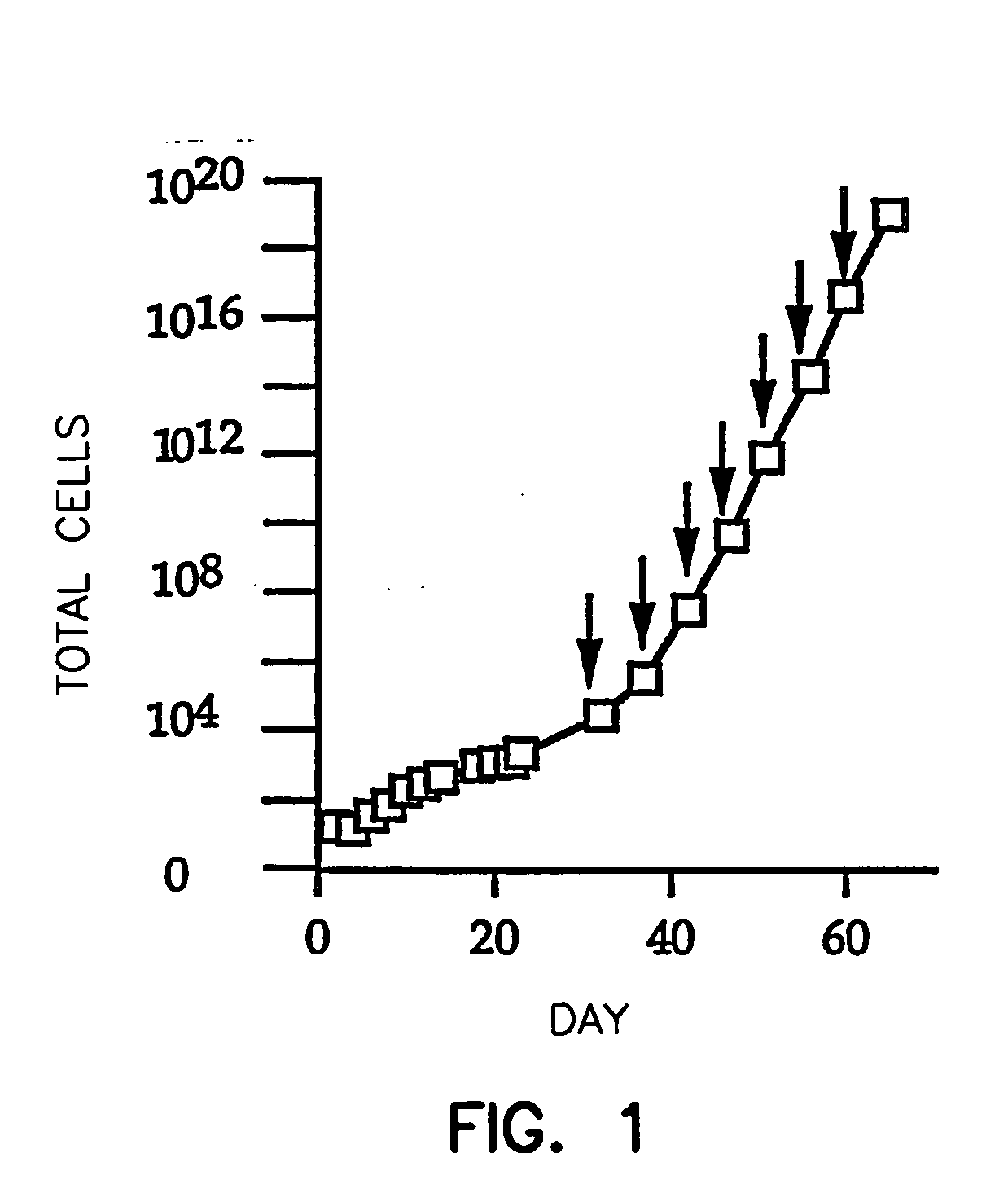
Transgenic circulating endothelial cells
a technology of circulating endothelial cells and circulating endothelial cells, which is applied in the direction of cell culture active agents, packaged goods types, peptide/protein ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of inaccessibility of vascular endothelial cells in the research field, and achieve the effect of improving the permeability of the vascular endothelial cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Culture of Endothelial Cells from Peripheral Blood
[0056] One hundred ml of fresh venous blood anti-coagulated with either heparin or citrate was diluted 1:2 with Hanks' Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS) containing 1 mM EDTA and 0.5% bovine serum albumin, carefully layered on an equal volume of Histopaque®-1077 (Sigma Chemical Co.) without disruption of the interface, and centrifuged at 400×G for 30 minutes at room temperature. The layer containing the mononuclear cells was collected, and the cells were washed 3 times by centrifuging at 250×G for 10 minutes, using the previously described MEC media (Gupta et al., Exp. Cell Res., 230, 244-251 (1997)) modified to contain 10% human male serum, to exclude the ECGS and comprising 1 μg / ml hydrocortisone. Washing with this culture medium is preferred over washing with buffer because the medium maintains higher levels of cell viability.
[0057] The buffy coat mononuclear cells were resuspended in EGM®-2 medium (Clonetics), and all buffy coat mon...
example 2
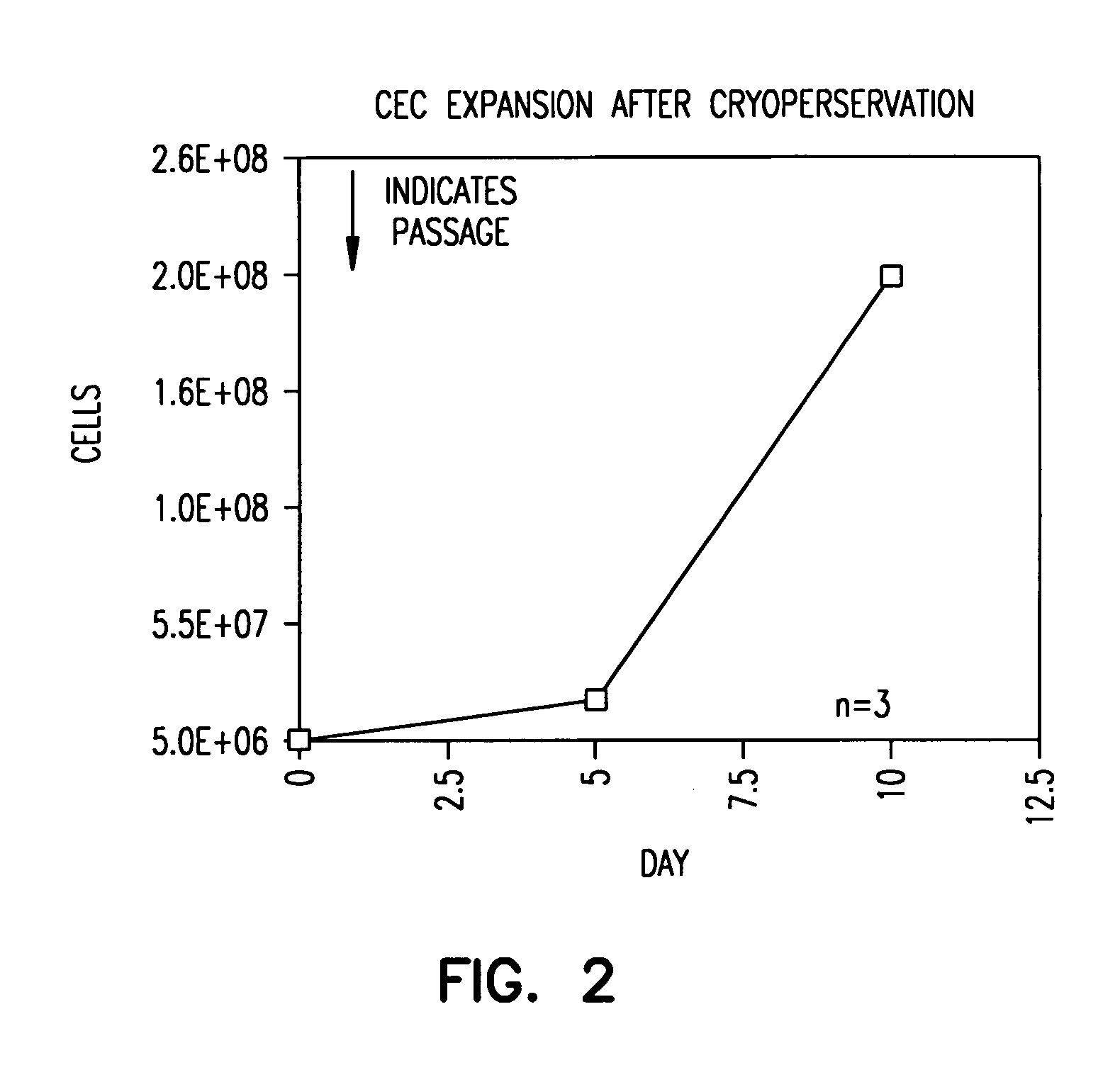
Cyropreservation of Cultured Endothelial Cells
[0062] Vigorous EC outgrowth can be obtained even after cryopreservation. This is important because the utility of the present method is greater if cultured EC can be cryopreserved for later use.
[0063] To show this, EC were cryopreserved after their outgrowth had reached the capacity of two T75 flasks. To do this, the cells were detached as above and washed twice with HBSS. Cells were resuspended in 100% fetal calf serum at a concentration of one-million cells per 950 μl serum, and then 50 μl dimethylsulfoxide was added. The suspension was mixed quickly and placed on ice for 5 minutes. Afterward, the cells were stored at −70° C. overnight, and they were then transferred to liquid nitrogen.
[0064] After six weeks of storage, the cells were thawed and one million cells were plated onto T75 flask with excess (20 ml) of EGM®-2 medium. Medium was changed again four hours after initial plating. The cells were then grown as in Example 1.
[006...
example 3
Study of Origin of CEC in Blood
[0066] The origin of the CEC identifiable in fresh blood is not known, nor is the relationship between CEC and the endothelial outgrowth from cultured blood. To answer this, 4 adults were studied who had undergone allogeneic marrow transplantation (for malignancy) 5-20 months earlier using opposite-gender donors (three female donors to three male recipients and one male donor to one female recipient). All 4 subjects are disease-free and have peripheral blood and / or marrow aspirates that are 100% donor by RFLP; two also had marrow cytogenetics showing 100% donor.
[0067] The CEC in fresh blood, plus the peripheral blood endothelial outgrowth from buffy coat mononuclear cells cultured with endothelial growth factors was studied using the culture conditions of Ex. 1. MAb P1H12 was used to identify cells as being endothelial, and fluorescence in situ hybridization was used to identify cells as having XX or XY genotype.
[0068] CEC in fresh blood were almost...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Biocompatibility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bioactive | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com