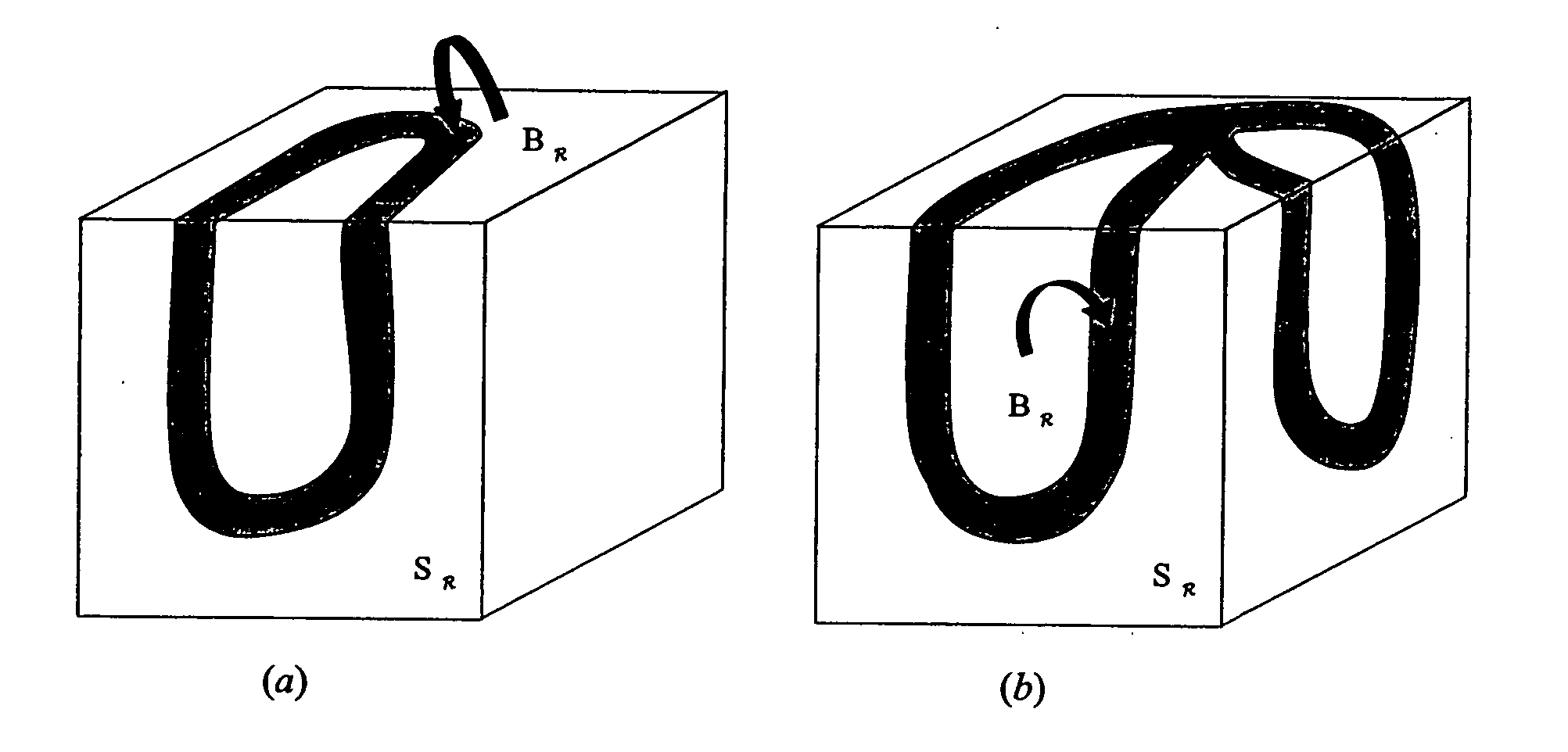
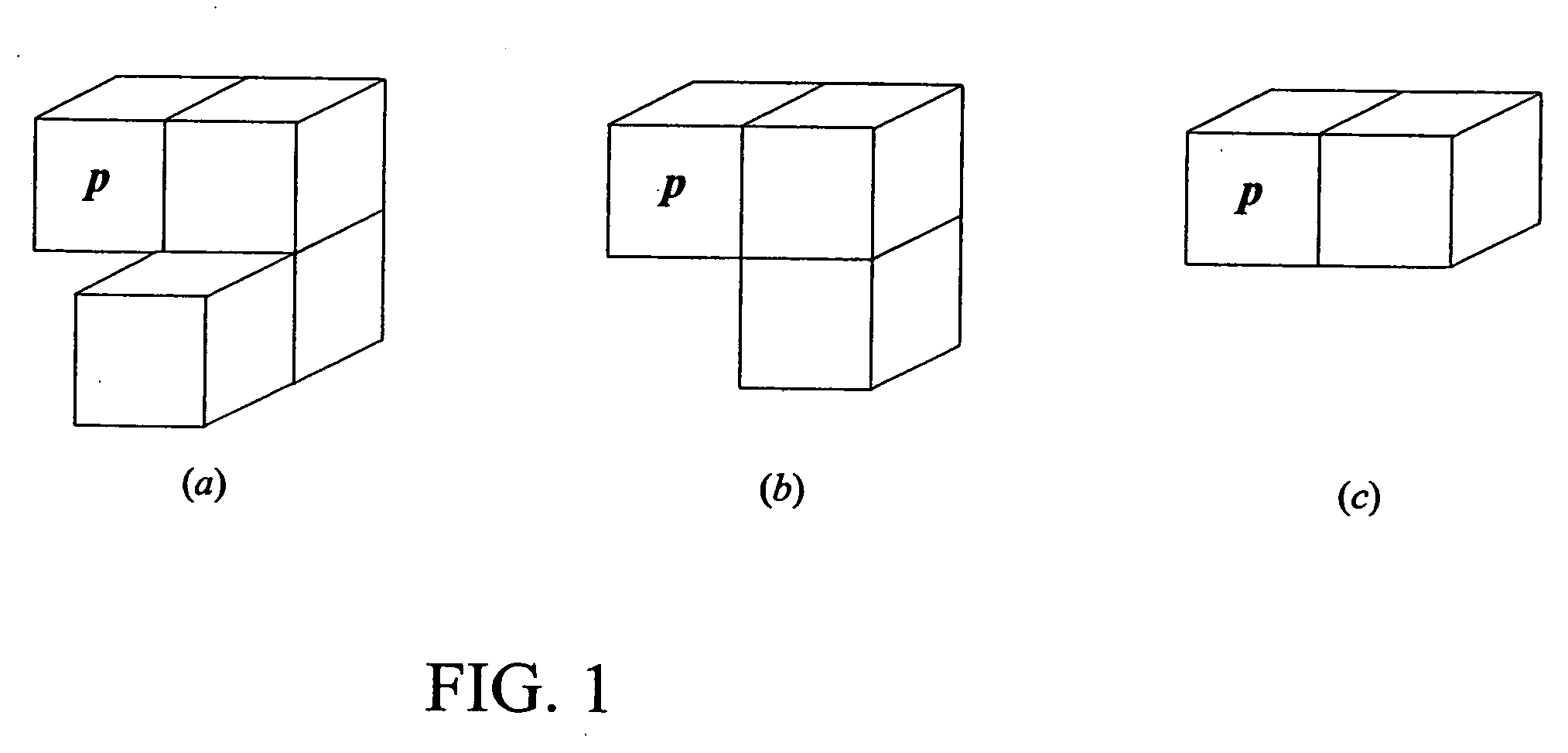
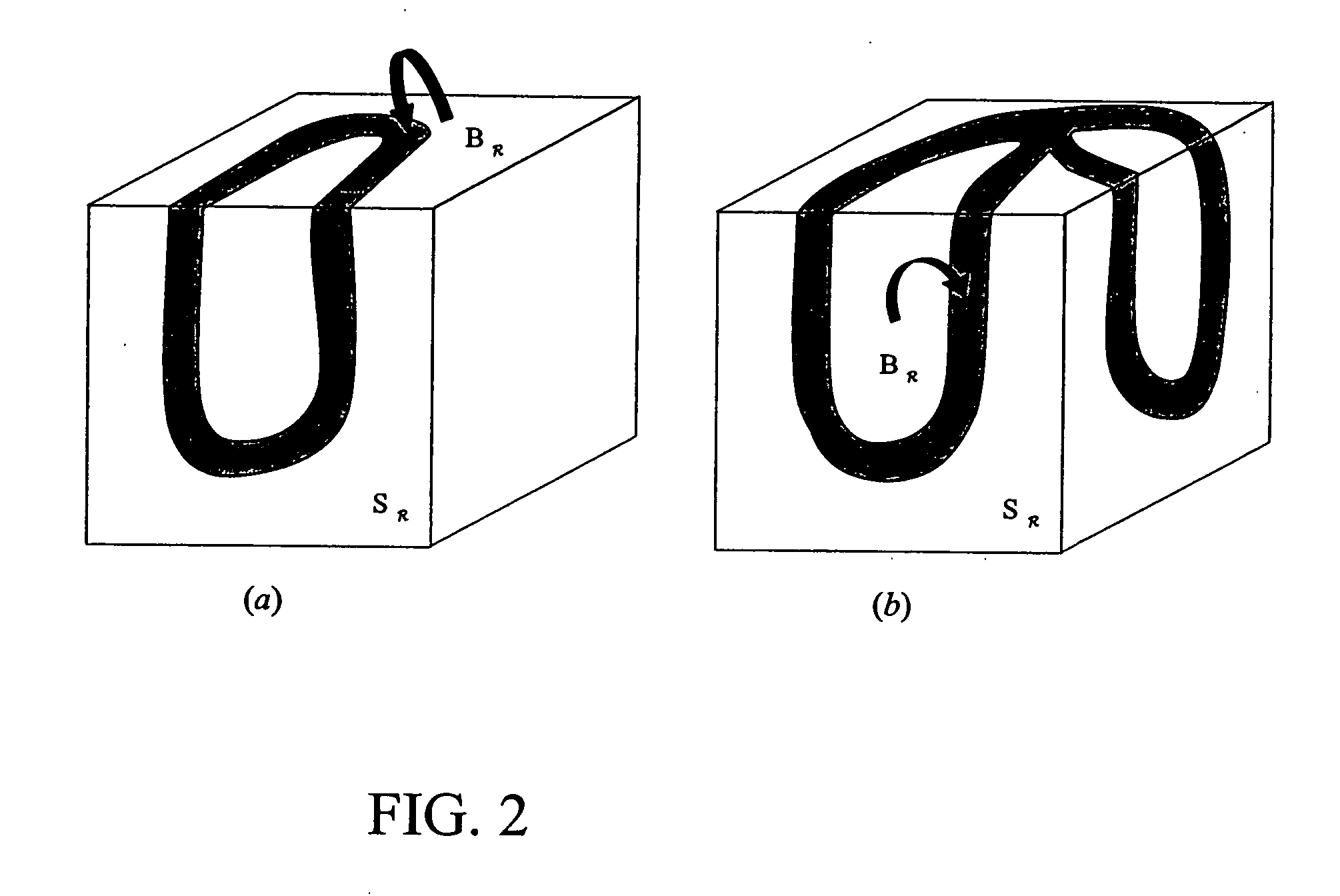
Digital topological analysis of trabecular bone MR images and prediction of osteoporosis fractures
a topological analysis and trabecular bone technology, applied in the field of digital topological analysis, can solve the problems of inability to distinguish between trabecular and cortical bones, ignoring the role of structure as a contributor to mechanical competence, and inability to accurately define the 3d structure found in trabecular bone networks in connectivity analysis of 2d sections, etc., to achieve the effect of effective us
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Validation and Applications of the Invention
[0121] Validation: Accuracy in Synthetic Images
[0122] Analysis of the synthetic images shows that for rod-like structures (i.e. curves) of greater than 0.9 voxel diameter the topological method has an absolute accuracy of 97%. However, at lower structural resolutions, accuracy was seen to decrease rapidly. The increase in classification errors at lower resolutions can be explained by partial volume mixing of low BVF voxels. Since a rod can intersect between one and four voxels within each slice, rods of 0.6 and 0.7 diameters result in maximum voxel BVFs ranging from 0.07 to 0.28 and 0.095 to 0.38, respectively. Recalling that the empirically determined BVF threshold for binarization was 0.25, one would expect that at low rod diameters, many of the low BVF voxels would disappear. At greater rod diameters, BVF increased sufficiently for more elements to survive after thresholding, resulting in increased classification accuracy. The reprodu...
example 2
Applications Ex Vivo to Bone Specimens: Prediction of Elastic Properties of Trabecular Bone
[0124] These properties were used to ascertain relationships with trabecular network competence of the bone specimens as represented by Young's modulus (YM) using regression analysis (JMP-IN, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, N.C.). Toward this goal Young's modulus data obtained in prior work on human wrist specimens were re-examined. The experiments are detailed in Hwang et al., 1997. In brief, YM was derived from stress-strain curves by uniaxial compression testing of cylindrical trabecular bone samples (9 mm diameter and length) drilled parallel to the long axis of the bone from the ultra-distal radius of 13 cadavers (Hwang et al., 1997).
[0125] The accuracy of topological classification is illustrated in a small region of an ex-vivo surface skeleton image, displayed as a voxel projection in FIG. 12, clearly showing the correct classification of surface and curve structures. The projection images ...
example 3
In Vivo Applications to Patients
[0129] Of particular medical significance is the application of topological analysis to patients with bone disease, which requires processing of images acquired in vivo. FIG. 14 shows three subjects of varying age and correspondingly different architectures. The images in FIG. 14(a) display both numerically and visually a pronounced rod-like architecture, unlike those in FIG. 14(c), which were predominantly plate-like. These differences in morphology can be understood considering that the images in FIG. 14(a) are from a 73 year old woman, whereas the images in FIG. 14(c) are from a 30 year old man. The images in FIG. 14(b), which display a mixed architecture of plates and rods, were from a 49 year-old woman. The topological parameters parallel the same trend seen visually, with surface-curve ratios of 5.9, 7.2, and 11.9, and erosion indices of 1.22, 1.07, and 0.72. The cross sections shown directly below each projection, show that the cylindrical cor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com