Method of fabricating semiconductor devices and method of adjusting lattice distance in device channel
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
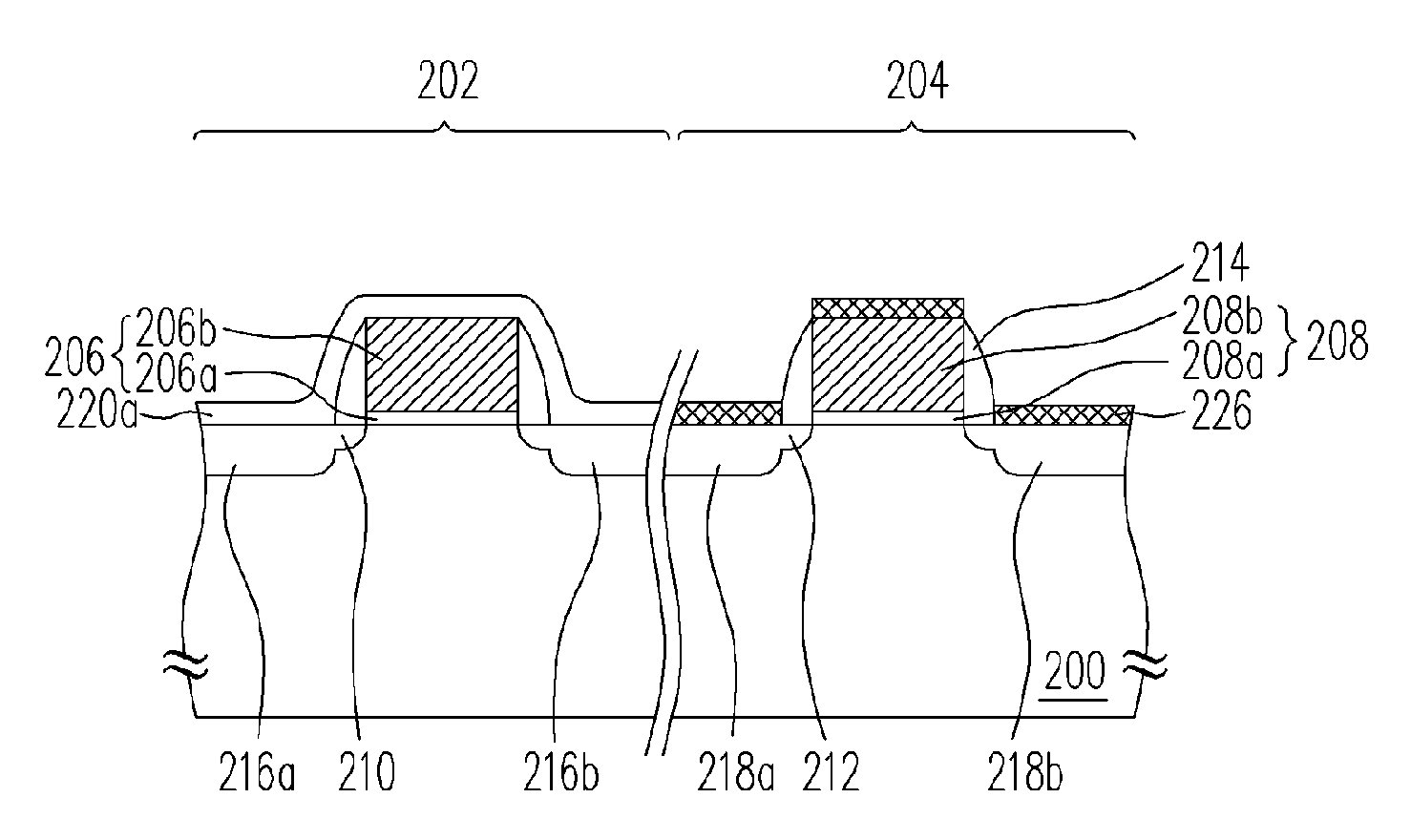
[0027]FIGS. 2A-2F are schematic cross sectional views showing the progression of a method of fabricating a semiconductor device according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 2A, a substrate 200 is provided. The substrate 200 includes, for example, a device area 202 and a peripheral circuit area 204. Gate structures 206 and 208 are formed over the substrate 200 of the device area 202 and the peripheral circuit area 204, respectively, wherein, the gate structure 206 can be a portion of a memory device or an electro-static discharge (ESD) protection circuit. The gate structure 206 includes the gate dielectric layer 206a and the gate electrode layer 206b. The gate structure 208 can be a portion of a logic device. The gate structure 208 includes the gate dielectric layer 208a and the gate electrode layer 208b. In addition, the material of the gate dielectric layers 206a and 208a can be, for example, silicon oxide. The material of the gate electrode layer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com