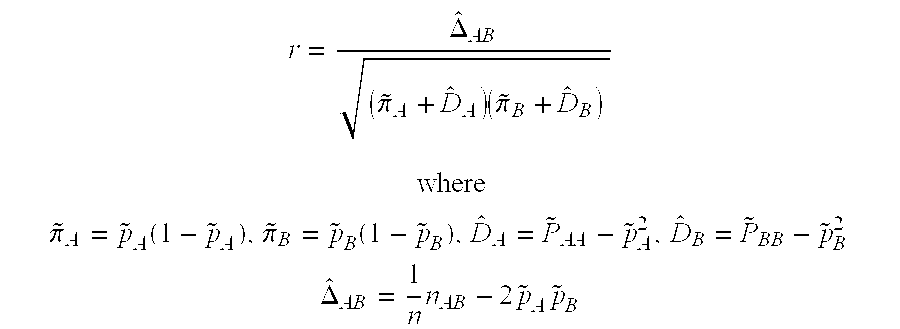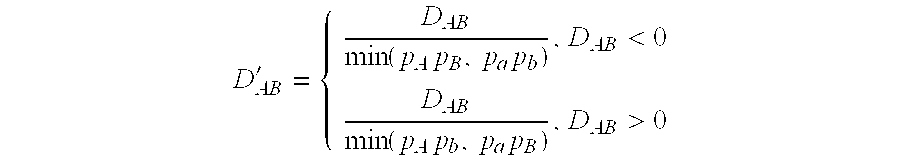Method of screening for drug hypersensitivity reaction
a drug hypersensitivity and reaction technology, applied in biochemistry apparatus and processes, organic chemistry, sugar derivatives, etc., can solve the problems of severe morbidity and mortality, prolong survival, and reduce the risk of hiv-1 infection complications, so as to increase the risk and increase the incidence of a hypersensitivity reaction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Study Design
[0083] A retrospective, case-control study was conducted with adult (>18 years of age) HIV-infected subjects who participated in a Glaxo Wellcome abacavir clinical development program. Subjects were classified as either “case” or “control” subjects based on the following. Case subjects had experienced an episode of suspected or confirmed hypersensitivity to abacavir; control subjects had received Abacavir for at least six weeks, but had not experienced an episode of confirmed or suspected HSR. The six-week treatment period was chosen based on the knowledge that the majority of HSR events occur within the first six weeks of treatment. Case narratives were collected at or close to the time of the suspected or confirmed hypersensitivity reaction. Control subjects were matched for study (if possible) ethnicity, gender, CD4+cell count (if available; four CD4+ ranges: 500 cells / mm3); and age (plus or minus 5 years). Wherever possible, treatment regime was also matched (“naive...
example 2
Screening TNFα
[0089] The presence of the TNFα G(-237A) polymorphism may be determined using a fluorescent dye and quenching agent-based PCR assay, such as the allele discrimination form of the 5′ nuclease assay (Lee and Bloch, Nucleic Acids Research 21:3761 (1993)). In brief, this assay uses two allele specific probes labeled differentially with fluorescent “reporter” dyes at the 5′ ends and with a common quenching agent at the 3′ ends. Normally the fluorescence of each reporter dye is quenched by the quenching agent when present in the same oligonucleotide molecule. The allele specific probes are used in conjunction with two primers, one of which hybridizes to the template 5′ of allele specific probes while the other hybridizes to the template 3′ of the such probes.
[0090] The presence of the TNFα G(-237)A polymorphisms was determined by the method of allelic discrimination using the 5′-nuclease assay. Two allele specific probes labeled with a different fluorescent dye at the 5′ en...
example 3
Screening HLA-B57
[0097] Genotyping of the HLA-B gene was performed in samples from 120 subjects (44 Cases and 76 Controls) in the research laboratories of the Anthony Nolan Bone Marrow Trust (Royal Free Hospital, London, UK). Typing was primarily conducted using Reference Strand-mediated Conformation Analysis (RSCA; see, e.g., Pel-Freez® Clinical Systems, LLC) as is known in the art. Arguello et al., Reviews in Immunogenetics, 1:209 (1999); Arguello et al., Tissue Antigens, 52:57 (1998). DNA sequencing and Sequence Specific Oligonucleotide Probe (SSOP) techniques (see, e.g., Yoshida et al., Hum Immunol 34:257 (1992); Smith et al., Hum Immunol 55:74 (1997)) were used when necessary as backup techniques to determine HLA genotype.
[0098] Of the Cases, 25 / 44 (57%) were found to have the HLA-B57 allele present (i.e., were either heterozygous or homozygous for the HLA-B57 allele), whereas only 3 / 76 (4%) of the Controls were found to have the HLA-B57 allele present (each was heterozygous ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| polymorphic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| min-width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com