Thermoelectric material having crystal grains well oriented in certain direction and process for producing the same
a crystal grain, well-oriented technology, applied in the direction of thermoelectric device junction materials, thermoelectric device manufacture/treatment, electrical apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of low merit figure, brittleness of thermoelectric material produced through the prior art unidirectional solidification process, and fine powder has reached the limit, etc., to achieve the effect of large merit figur
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Process Sequence
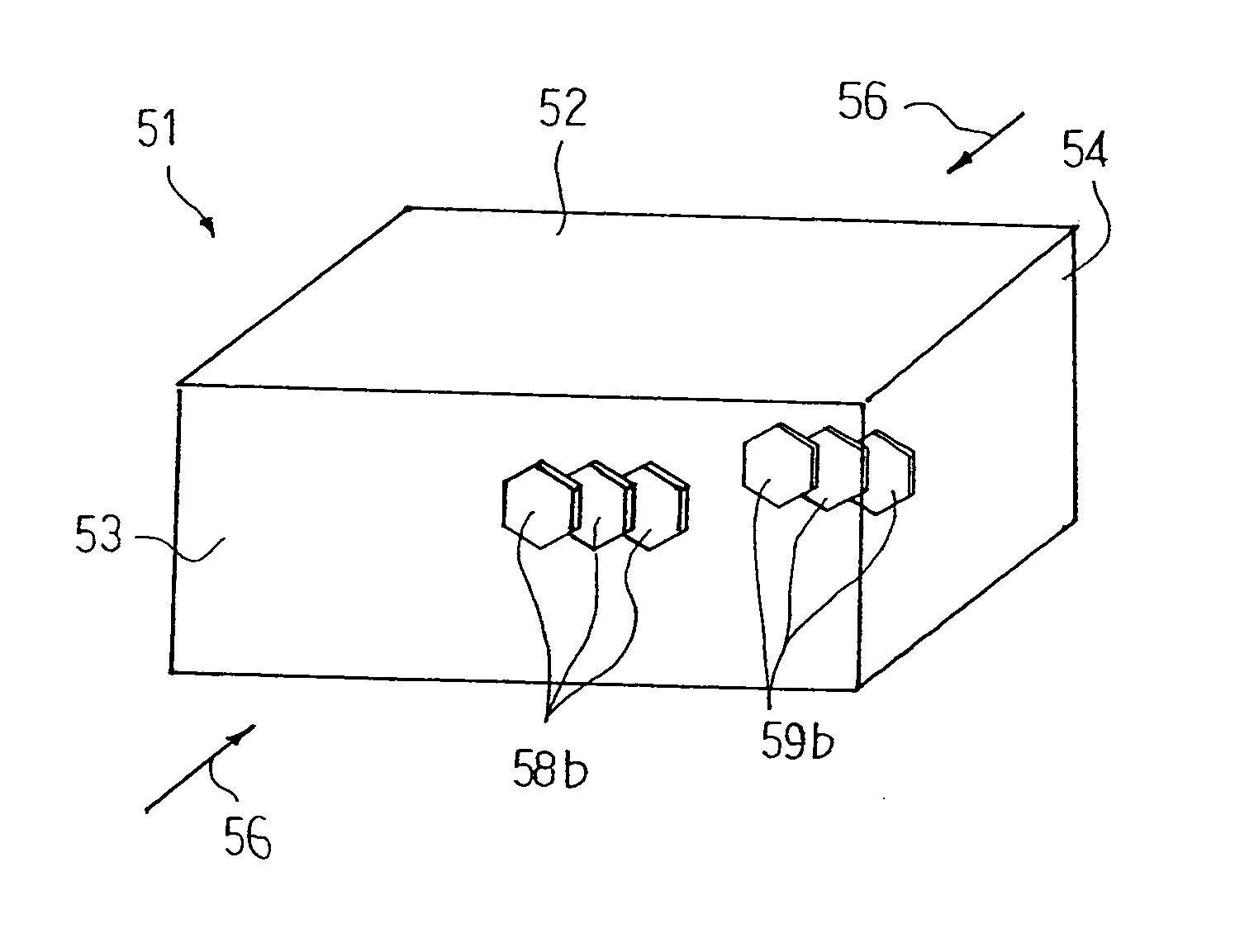
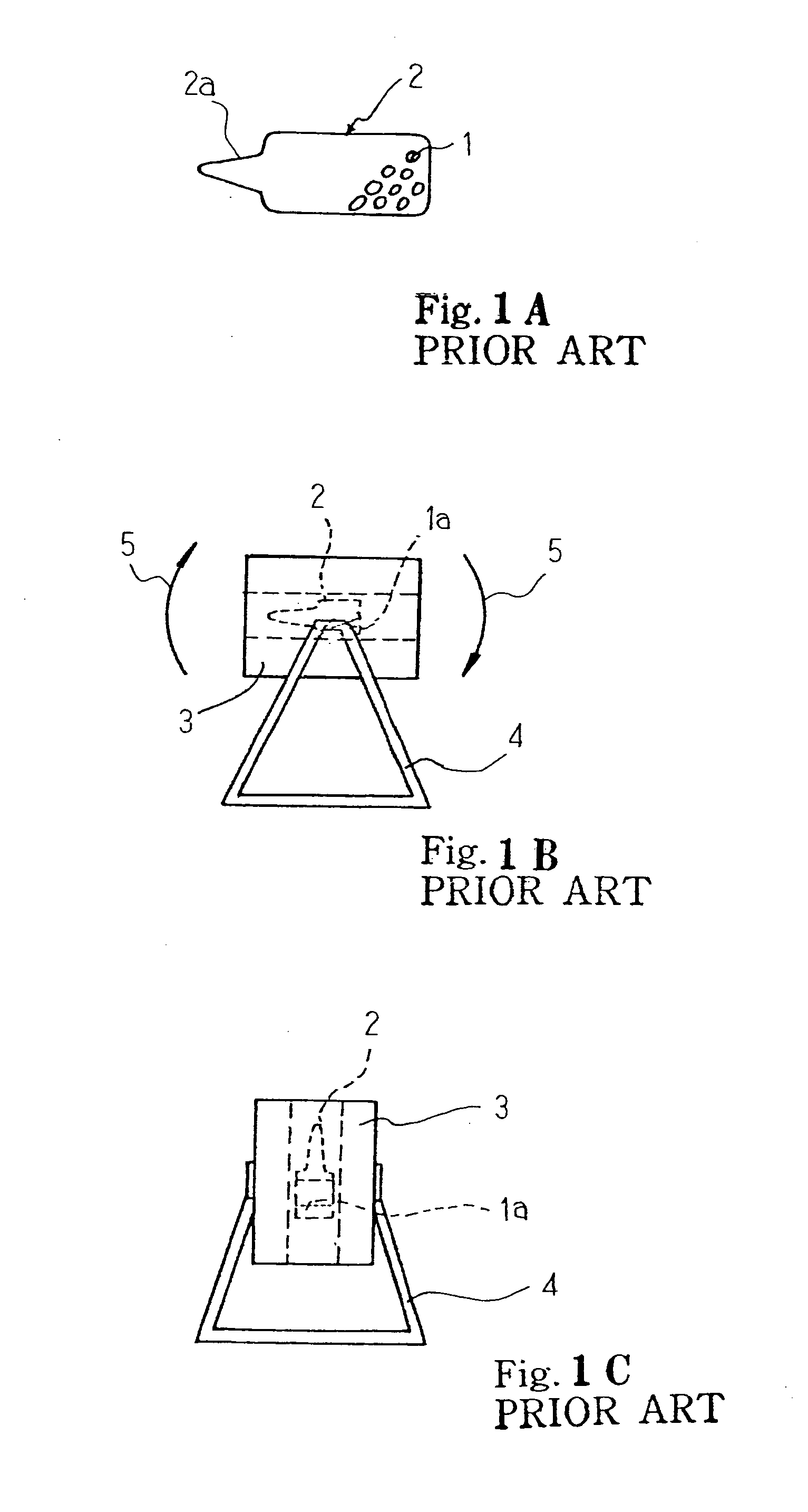
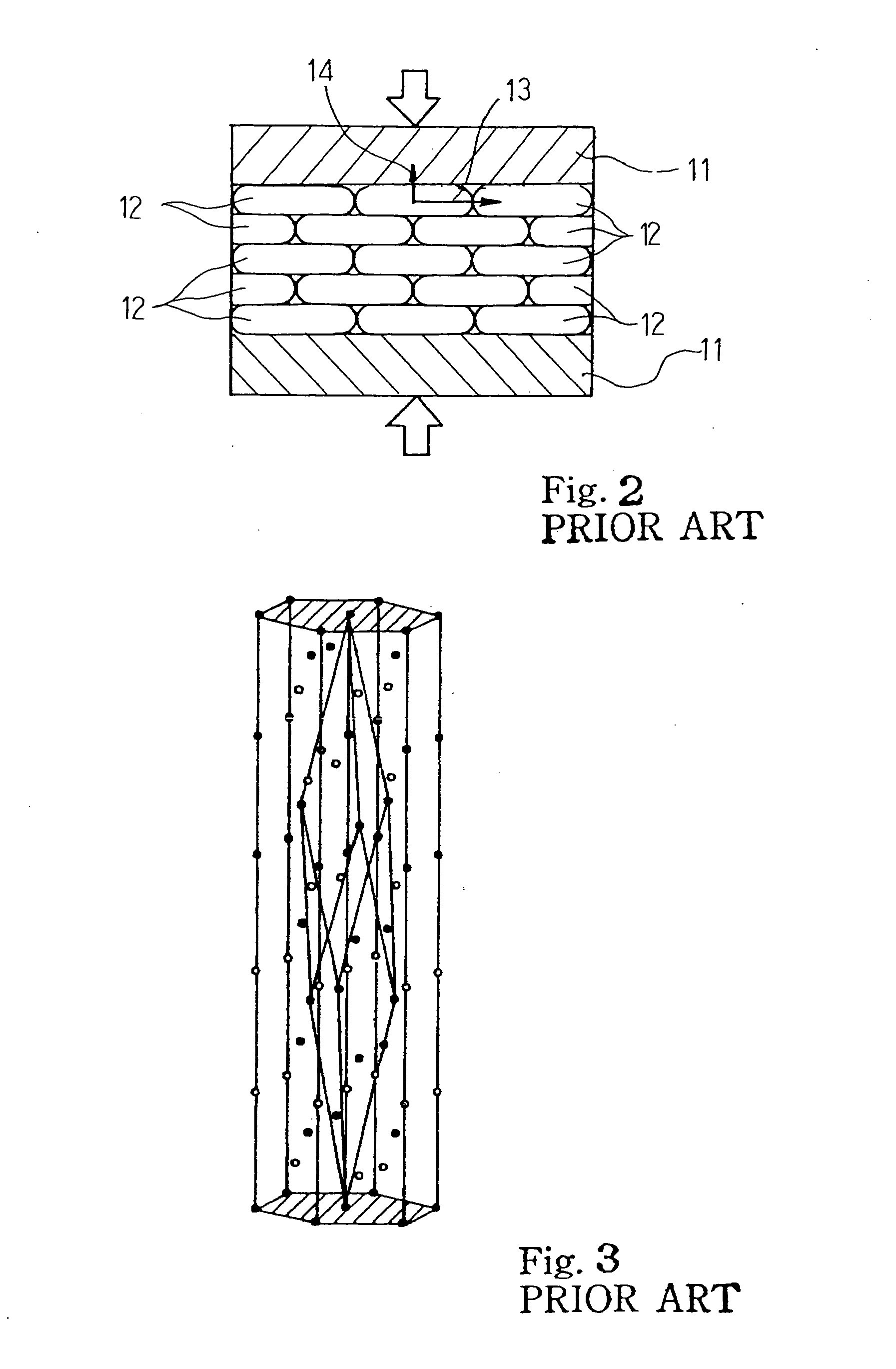
[0043]FIG. 4 shows a process sequence for producing thermoelectric material embodying the present invention. The process includes seven steps S1 to S7. The process starts with blending constituent elements of the thermoelectric material at a predetermined composition ratio as by step S1. The constituent elements are scaled, and, thereafter, are mixed with one another. The constituent elements are dependent on the composition of the thermoelectric material. In case where the thermoelectric material is in the bismuth-antimony-tellurium-selenium system, i.e., Bi—Sb—Te—Se system, the bismuth, antimony, tellurium and selenium are the constituent elements. The mixture of the constituent elements is hereinbelow referred to as “pellets”.
[0044] Subsequently, the pellets are sealed in an ampul as by step S2. The pellets are heated over the melting point, and an ingot is produced from the pellets in the ampul as by step S3. The ingot is taken out from the ampul. The ingot is...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| aspect ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| aspect ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| partial pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com