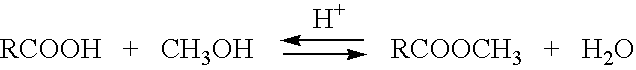Production of biodiesel from triglycerides via a thermal route
a thermal route and biodiesel technology, applied in the direction of fatty acid production, liquid carbonaceous fuels, liquid hydrocarbon mixture production, etc., can solve the problems of inoperable process, difficult conversion of free fatty acids and triglycerides into useful fuels by any traditional method, and the potential is presently underexplored
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Conversion of Restaurant Trap Grease into Mixed Biodiesel / Diesel Product
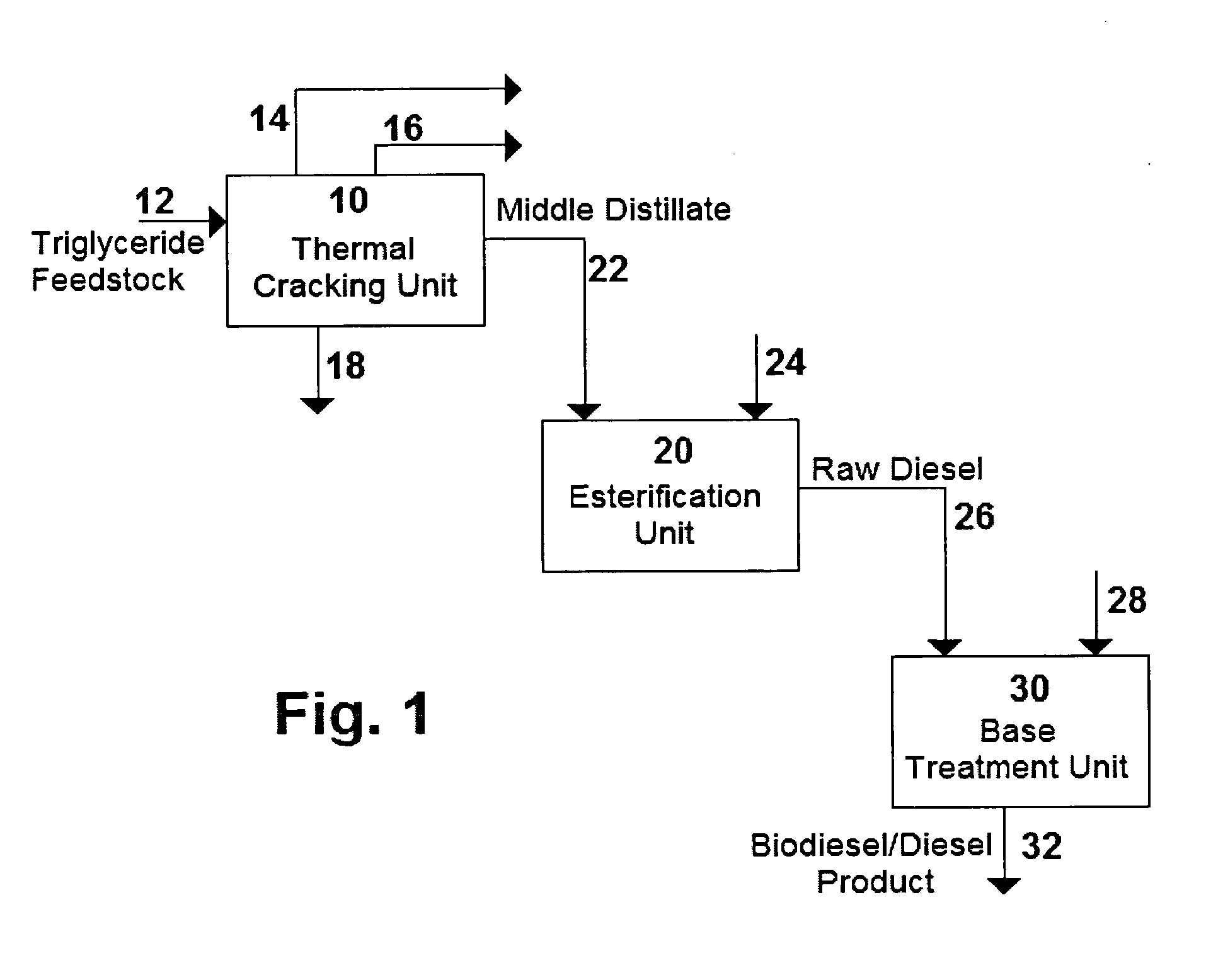
[0029] Restaurant trap grease having an average density of 0.925 g / mL was fed to a thermal cracking unit where it was cracked at a temperature of 418.5° C. and a pressure of 29 psig (301 kPa) for 40 minutes. Thermal cracking produced a gas stream, a naphtha stream, a middle distillate stream with a maximum boiling point of approximately 343° C., as well as water and residue. The middle distillates stream made up 63.0 wt % of the total cracked product and had an acid number of 83.93 mg KOH / g.
[0030] The middle distillate stream was then fed to an acid esterification unit, where it was contacted with methanol in the presence of an Amberlyst 36 catalyst. Esterification was conducted at a temperature of 90° C. and at atmospheric pressure for 20 hours.
[0031] Esterification produced a raw diesel stream which was then treated with a calcium hydroxide solution, Ca(OH)2(aq), to produce a final mixed biodiesel / diesel pr...
example 2
Conversion of Rendered Animal Fat into Mixed Biodiesel / Diesel Product
[0032] Rendered animal fat, having an average density of 0.918 g / mL was fed to a thermal cracking unit in which it was cracked at 411° C. and atmospheric pressure for 40 minutes. The thermally cracked product contained 68.6 wt % middle distillates having a maximum boiling point of 345° C., naphtha and the remainder gas, water and residues.
[0033] The middle distillate stream, having a viscosity of 8.50 cSt, and an acid number of 146.96 mg KOH / g, was then fed to an acid esterification unit, where it was contacted with methanol in the presence of an Amberlyst 36 catalyst. Esterification was conducted at a temperature of 90° C. and at atmospheric pressure for 20 hours.
[0034] The resultant raw diesel stream was then treated with a calcium hydroxide solution, Ca(OH)2(aq), to produce a final mixed biodiesel / diesel product having an acid number of 0.75 mg KOH / g. The final product was found to have 18 ppm sulphur and 158...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com