Modulators of coagulation factors with enhanced stability
a coagulation factor and pharmacological activity technology, applied in the field of coagulation factor pharmacological activity regulation, can solve the problems of unrealized use of unmodified rna as a therapeutic agent, no available agent meets the therapeutic endpoints of both bioavailability and efficacy, and the major cause of death of adult populations in developed nations. , to achieve the effect of convenient neutralization, improved bioavailability and favorable anticoagulant properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Substitution of 2′-O-methyl for 2′-hydroxyl Sugars in Sectors
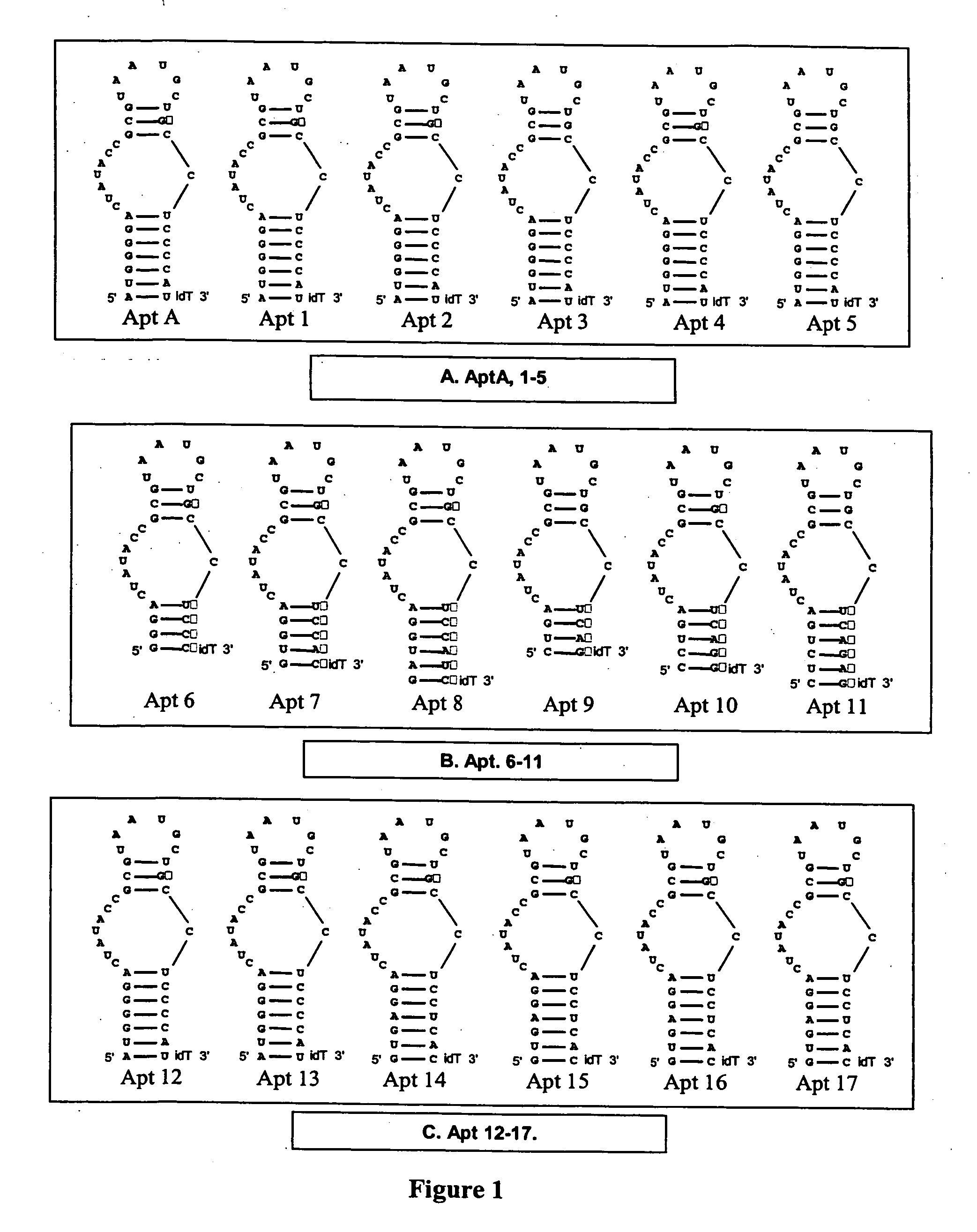
[0332] 2′-Hydroxyl purines were substituted with 2′-O-methyl purines in the 4 secondary structure units of in which purine residues are present: Stem 1 (Apt 1); Loop 1 (Apt 2); Stem 2 (Apt 3); Loop 2 (Apt 4) (see FIG. 1A).
[0333] Procedure: The anticoagulant activity of AptA derivatives Apt 1-5 was evaluated in standard APTT coagulation assays over compound concentrations ranging from 1 uM to low nanomolar (FIG. 2). The “neutralizability” of Apt1-5 was evaluated in standard APTT antidote assays over AptA antidote concentrations (AptA AD; see sequence listings) ranging from 5 uM and down (FIG. 2). For these assays, the concentration of AptA and derivatives was fixed at 125 nM.
[0334] Apt 4 showed gain of anticoagulant activity (FIG. 2); Apt 1-3 showed moderate loss of activity; and Apt 5 showed severe loss of activity. Apt 1-3 exhibit enhanced neutralization, suggesting that introduction of 2′ -O-methyl residues within the...
example 2
Stem 1 Modifications
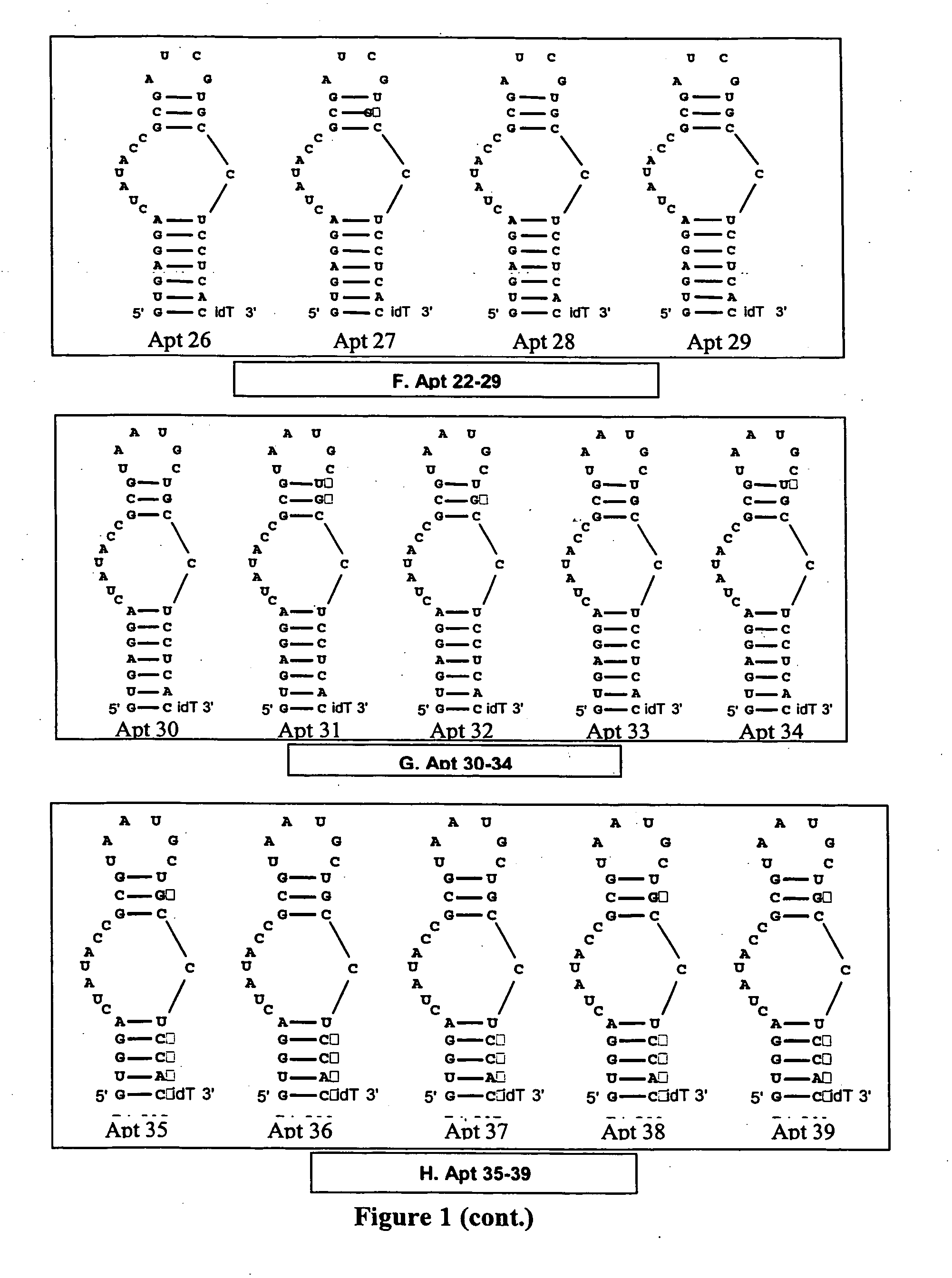
[0336] Two “families” of stem 1 variants were designed (Apt 6-8 and 9-11; FIG. 1B) consisting of 4, 5, and 6 basepair stems. All constructs were designed in the Apt-2 background. Stem 1 sequences were evaluated for the ability to design complementary antidote oligonucleotides to them such that the antidotes contain minimal secondary structure, and for the ability of the aptamer to assume the proper secondary structure.
[0337] Stems were wholly 2′-O-methyl modified. Antidote oligonucleotides were designed specific for Apt 6-11 that bind to their respective target aptamer in the same register as AptA AD (see sequence listings below).
[0338] Experiments: The anticoagulant activity of Apt 6-11 was evaluated in standard APTT coagulation assays over compound concentrations ranging from 1 uM to low nanomolar. The antidote control of Apt 6-11 was evaluated in standard APTT antidote assays over antidote concentrations ranging from 5 uM and down. For these assays, the con...
example 3
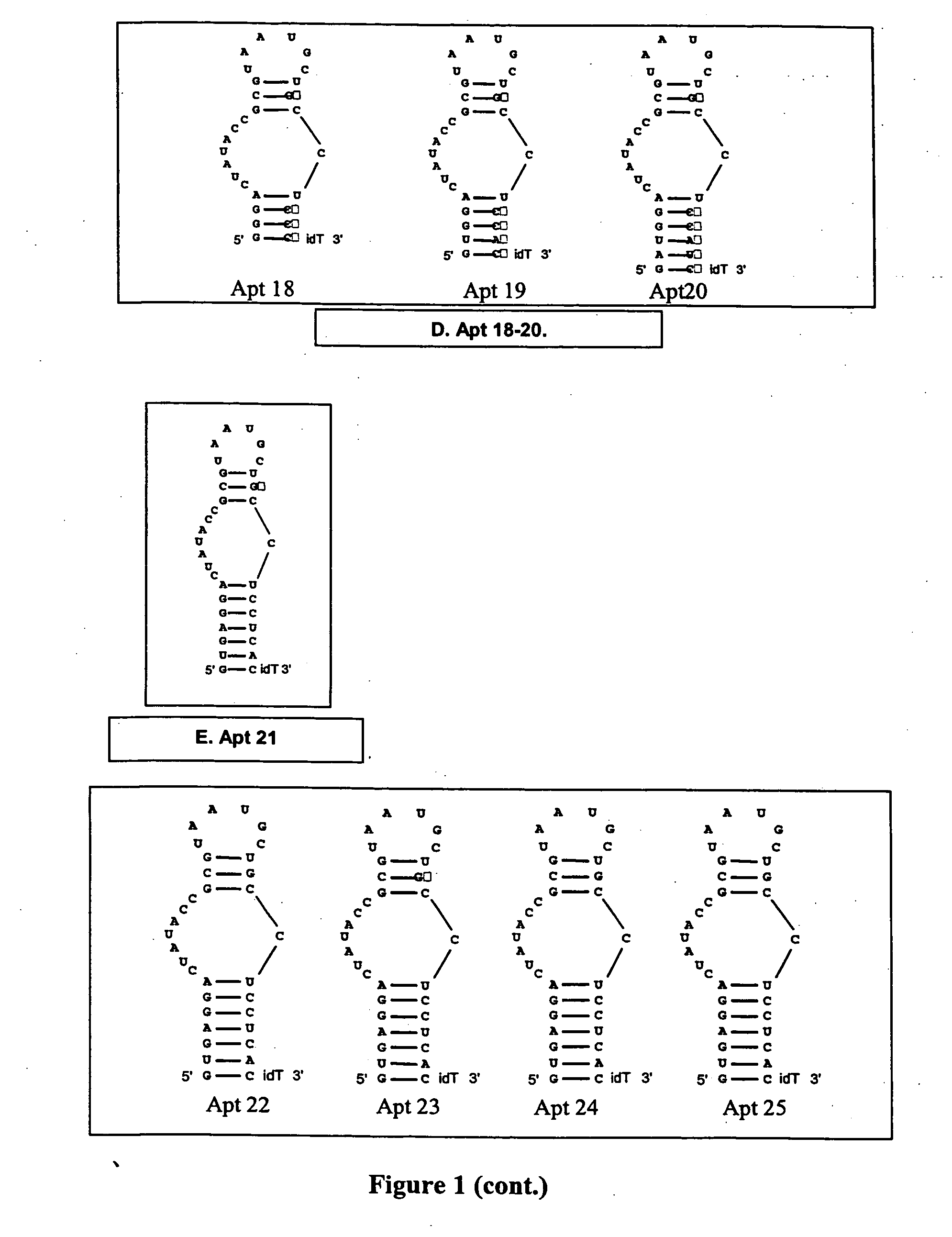
[0341] The anticoagulant activity of Apt 12-17 was evaluated in standard APTT coagulation assays over compound concentrations ranging from 1 uM to low nanomolar. The “neutralizability” of Apt 12-17 was evaluated in standard APTT antidote assays over antidote concentrations ranging from 5 uM and down. For Apt 12, 14, 15, and 16, the aptamer concentration was fixed at 125 nM in these assays, and for Apt 13 and 17, the aptamer concentration was fixed at 250 nM.
[0342] Comparison of the anticoagulant activity of Apt 12 with Apt 13 and Apt17 (FIG. 5) demonstrates that the loss of activity observed for Apt6-11 is due to the presence of 2′-O-methyl substitutions at one or more critical residues. Comparison of the anticoagulant activity of Apt14 to Apt12 indicates that the stretch of 4 consecutive guanosines within stem 1 can be altered without a significant impact on anticoagulant activity. Comparison of Apt15 and 16 with Apt 2, 12 and 17 a) demonstrates that the pre...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com