Load bearing textile clamp
a textile clamp and load bearing technology, applied in the direction of snap fasteners, draperies, buckles, etc., can solve the problems of inability of sails to transfer potential wind energy into force, the range of applications of industrial textiles up to the development of modern synthetic materials was self-limiting, and the textiles of natural fibers quickly became impractical. achieve the effect of increasing load and increasing load transfer efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
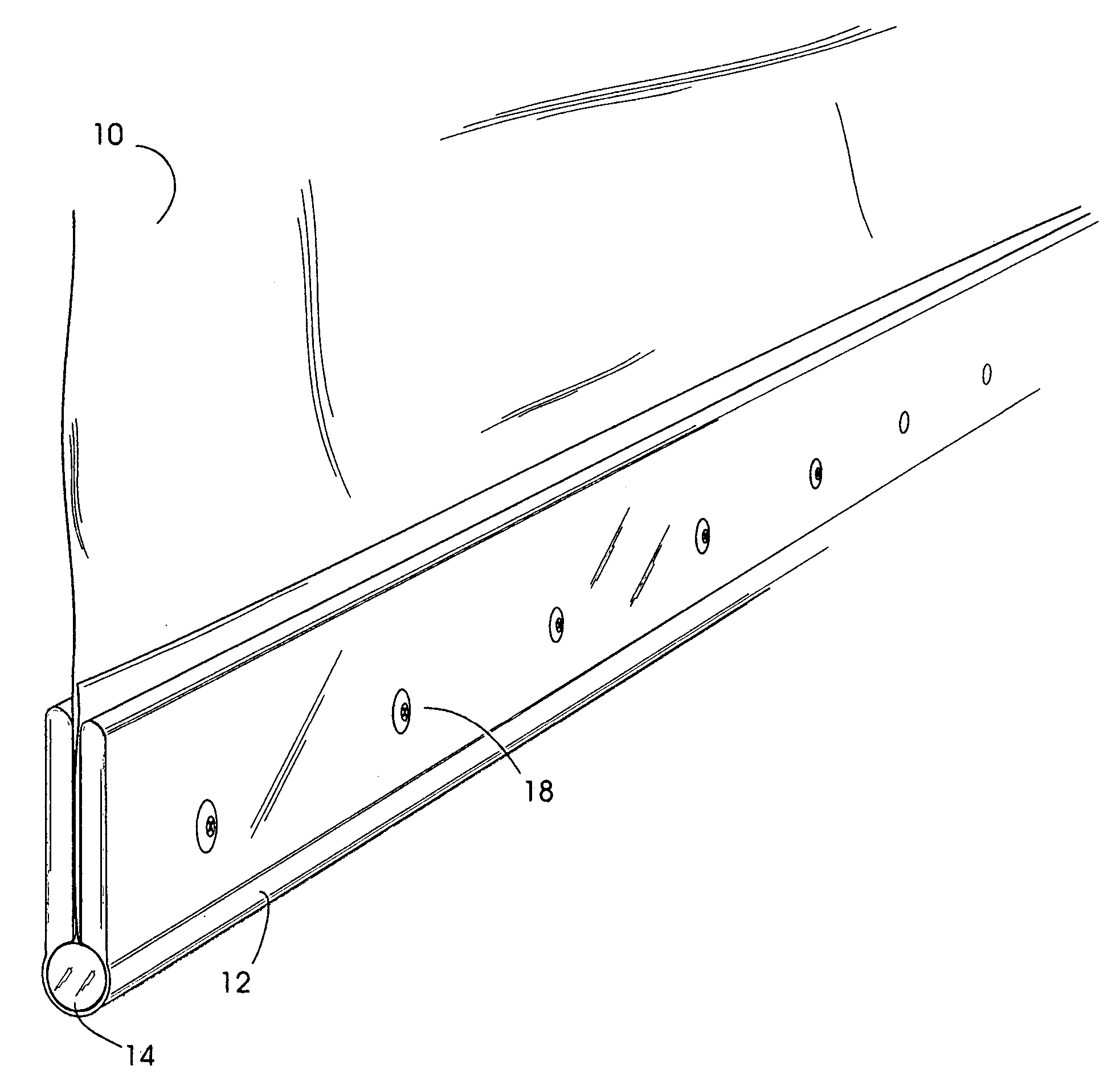
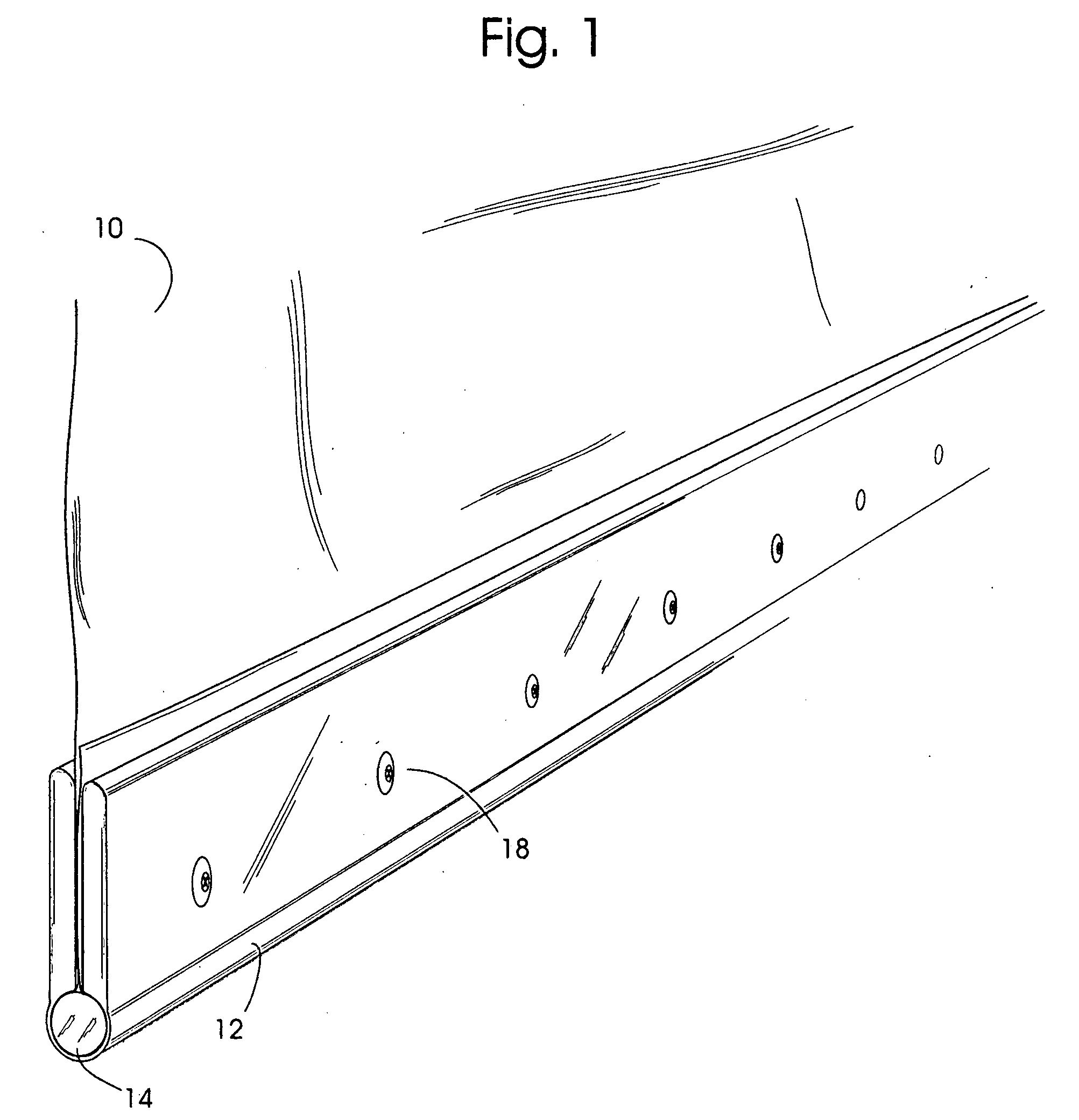
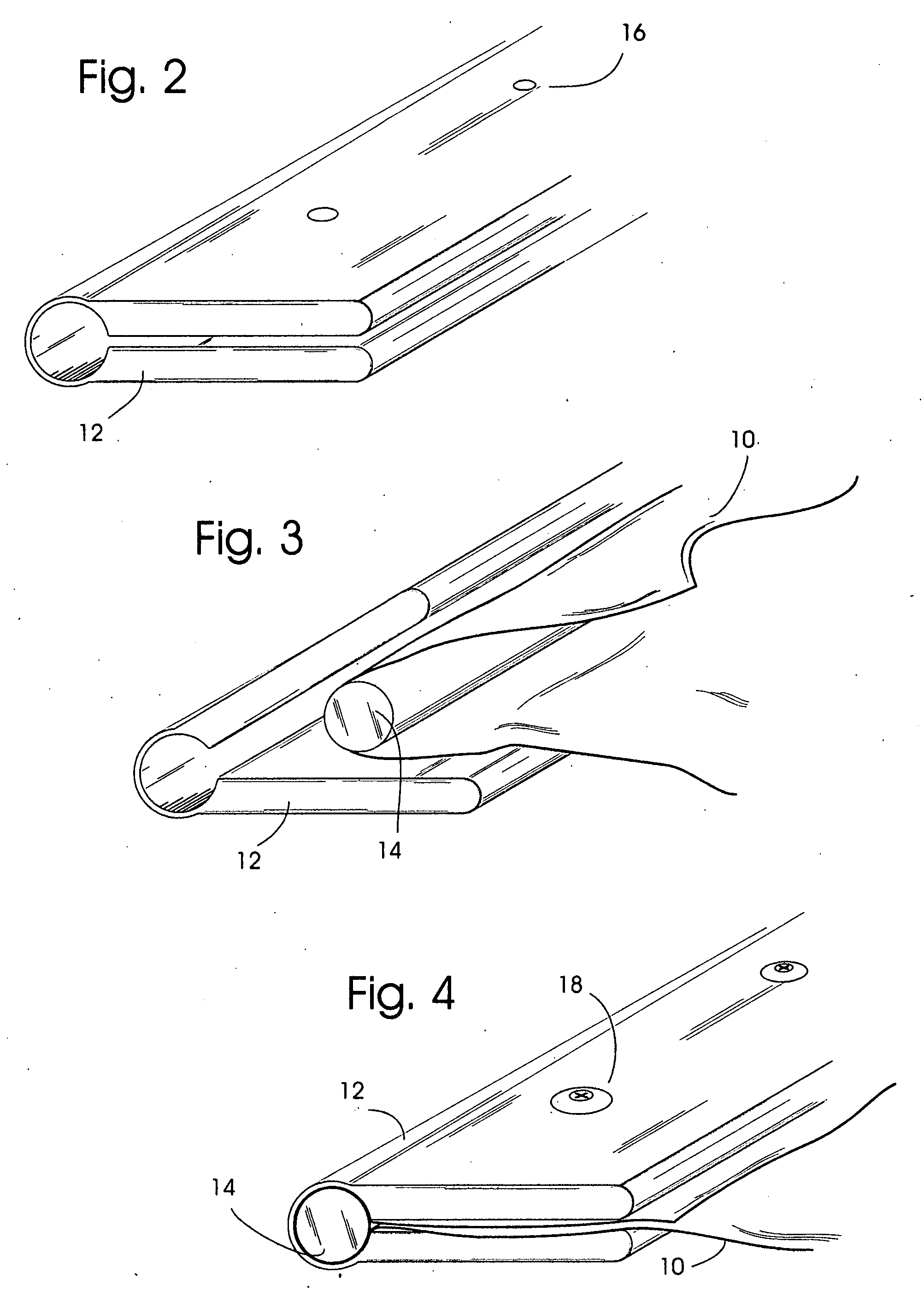
[0034] This invention describes an intermediary device between a load-bearing textile and a secondary structure which secures the textile in a manner to transfer loads from the textile into an anchor in a fast, cost effective, and strong field assembled clamp that retains much of the strength of the textile and resists load induced deformation from point loading and environmental degradation. The invention replaces the typical and laborious task of gluing and / or sewing reinforcements and / or affixing grommets and / or plates into textiles so that they may carry high loads.
[0035] These goals are achieved by the invention by incorporating at the edge of the textile panel a round turn around a length of rod inside a corresponding length of an essentially U-shaped sleeve that forms a compressive clamp around the assembly. To apply the clamp to a textile panel, the edge of the textile is folded once around the rod with sufficient overlap, and then the rod and textile are inserted into the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com