Flow Distribution Channels To Control Flow in Process Channels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Flow Distribution With Flow Distribution Features
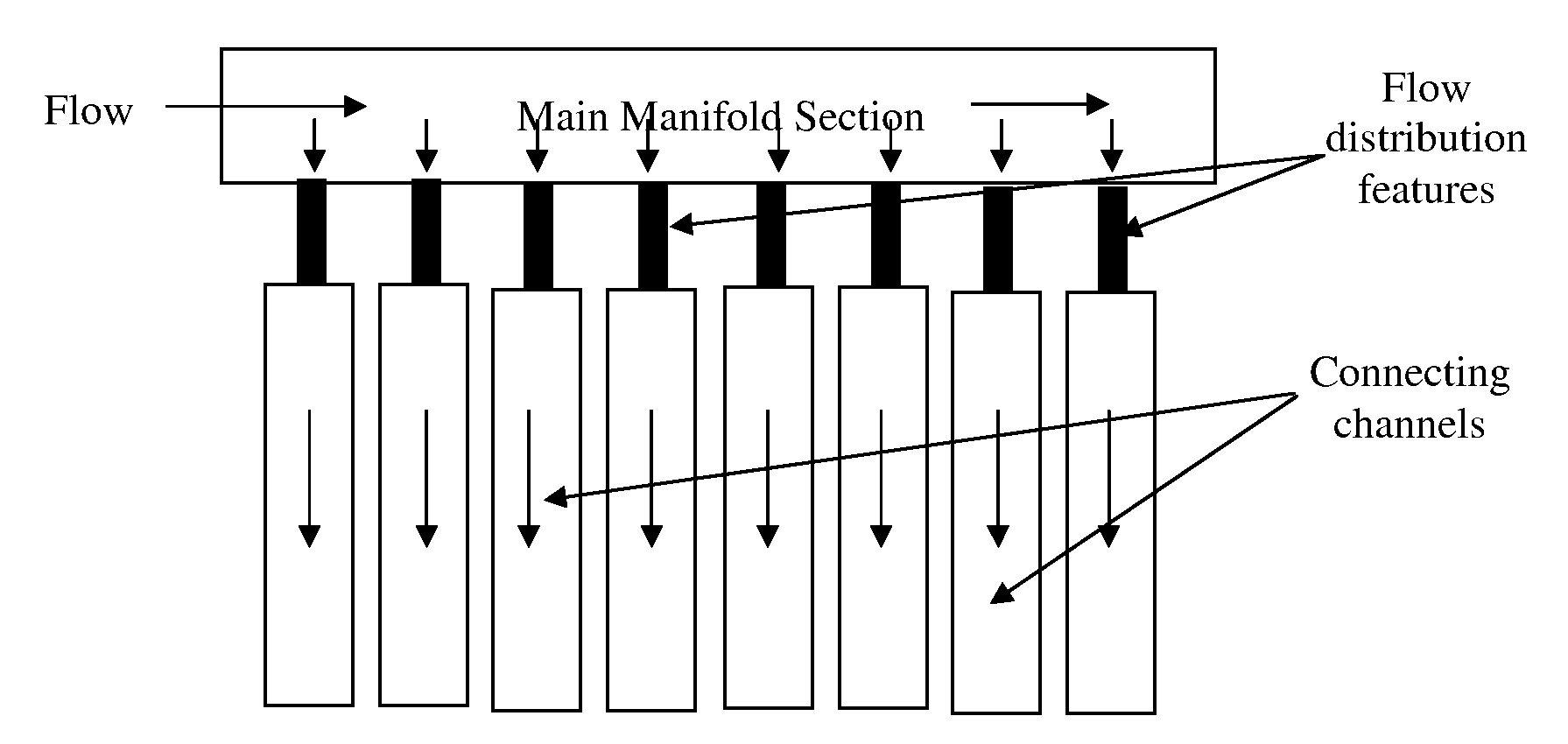
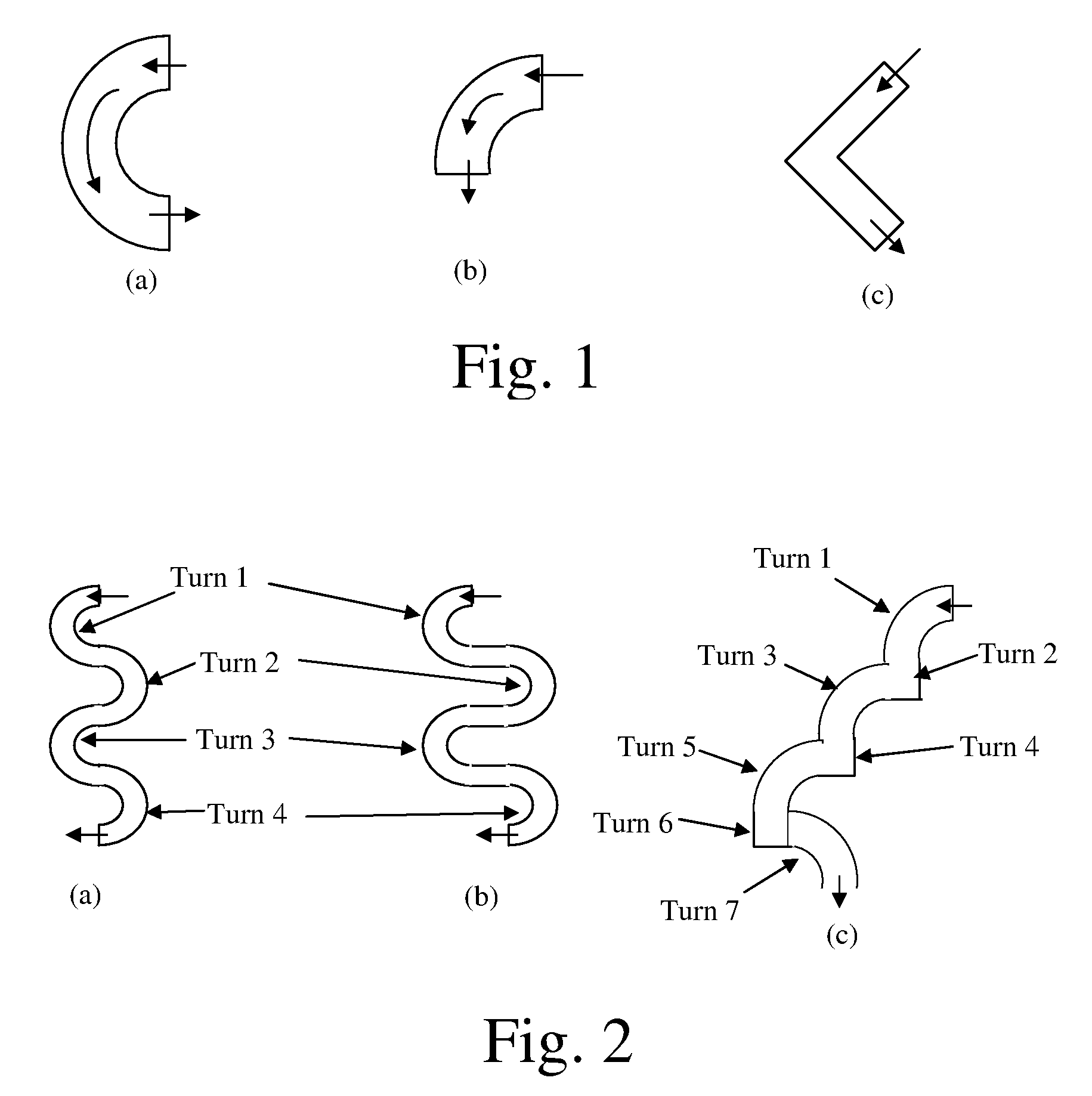
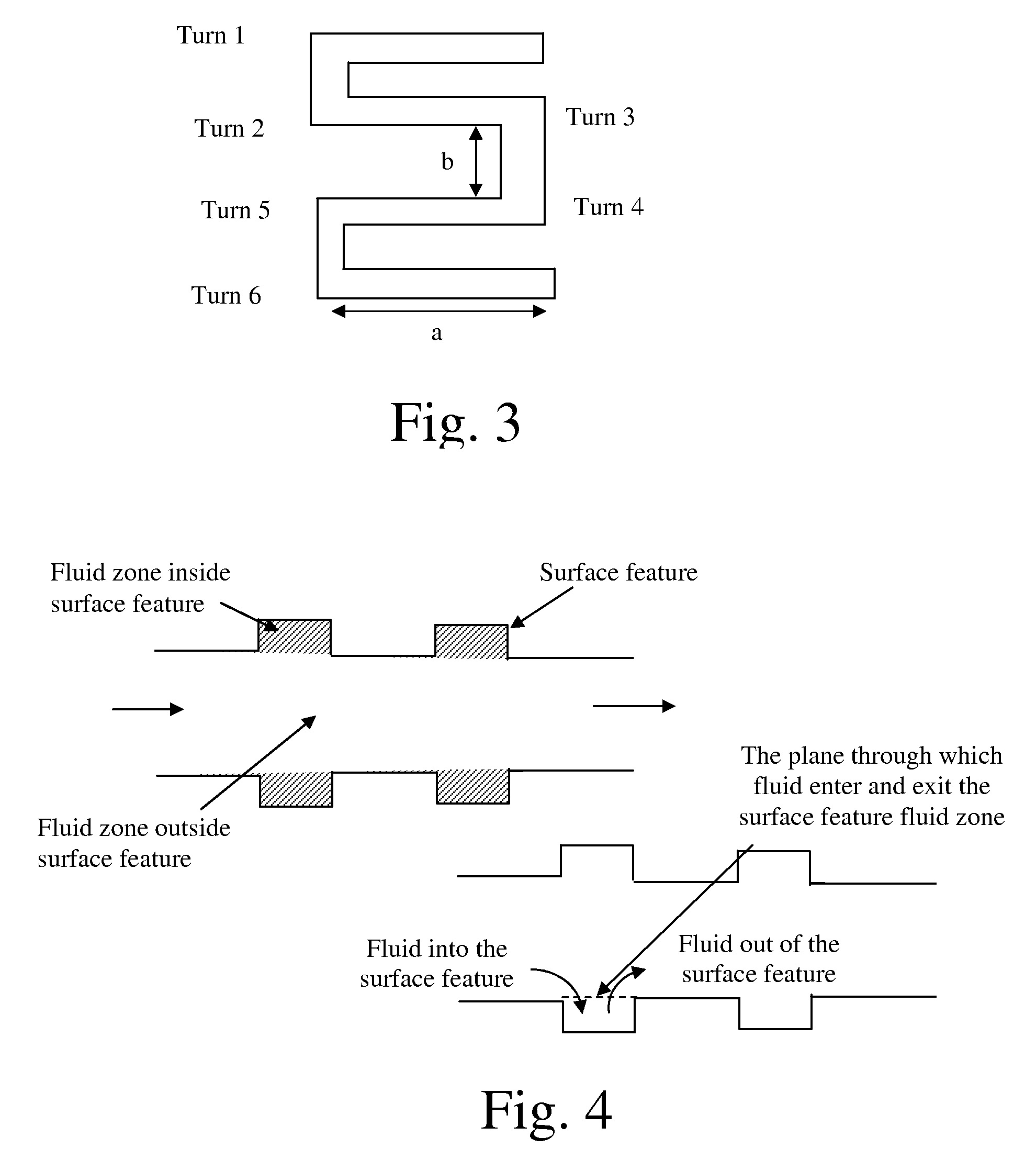
[0092] A case study was done to see the improvement in the flow distribution using flow distribution features. The general schematic of the device is shown in FIG. 5 but with a bottom manifold. The top and bottom main manifold sections were 12.7 mm×2.54 mm in cross-section. The connecting channels were 5.08 mm×0.76 mm in dimensions. The length of connecting channels was 127 mm. The connecting channels were separated by 0.508 mm wall. The number of connecting channels was 19. FIG. 4 shows the dimensions of the flow distribution features. The flow distribution features were in serpentine shape. The cross-section of the flow distribution channel was 0.76 mm×0.38 mm. The manifold, flow distribution channels and connecting (process) channels were in a common plane.
[0093] The fluid used was ethylene at 230 psig and −30° C. The total flow rate entering the main manifold section was 0.487 kg / hr. The performance of flow distribution was defi...
example 2
Flow Distribution Features Provide Uniform Flow Distribution Over a Wide Range of Turn-up and Turn-down Flow Rates From Nominal
[0098] A geometry the same as in Example 1 was used to show that the flow distribution features provide relatively uniform flow distribution for turn-up and turn-down flow rates. The flow distribution results were compared to the flow distribution obtained in the same geometry but without flow distribution features. The fluid, temperature and outlet pressure conditions were kept for both the cases: with flow distribution feature and without flow distribution features. The fluid used was ethylene at 230 psig and −30° C. The nominal total flow rate entering the main manifold section was 0.487 kg / hr.
[0099]FIG. 29 shows the quality factors with different turn-up and turn-down factors from nominal flow rates for design with flow distribution features and without flow distribution features. A turn-up / turn-down ratio of 0.8 means 80% of nominal flow rate. A turn-...
example 3
Flow Distribution for Emulsion
[0101] An emulsion is formed by mixing continuous phase liquid with dispersed phase liquid through a porous medium. It is desired for manufacturing that the porous medium through which continuous and dispersed phases are mixed should be replaceable preferably with mixing of the continuous and dispersed phases while flowing in cross-flow direction. However depending upon the requirement, the continuous and dispersed phases can be mixed while flowing co-current or counter-current to each other.
[0102] In this example, only a repeating unit was modeled to describe the performance of the device. The repeating unit has three layers stacked together. The continuous phase enters the first layer as shown in the schematic in the FIG. 9. The flow enters the inlet manifold section. The cross-section of the manifold was 25.4 mm wide×5.08 mm depth. The connecting channel dimensions were 12.7 mm wide×2.03 mm depth×305 mm length. There were total 16 connecting channe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com