Treatment for post partum hemorrhage
a technology for treating postpartum hemorrhage and uterine arteries, which is applied in the field of treatment of postpartum hemorrhage, can solve the problems of pharmaceutical agents producing side effects not just in the uterus but throughout the body, the uterine arteries cannot be palpated during a bimanual pelvic examination, and the uterine arteries cannot be analyzed. it can reduce or terminate the risk of further hemorrhage, reduce or eliminate blood flow, and reduce the risk of a
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
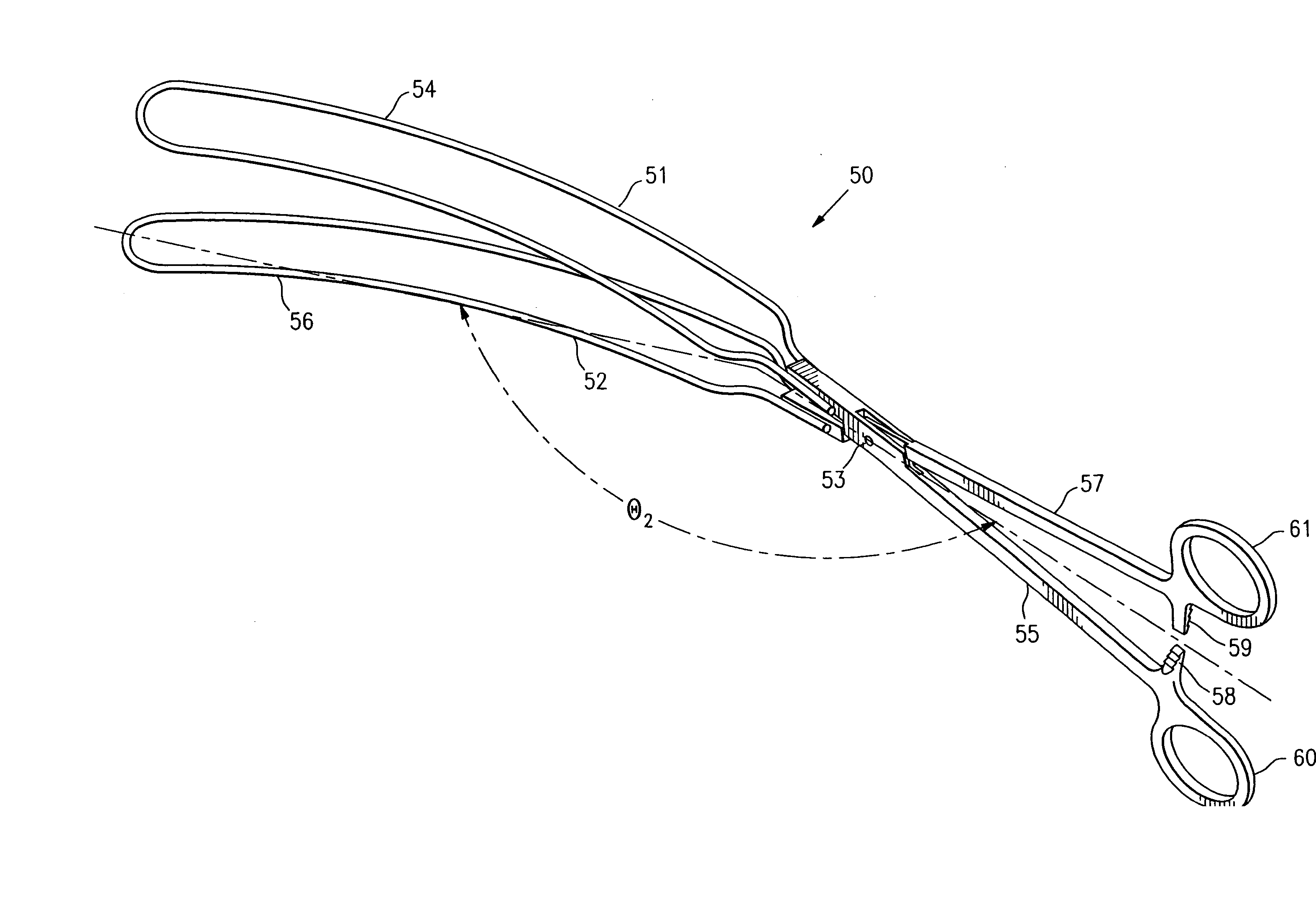
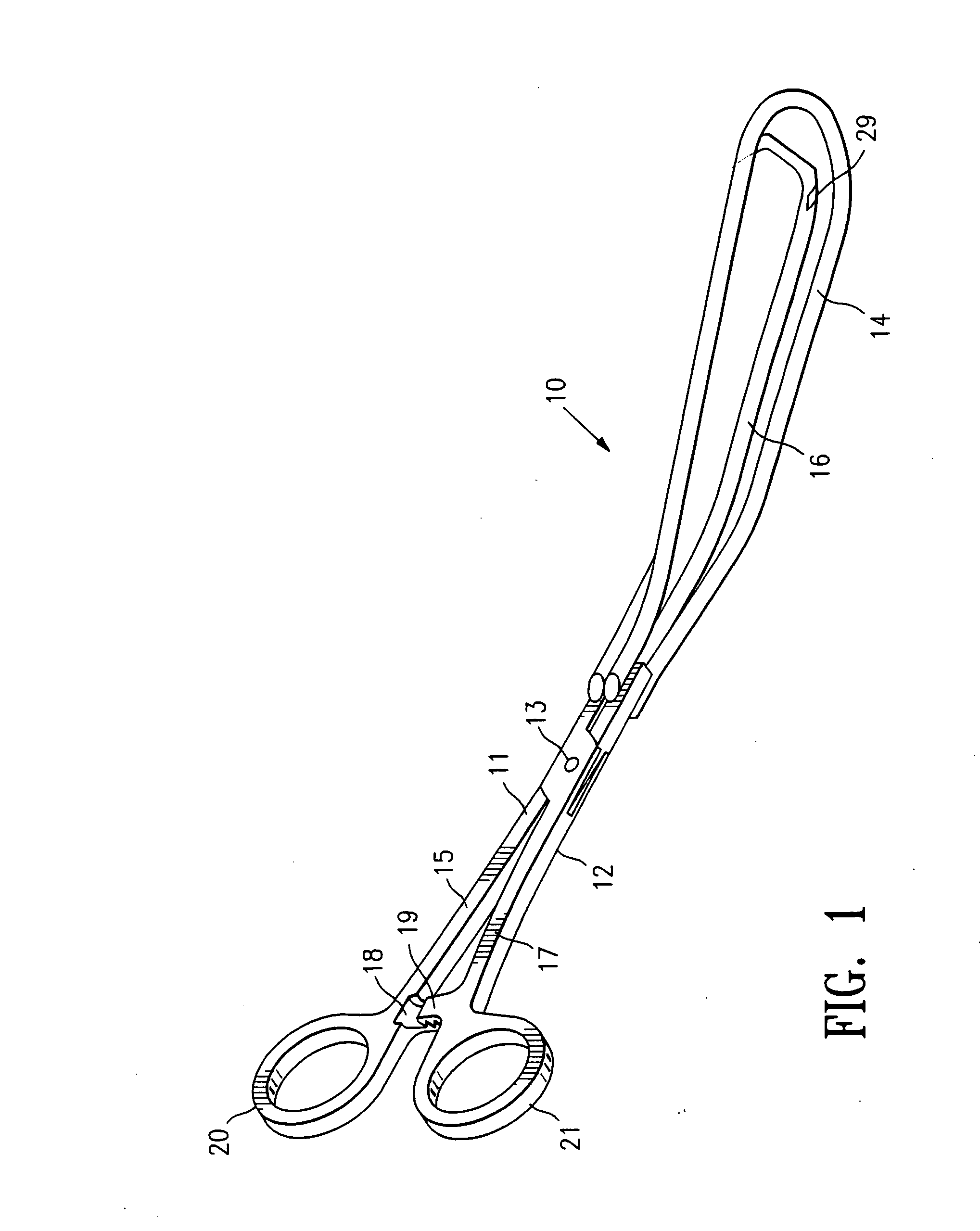
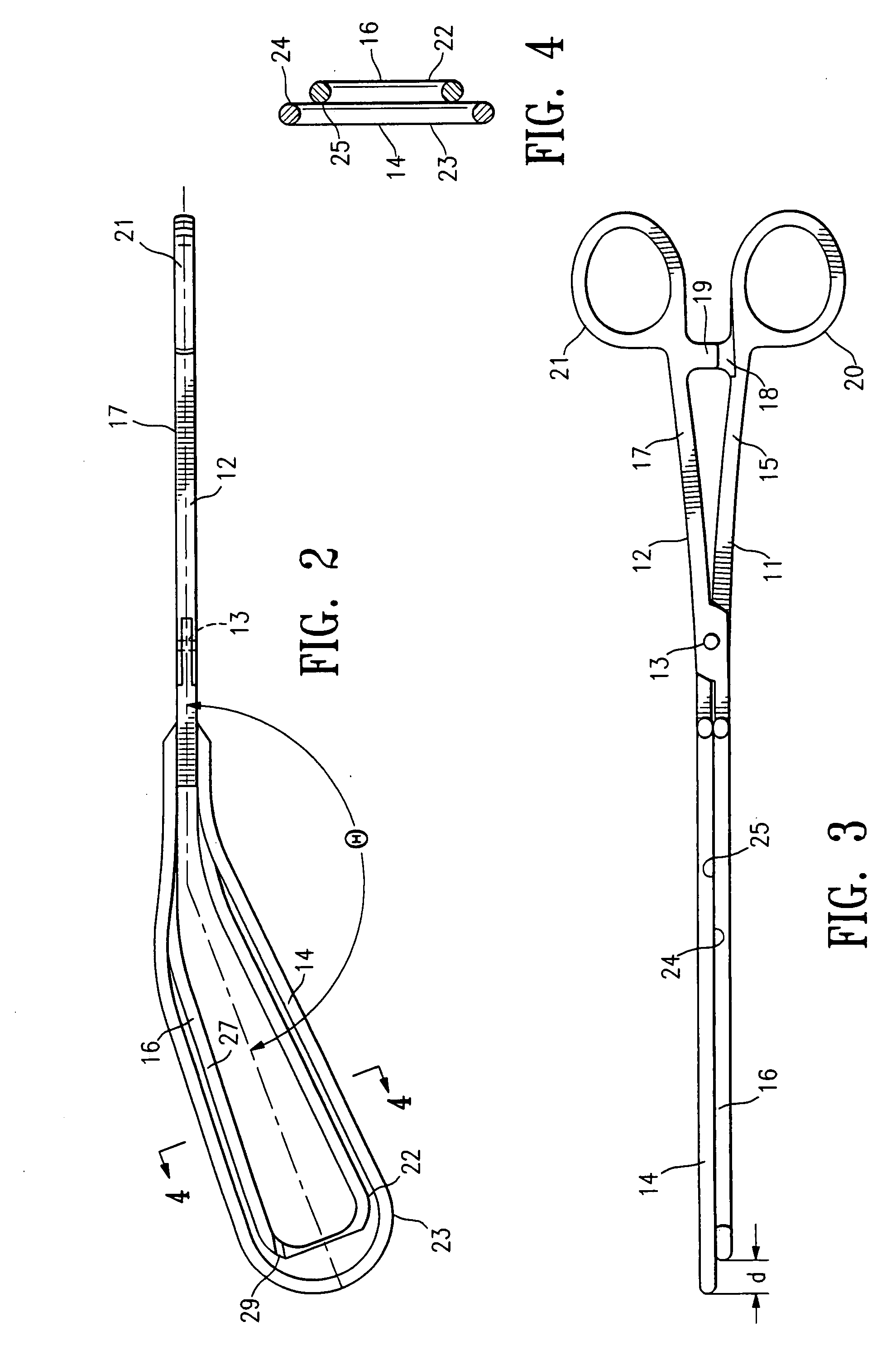
[0041]FIGS. 1-5 illustrate a clamping device 10 embodying features of the invention including first and second clamping members 11 and 12 which are pivotally connected at pivot point 13. First clamping member 11 has a first clamping element 14 secured to the distal end of handle 15. Second clamping member 12 has a second clamping element 16 secured to the distal end of handle 17. The handles 15 and 17 are provided with ratchet members 18 and 19 respectively to provide a releasable locking connection therebetween and finger grips 20 and 21 respectively for rotating the handles about the pivot point 13 to open and close the clamping elements 14 and 16. Each of the clamping elements 14 and 16 are at angles with respect to the longitudinal axis of the handles 15 and 17 to facilitate deployment within the patient's post partum vaginal canal and uterine cervix. The clamping elements 14 and 16 form an obtuse included angle θ with respect to the longitudinal axis of handles 15 and 17 so as ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com