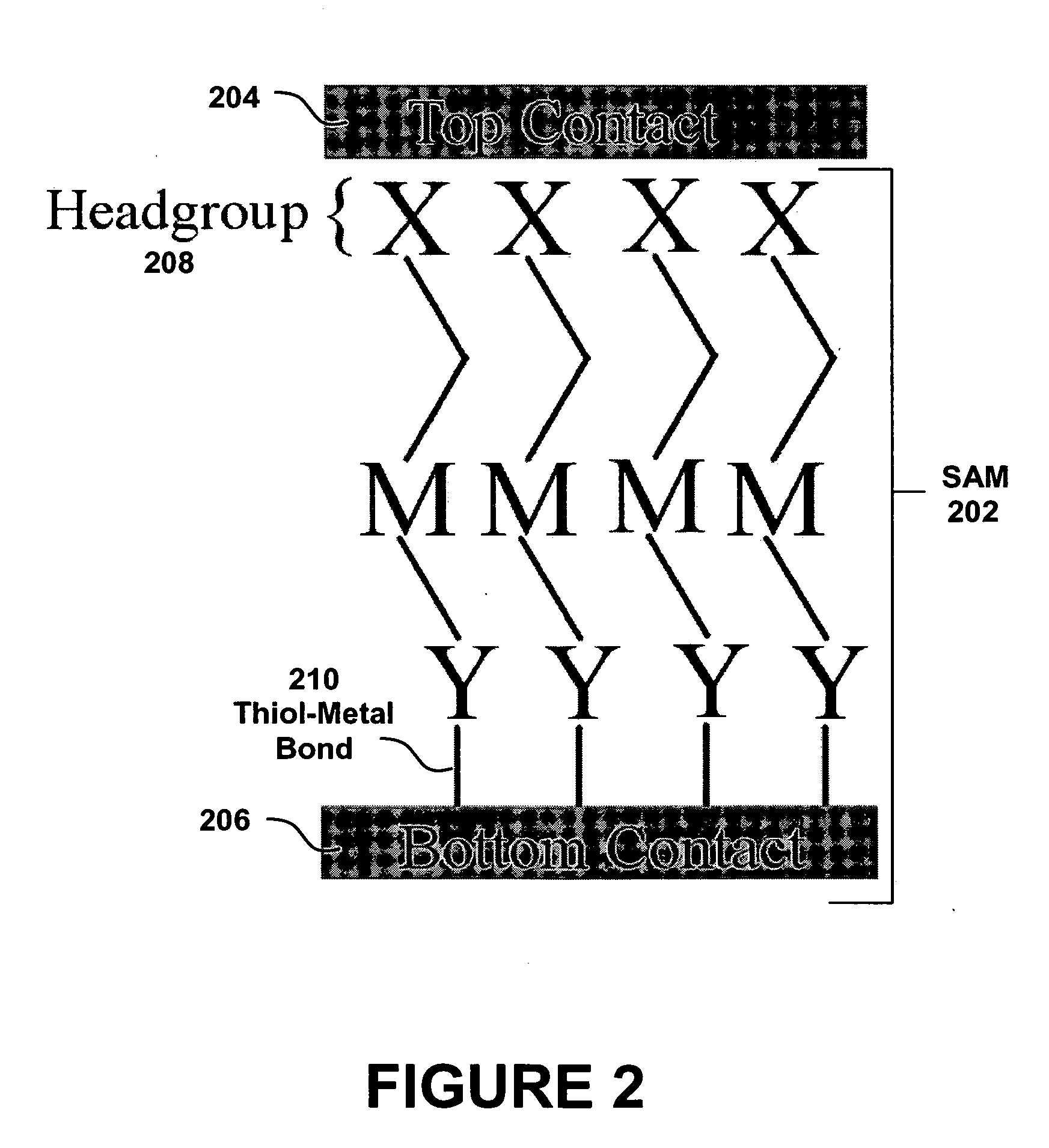
[0027] The present embodiment details a method for attaching metal contacts to individual molecules and / or aggregates of molecules that form a molecular film by using ELD to form a metal contact on a MF. These molecules contain a functional group, in one embodiment, carboxylic acid (—COOH), tailored to selectively attach a contact to the molecule or molecular film at the site of the functional group. This contact is attached by growing a metal particle using ELD. ELD is an autocatalytic process where metal ions in solution are reduced at a surface in the absence of an externally applied electric field through surface mediated redox reactions. The deposition of metal at a surface is dependent upon, and fundamentally controlled by, the interaction of metal ions and subsequent reduction. In the case of organically modified surfaces (e.g. self-assembled monolayers), this interaction is often insufficient to initiate ELD. To offset this limitation, these surfaces are frequently exposed t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com