Optical or electronic module and method for its production
a technology production methods, applied in the field of optical or electronic modules, can solve the problems of damage to sensitive bonding wire connections, high thermal expansion coefficient of embedded materials, and inability to create optical paths within embedded materials, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the thermal properties of modules
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] One or more aspects of the present invention will now be described with reference to the drawing figures, wherein like reference numerals are used to refer to like elements throughout. It should be understood that the drawing figures and following descriptions are merely illustrative and that they should not be taken in a limiting sense. In the following description, for purposes of explanation, numerous specific details are set forth in order to provide a thorough understanding of the present invention. It will be evident to one skilled in the art, however, that the present invention may be practiced without these specific details. Thus, it will be appreciated that variations of the illustrated systems and methods apart from those illustrated and described herein may exist and that such variations are deemed as falling within the scope of the present invention and the appended claims.
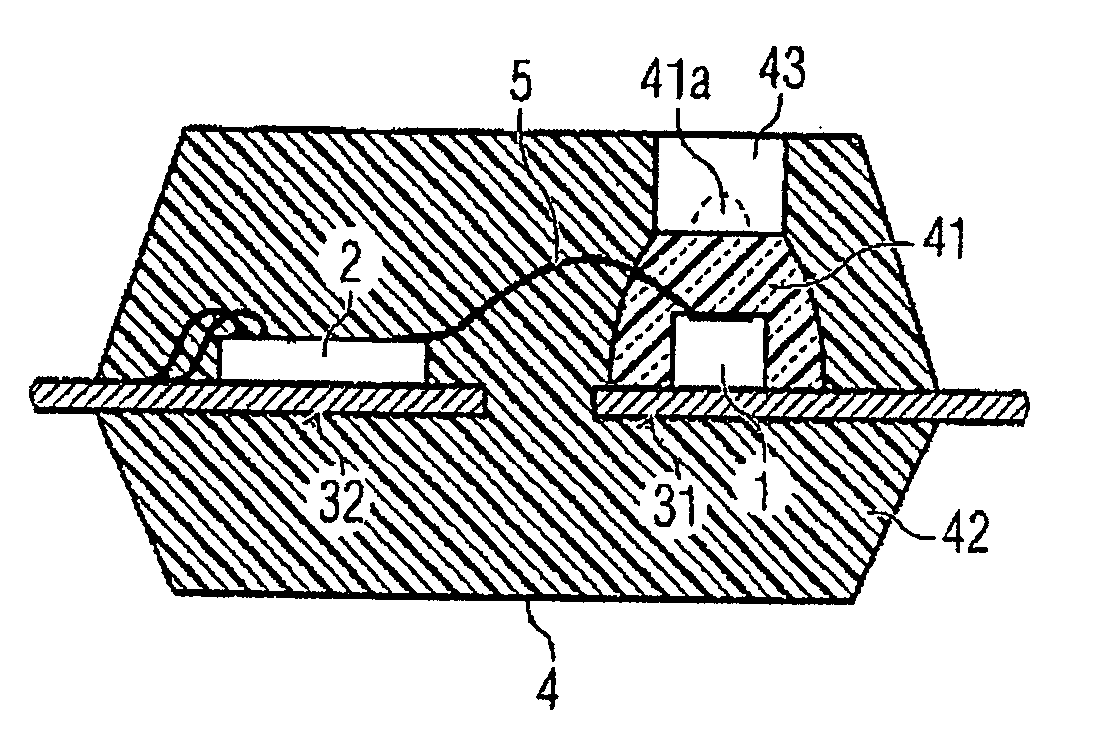
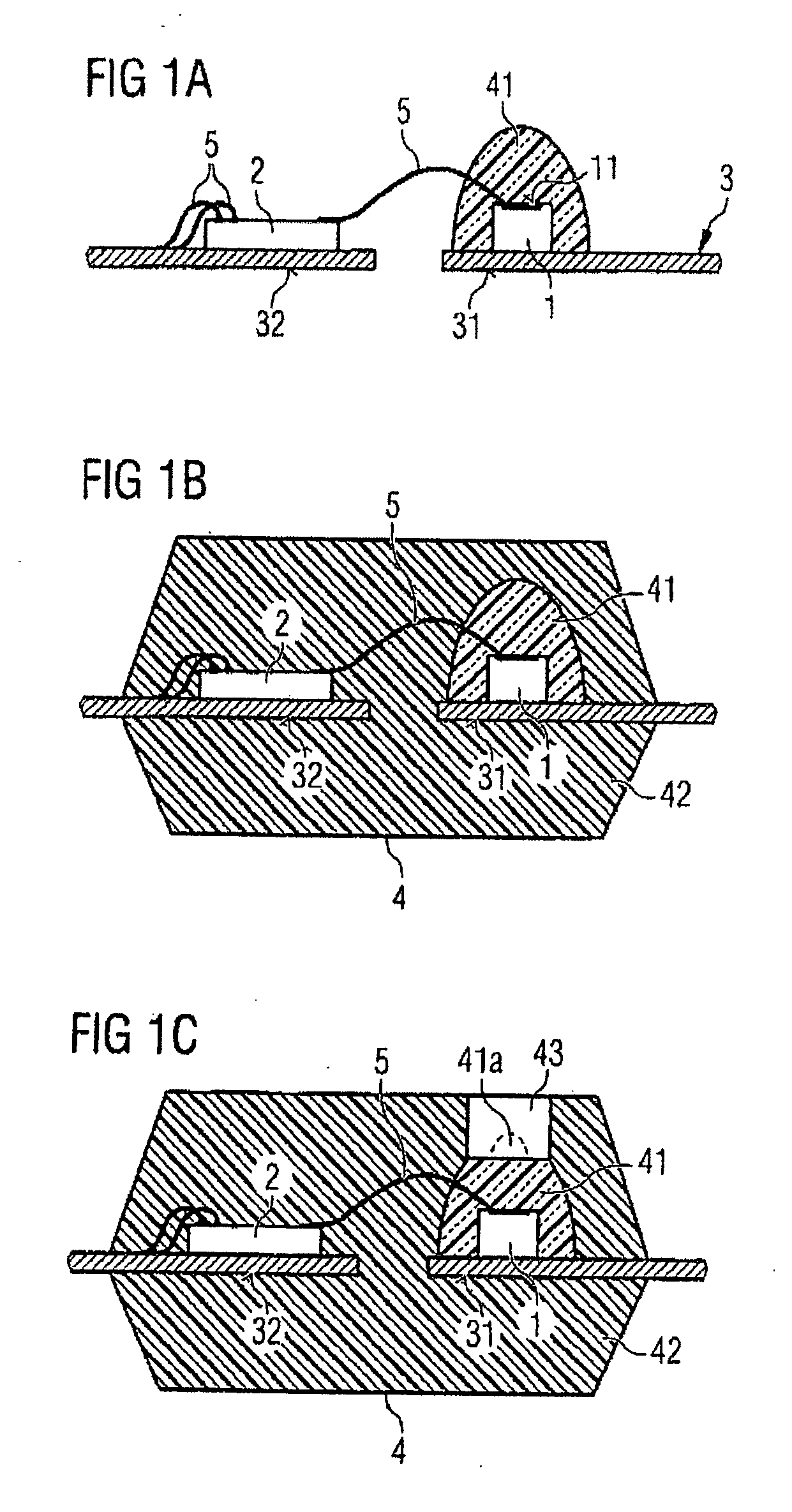
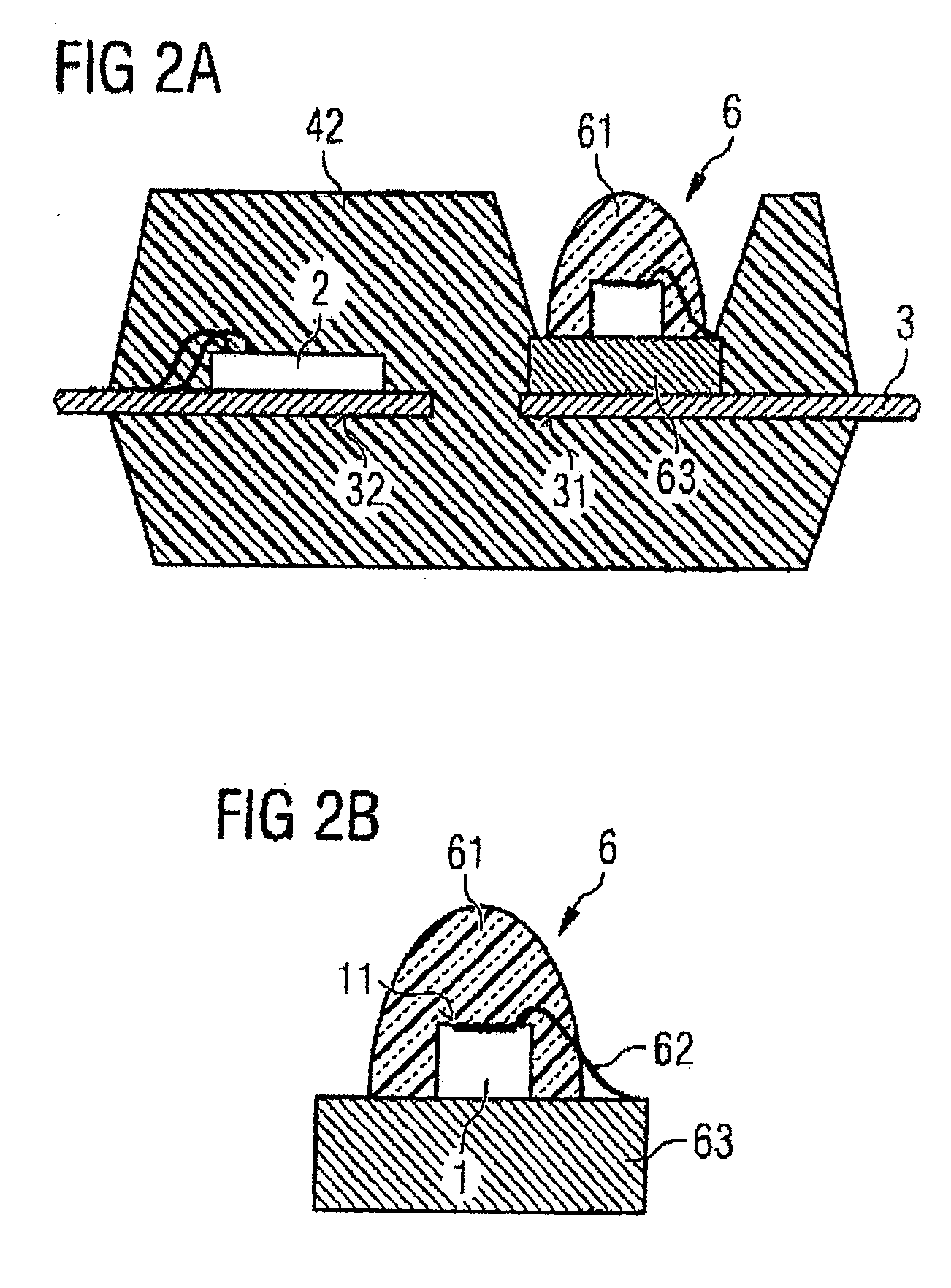
[0040]FIG. 1c illustrates a first exemplary embodiment of an optical module according to on...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com