Method to inhibit cell growth using oligonucleotides
a technology of oligonucleotides and oligonucleotide, which is applied in the directions of aerosol delivery, extracellular fluid disorder, peptide/protein ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of morbidity and mortality rates that have not significantly improved, and achieve the effects of reducing the occurrence of skin cancer, preventing spongiosis, blistering or dyskeratosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0123] Based on our observation that the oligonucleotides of the present invention have the same relative molar efficacy in causing pigmentation in melanocytes, apoptosis and cellular senescence in malignant cells, a retrospective comparison of activities of a number of oligonucleotides was made and the relative molar efficacy of the oligonucleotides with respect to one another was calculated with the results set out in Table 1. Based on these results, we have concluded that the following parameters are among those that are important in determining efficacy of the oligonucleotides of the present invention. [0124] 1) percent tolemere identity; [0125] 2) number of hydrolyzable linkages; [0126] 3) guanine content; [0127] 4) sequence motif
[0128] The comparisons also reveal that the presence of cytosine residues in the oligonucleotides can have a negative impact on molar efficiency.
TABLE 1Relative Molar Efficacy of Tested T-OligosSequenceActivity T0* TT1 AA0 TTA1.5 TTAG2* GAGTATGA...
example 2
Sequence Parameters
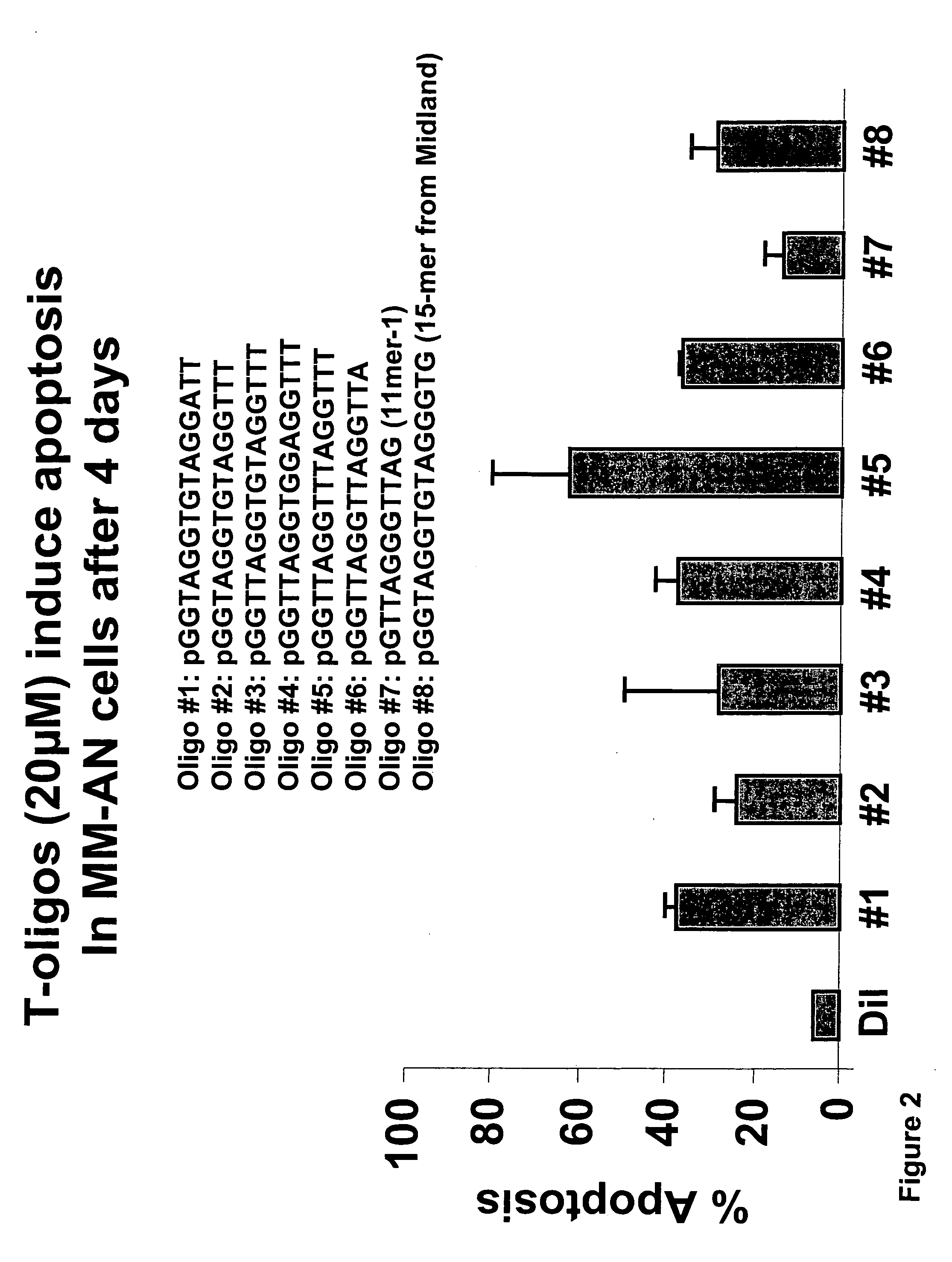
[0129] In order to further examine the effect of various nucleotide sequence parameters on the relative efficacy of T-oligos to induce apoptosis in MM-AN melanoma several oligonucleotides were synthesized which had varying % identity with the telomere repeat and which were varied with respect to the number of bases, number of guanine bases, number of GT's, number of GGT's, and the number of GGTTs. Apoptosis studies were undertaken as described in PCT / US03 / 11393 incorporated herein by reference. (See e.g. Examples 13, 28) MM-An melanoma cells were exposed to each of the T-oligos shown in Table 3 at a concentration of 40 μM for 96 hours. After 96 hours the cells were stained with propidium iodide and the percent of DNA content in the sub GI portion of the cell cycle was determined by FACS analysis. Relative activity was determined by comparison to the relative activities shown in Table 1. The sequence parameters that were investigated include: % identity with the t...
example 3
Dose-Response Effects of T-Oligos on Apoptosis in MM-AN Cells
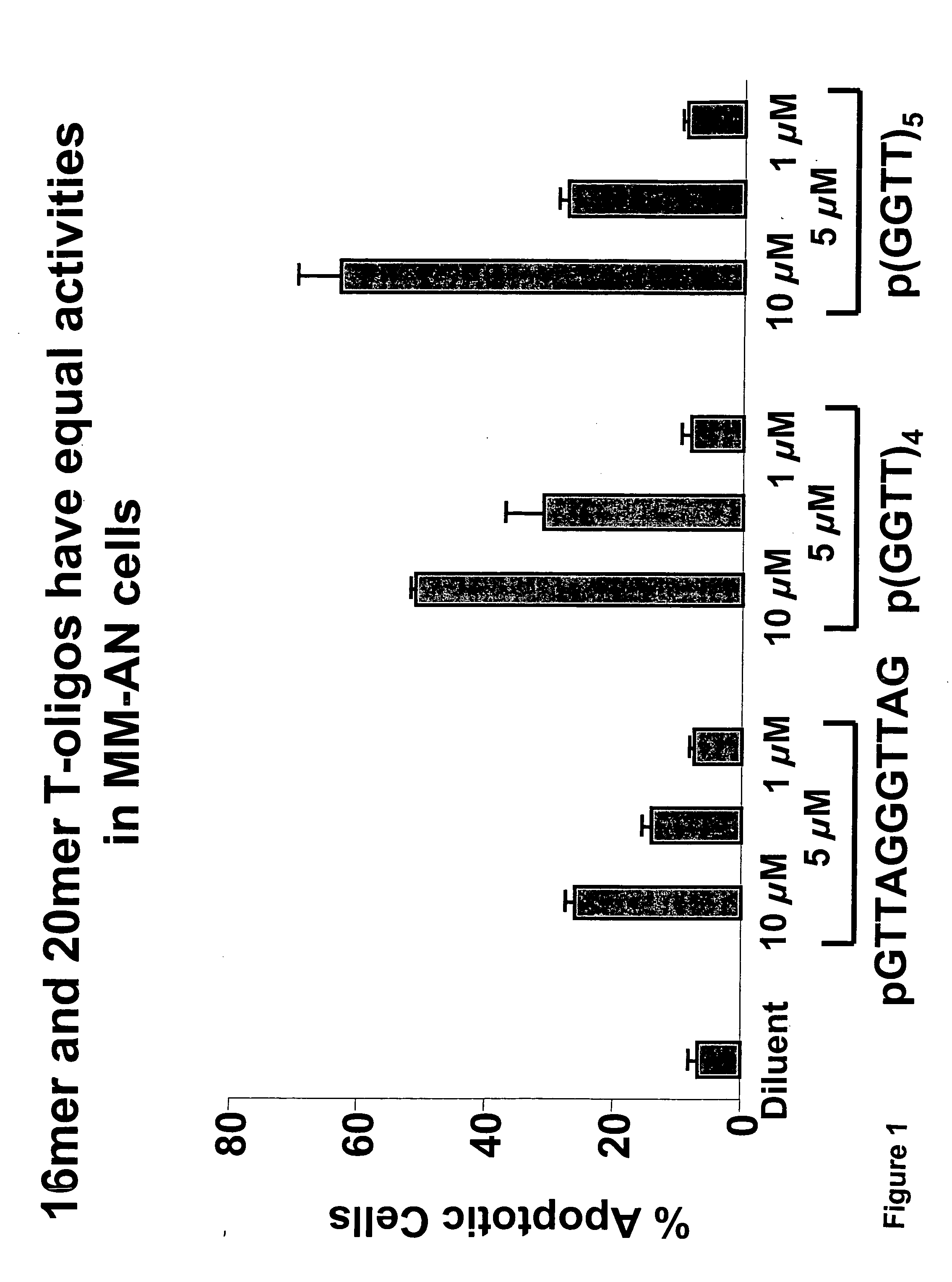
[0131] Experiments were conducted comparing the ability of different T-oligos at a range of concentrations to induce apoptosis in MM-AN melanoma cells. Apoptosis studies were undertaken as described in PCT / US03 / 11393 (See e.g. Examples 13 and 28) and treated once in triplicate with each T-oligo at each dose (1, 5 and 10 μM) and subjected to FACS analysis after 96 hours as described in PCT / US03 / 11393. The T-oligos used were pGTTAGGGTTAG (SEQ ID NO:5), p(GGTT)4 (SEQ ID NO:29) and p(GGTT)5 (SEQ ID NO:35). Results are shown in FIGS. 1 and 4. The results are compatible with earlier experiments and show that the standard (GTTAGGGTTAG) (SEQ ID NO:5) is less effective at inducing apoptosis than either the p(GGTT)4 SEQ ID NO:29 or p(GGTT)5 (SEQ ID NO:35), which were comparable in efficacy. In a separate experiment (GGTT)4 with and without 5′ phosphorylation were equally active in the MM-AN cell assay for apoptosis. Maximally effec...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com