Power supply device for out putting stable programmable power supply
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] To make it easier for our examiner to understand the objective of the invention, its structure, innovative features, and performance, we use a preferred embodiment together with the attached drawings for the detailed description of the invention.
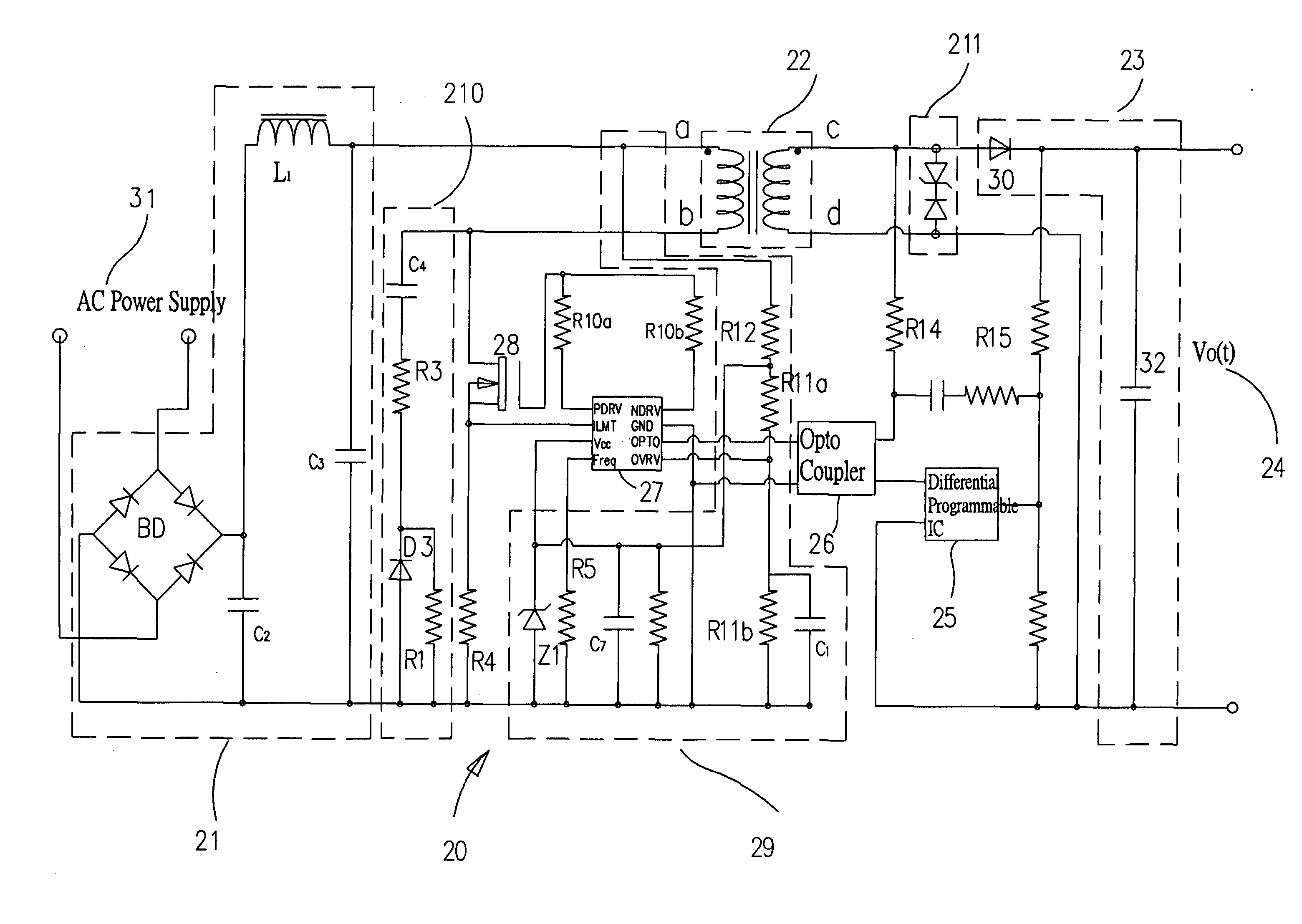
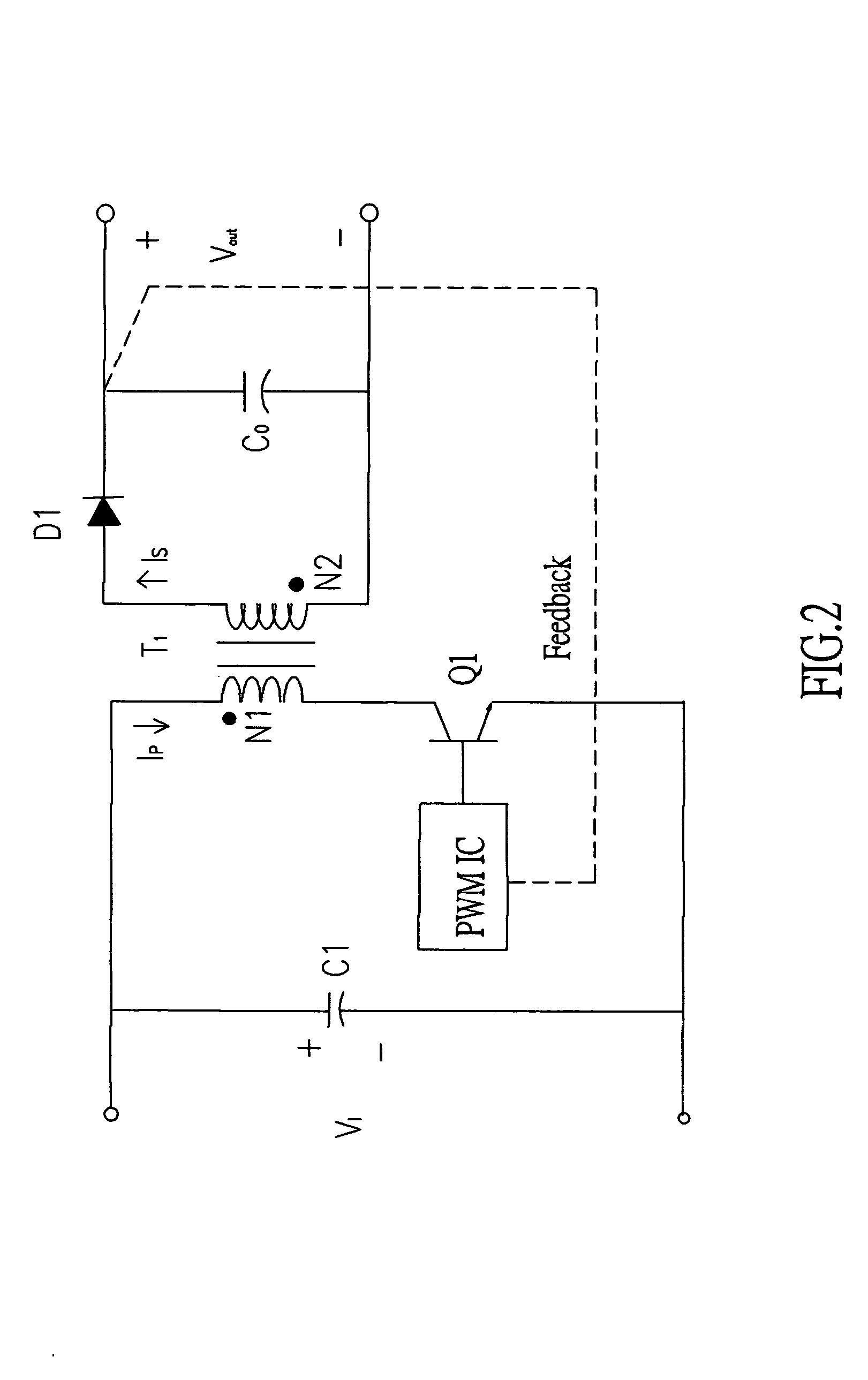
[0020] The present invention discloses a power supply device for outputting a stable programmable power supply. Please refer to FIGS. 2 and 3. The power supply device 20 comprises a rectify / filter circuit 21, a transformer 22, a secondary filter circuit 23, and a DC output terminal 24; wherein the rectify / filter circuit 21 is connected to an AC power supply 31, and a capacitor C2 and an inductor L1 constitute a full wave rectify circuit for rectifying and filtering the AC power supply 31 to obtain a more stable DC power supply, and the transformer 22 is connected to a rectify / filter circuit 21 for rectifying and filtering and lowering the voltage of the AC power supply modulated by the programmable switching circuit. After a secondar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com