Expanded PTFE articles and method of making same
a technology of expanded ptfe and articles, applied in the field of unique expanded ptfe articles, can solve the problems of ineffective modification of bulk substrate properties, porosity and permeability, treatment with or following amorphous locking,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Precursor material:
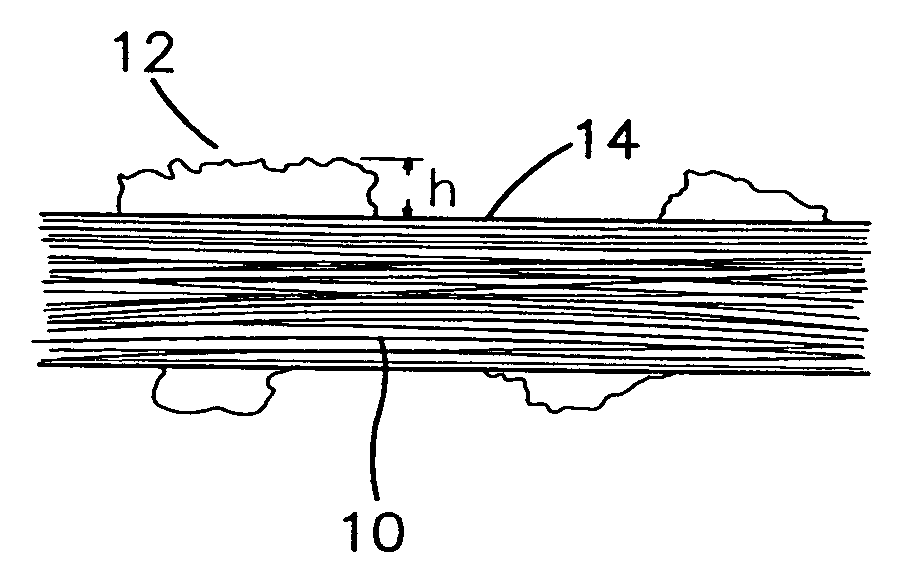
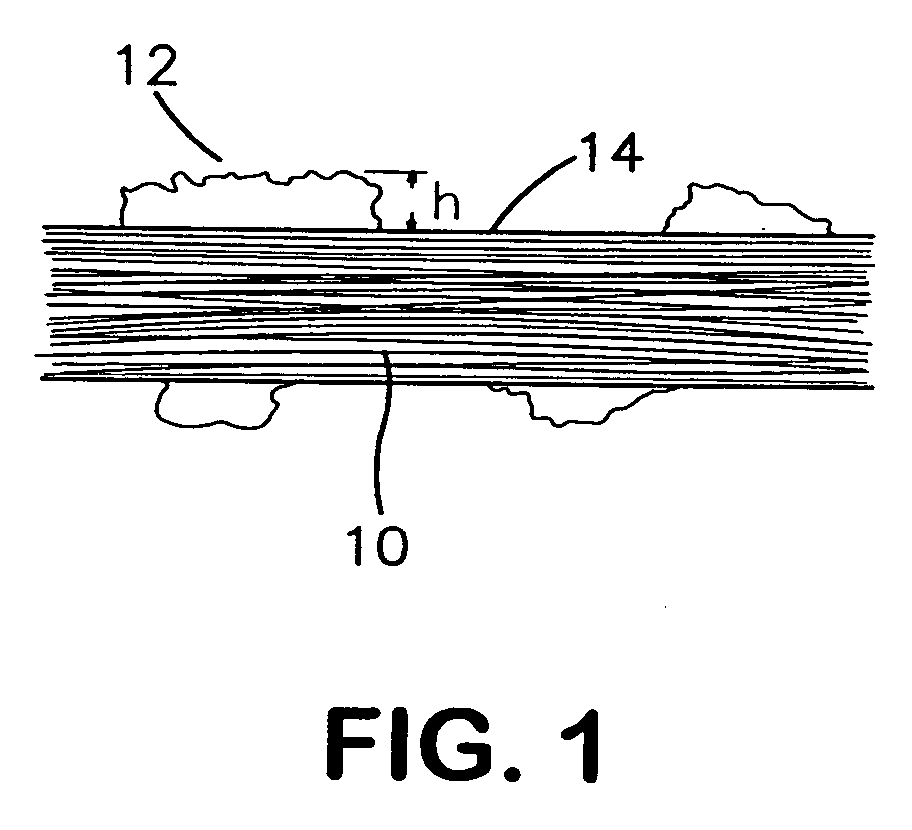
[0109] Expanded PTFE dental floss material made in accordance with the teachings of U.S. Pat. No. 5,518,012 was the precursor for the two continuous processing techniques performed in this example, described below as (a) and (b). This dental floss was an ePTFE flat fiber possessing the following properties: bulk density of 1.52 g / cc, thickness of 0.05 mm, width of 1.2 mm, and matrix tensile strength of 81,401 psi in the length direction, drag resistance of 0.148 and Fiber Fray Score of greater than 200 (exact numbers were not calculated because of the abundance of hairs). Representative scanning electron photomicrographs of the precursor material, all taken at 500× magnification, appear in FIGS. 4 through 6. The dashed bars present at the lower right of these and all other micrographs presented herein indicate the magnification scale. For example, the distance between the first and last dash marks in FIG. 4 corresponds to a length of 100 microns. The precursor m...
example 2
[0117] The same precursor material as described in Example 1 was used in this example. The precursor material samples were subjected to the same plasma treatment described in Example 1, part (a), then the plasma-treated samples were axially restrained and placed in a forced air oven set to 335° C. for about 10 minutes.
[0118] Surface and longitudinal cross-section scanning electron photomicrographs were obtained for this inventive material. FIG. 13 is a surface photomicrograph of the floss material sample taken at 1000× magnification. The islands that are characteristic of articles of the present invention are evident in this photomicrograph. As with the islands observed in Example 1, the island surfaces appear smooth and the individual islands are of greater surface area than any of the underlying nodes.
[0119] The inventive article had the following properties: bulk density of 1.46 g / cc, longitudinal matrix tensile strength of 64,345 psi, width of 1.1 mm, and thickness of 0.17 mm....
example 3
Precursor material:
[0120] Expanded PTFE dental floss made in accordance with the teachings of U.S. Pat. No. 6,539,951 was the precursor material for this example. This dental floss consisted essentially of ePTFE and possessed the following properties: bulk density of 0.80 g / cc, thickness of 0.08 mm, width of 1.9 mm, matrix tensile strength of 63,949 psi, and drag coefficient of 0.172. Photomicrographs of the surface and cross-section, respectively, of this precursor material appear in FIGS. 14 (500×) and 15 (1000×).
Experimental procedure:
[0121] For the present example, the precursor material was plasma-treated, then heat treated in accordance with the steps described in Example 1, part (a). FIG. 16 (surface, 200×), FIG. 17 (surface, 500×), and FIG. 18 (cross-section, 1000×) are photomicrographs of the microstructure of the inventive material. As with the prior examples, the individual islands are seen to have a much larger surface area than any of the nodes of the underlying no...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com