Chemical reactor with heat pipe cooling
a technology of chemical reactors and heat pipes, applied in indirect heat exchangers, lighting and heating apparatuses, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of limited convection heat transfer and evaporative cooling, and achieve the effect of prolonging service life and low maintenance cos
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
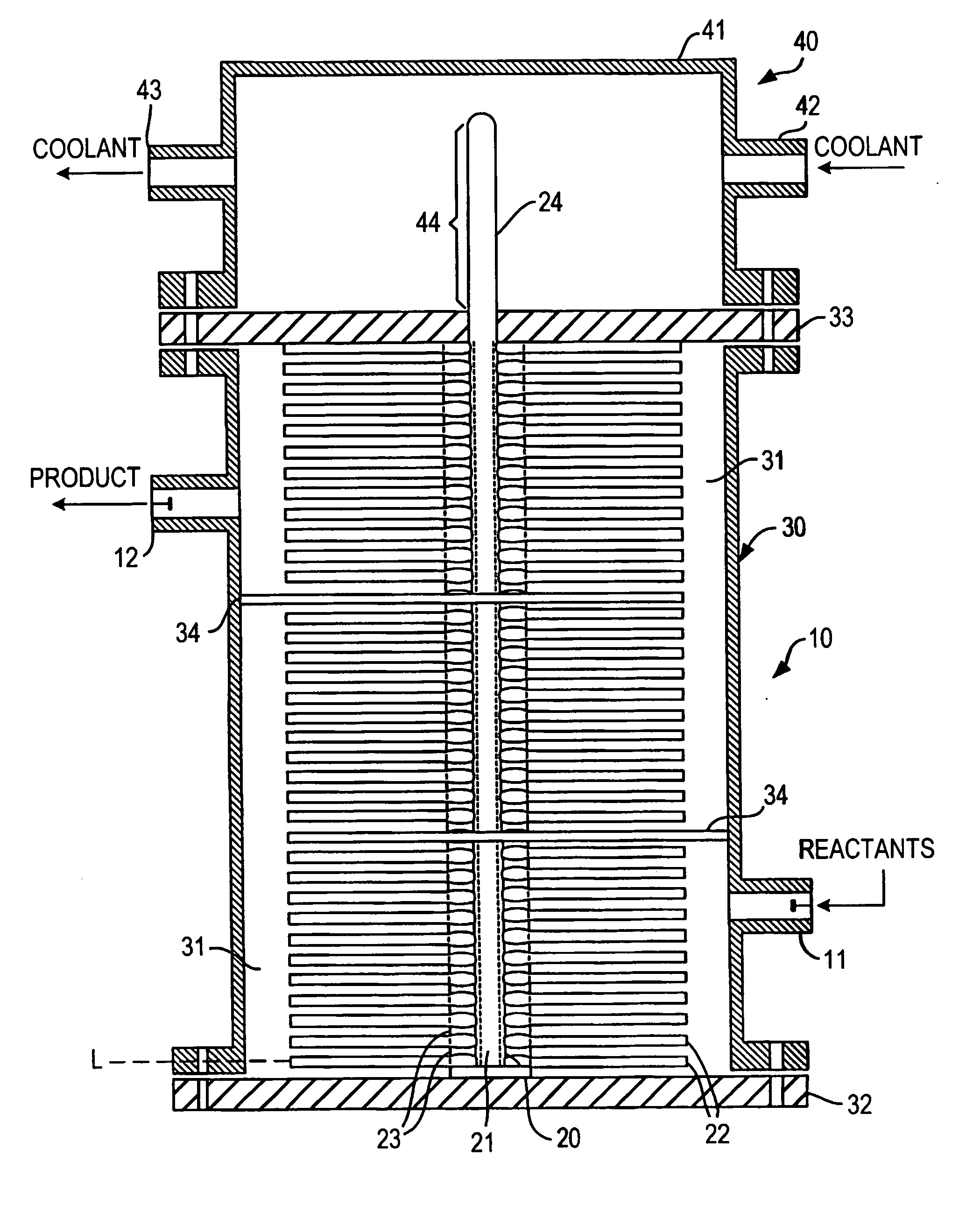
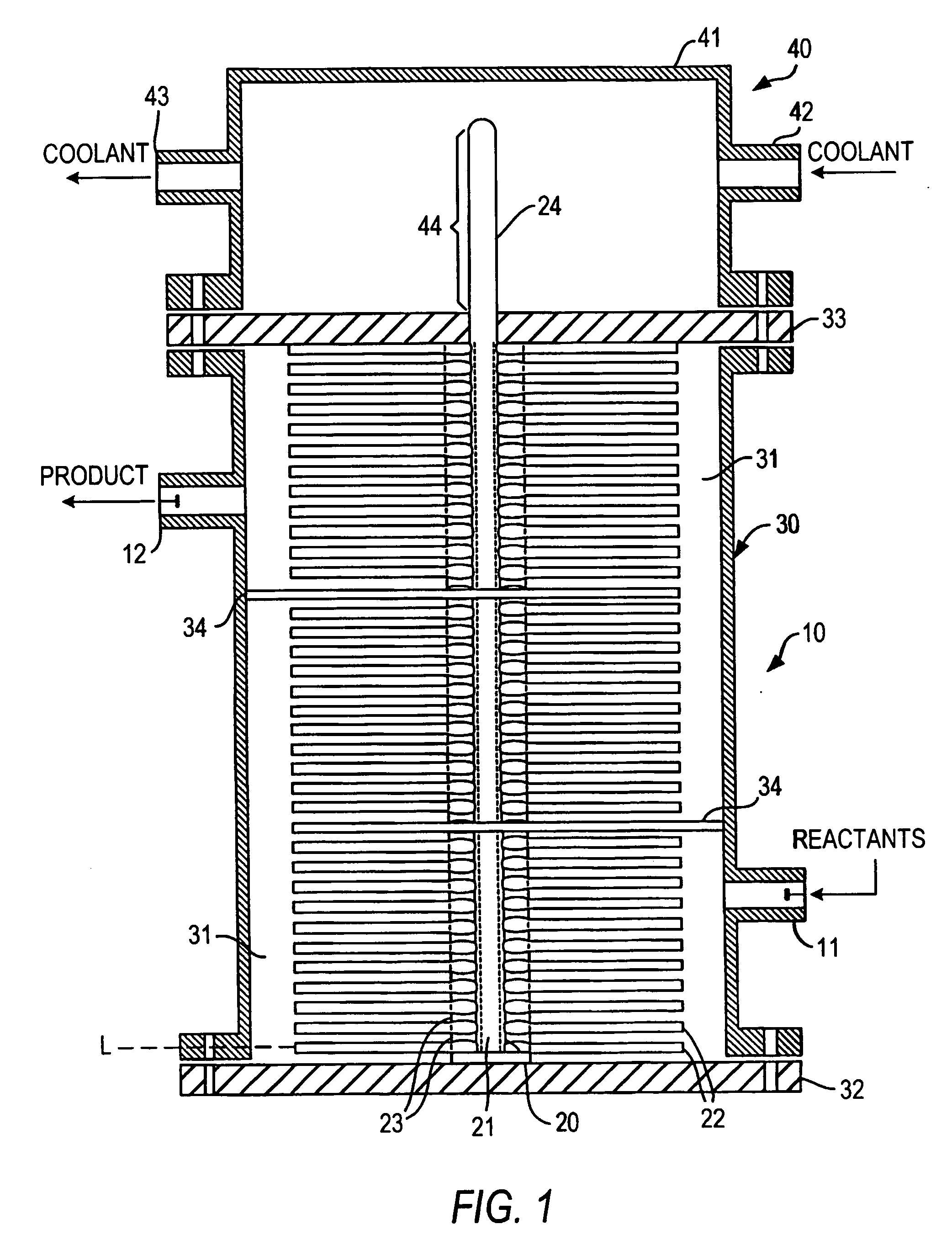
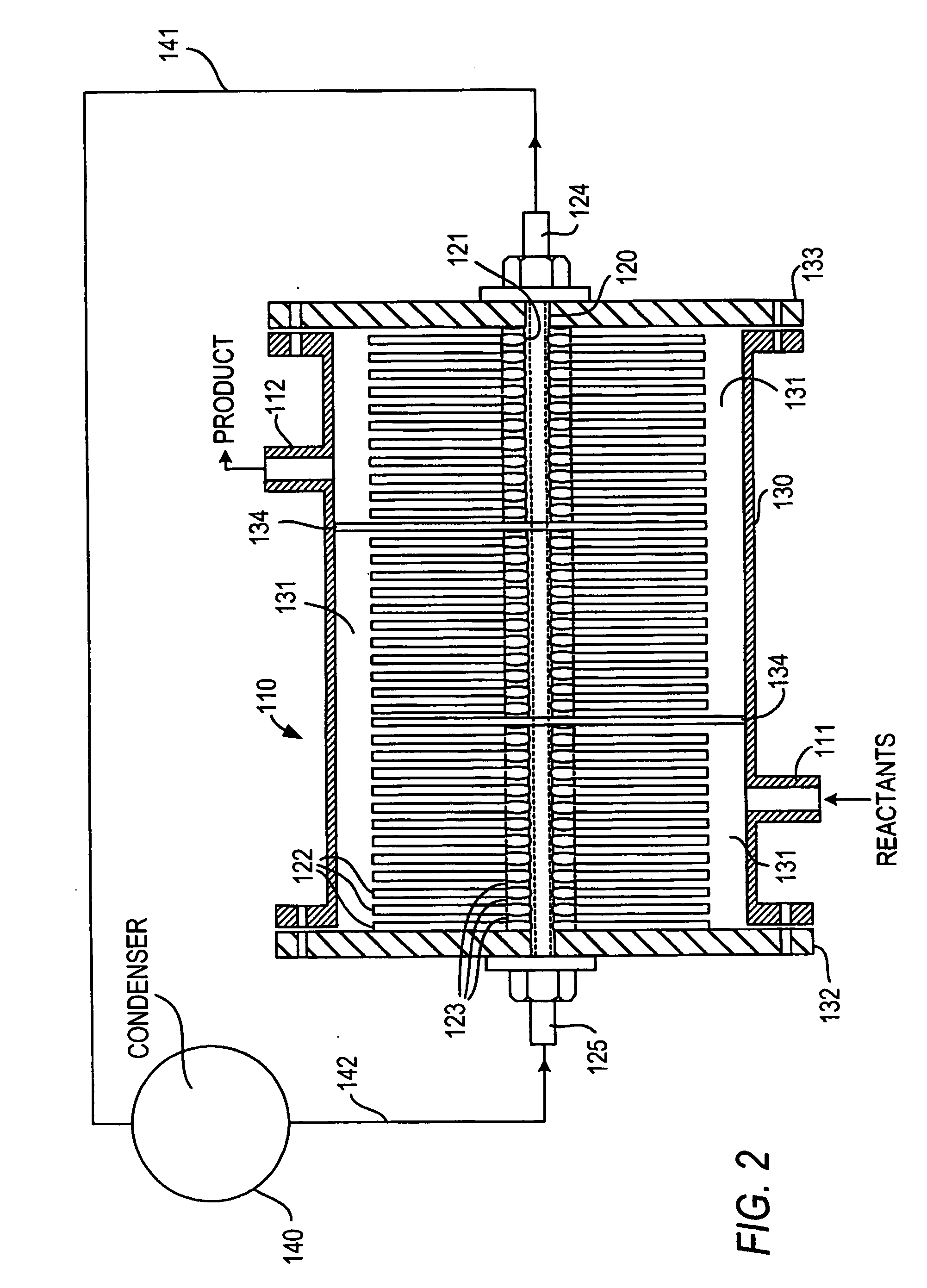
[0066] The following example illustrates the efficacy of the reactors of the invention to maintain essentially isothermal conditions in chemicals and especially polymerization reactions.
[0067] Polystyrene mass polymerization technologies are differentiated by the configuration of the main polymerization reactors used to bring conversion from 30% to 45% solids to 65% to 85% solids. During the course of the polymerization reaction large amounts of heat is evolved. If this heat of reaction is not removed, the reactor temperature will increase causing an unwanted and uncontrolled spread of the polymer molecular weight which adversely affects polymer properties.
[0068] A polystyrene mass polymerization is conducted in a reactor according to the invention consisting of a jacketed vertical pipe containing several straight heat pipes onto which are fitted a number of fins. The inside of the heat pipes is covered with a porous medium from which a heat transfer fluid is vaporized to provide ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com