Product and process for inhibition of biofilm development
a biofilm and process technology, applied in the direction of biocide, peptide/protein ingredients, catheter, etc., can solve the problems of undesirable biofilm development, inability to correct cf by gene therapy, etc., to and inhibit the formation or polymerization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0108] The following example demonstrates the effect of human neutrophils on initial P. aeruginosa biofilm development.
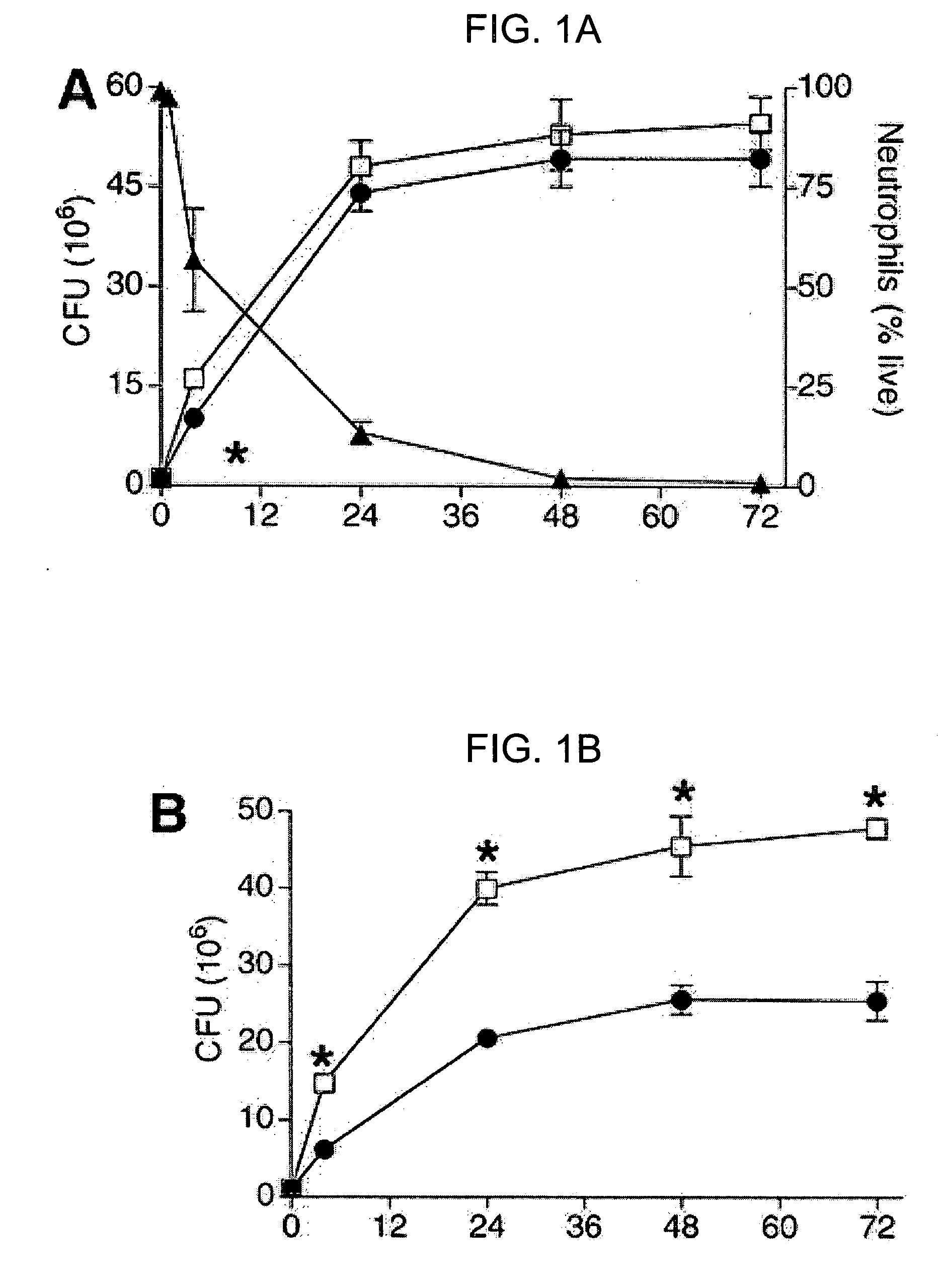
[0109] Referring to FIG. 1A, biofilm development of P. aeruginosa (□) was compared with P. aeruginosa in the presence of neutrophils (●). Neutrophil cytotoxicity (▴) equaled 92% after 24 hrs of exposure to P. aeruginosa (FIG. 1A; lot (right axis) depicts mean percent of viable neutrophils±SD (n=4)). In the presence of neutrophils, a reduction in the number of surviving P. aeruginosa was detected at 4 hours, while at later timepoints, the bactericidal effects of the neutrophil no longer reached significance (FIG. 1A; plot depicts mean±SD of CFU (n=4). *p<0.05 by Student's t-test).
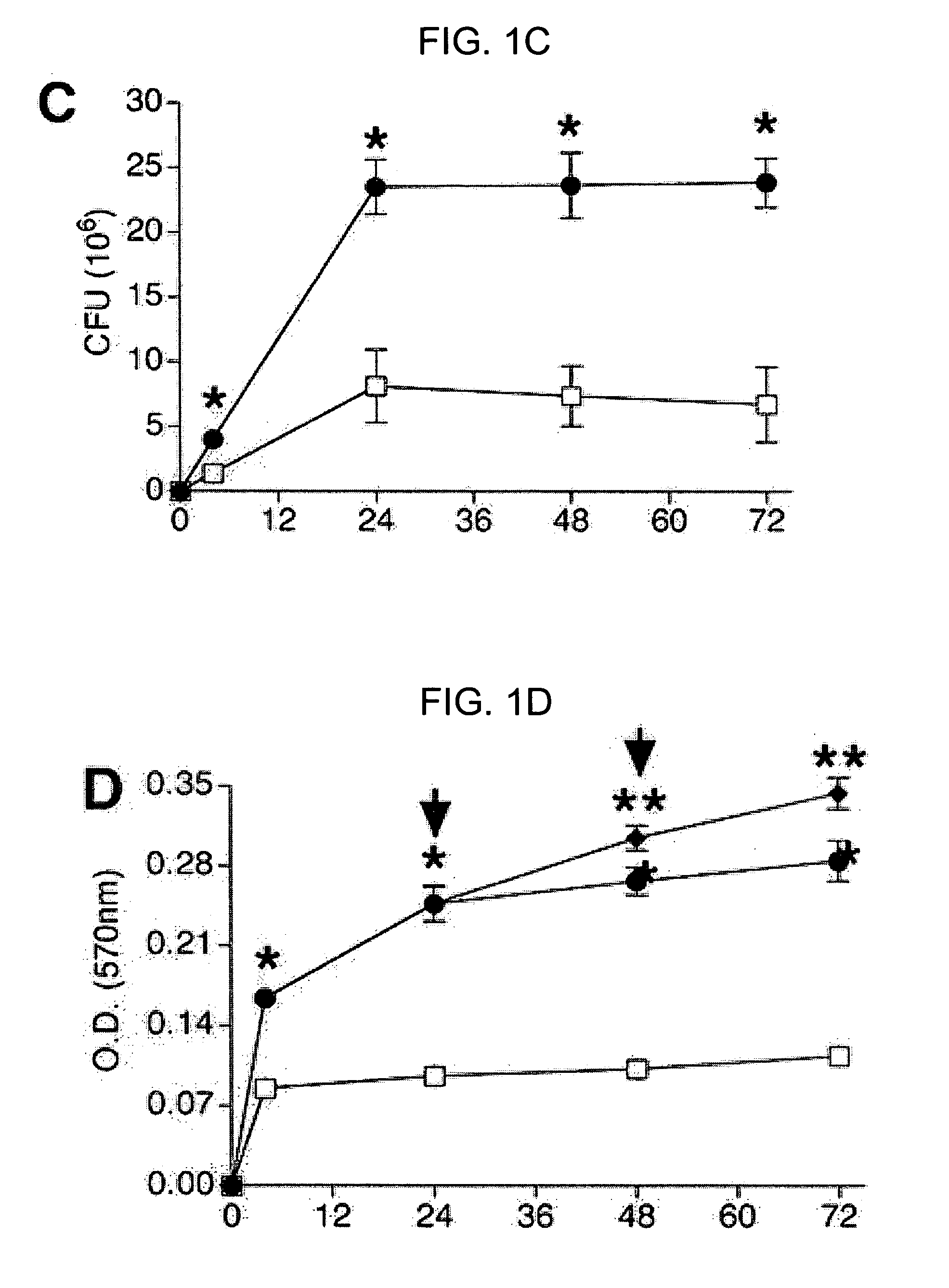
[0110] When measured simultaneously, the number of viable P. aeruginosa in the planktonic state was significantly decreased by the presence of neutrophils, while the number of viable P. aeruginosa in the biofilm state was significantly increased (FIGS. 1B-C). Referring to FIG. 1B, the pres...
example 2
[0116] The following example shows the enhancement of P. aeruginosa biofilm formation by lysed neutrophils.
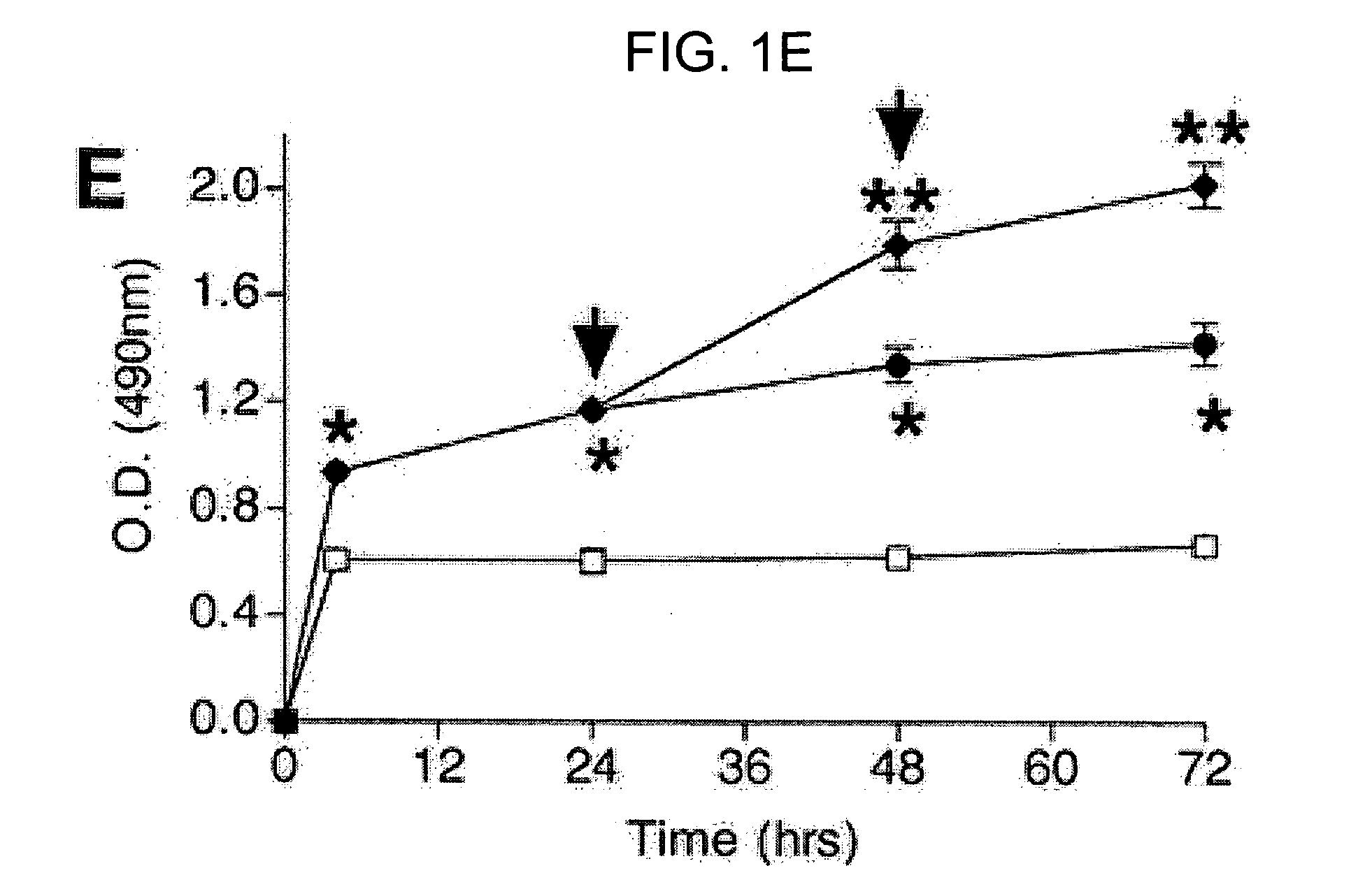
[0117] Since neutrophil necrosis is rapid in the presence of P. aeruginosa, the capacity of the cellular content of lysed neutrophils to evoke enhanced P. aeruginosa biofilm development was tested. Parameters of biofilm development of P. aeruginosa (□) were compared with P. aeruginosa in the presence of lysed neutrophils (●) at time intervals from 0 to 72 hrs. Combining P. aeruginosa with neutrophil lysates significantly enhanced biofilm formation as measured by CV staining and exopolysaccharide synthesis, and supplementing the early biofilm with additional quantities of lysed neutrophils at 24 and 48 hrs further enhanced biofilm production (FIGS. 2A,C). Referring to FIG. 2A, crystal violet staining of biofilm density demonstrated that the presence of lysed neutrophils resulted in a greater quantity of biofilm compared to P. aeruginosa in the absence of neutrophils by 4 hrs. W...
example 3
[0119] The following example demonstrates the enhancement of P. aeruginosa biofilm formation by isolated neutrophil components.
[0120] The data described in the Examples above indicates that neutrophil cellular contents are largely responsible for enhanced P. aeruginosa biofilm formation. Analysis of CF sputum demonstrates high concentrations of granule proteins, actin and DNA released from necrotic neutrophils (18, 28, 38). The capacity of each of these compounds to mediate enhanced early P. aeruginosa biofilm formation was tested. Referring to FIG. 3A, P. aeruginosa (▾) was combined with granule proteins (quantity equivalent to 5×106 neutrophils) compared to P. aeruginosa (□) in the absence of granule proteins and P. aeruginosa combined with live neutrophils (●). Supplementing planktonic P. aeruginosa with purified granule proteins failed to enhance biofilm production over a range of concentrations (FIG. 3A; Plot depicts mean±SD of O.D. crystal violet measurements (n=4). *p<0.05 b...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com