Latent Curing Agent
a curing agent and curing agent technology, applied in the field of aluminum chelate-based latent curing agents, can solve the problems of difficult control of curing conditions, difficult to say that latency properties are sufficient, and low temperature of curing agent mixing, etc., to achieve excellent cationic polymerizability, reducing the temperature of the solution of the polymerized material, and reducing the nucleophilicity of ether oxygen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0053]Hereinafter, the present invention will be specifically described by way of examples. Group A of Examples and Comparative Examples is an example for evaluating a shell ratio and latency properties of the curing agent. Group B of Examples is an example for evaluating the primary particle diameter (the presence and absence of aggregation) and the latency properties of the curing agent particles affected by treatment with the isocyanate compound.
example a1
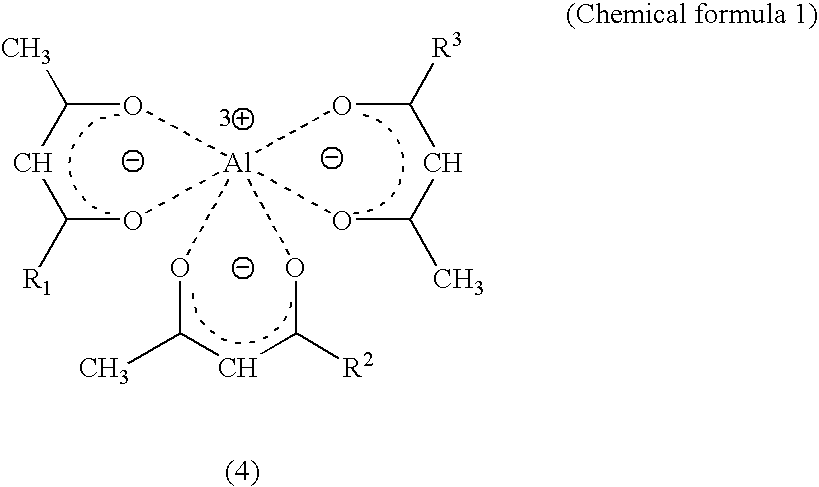
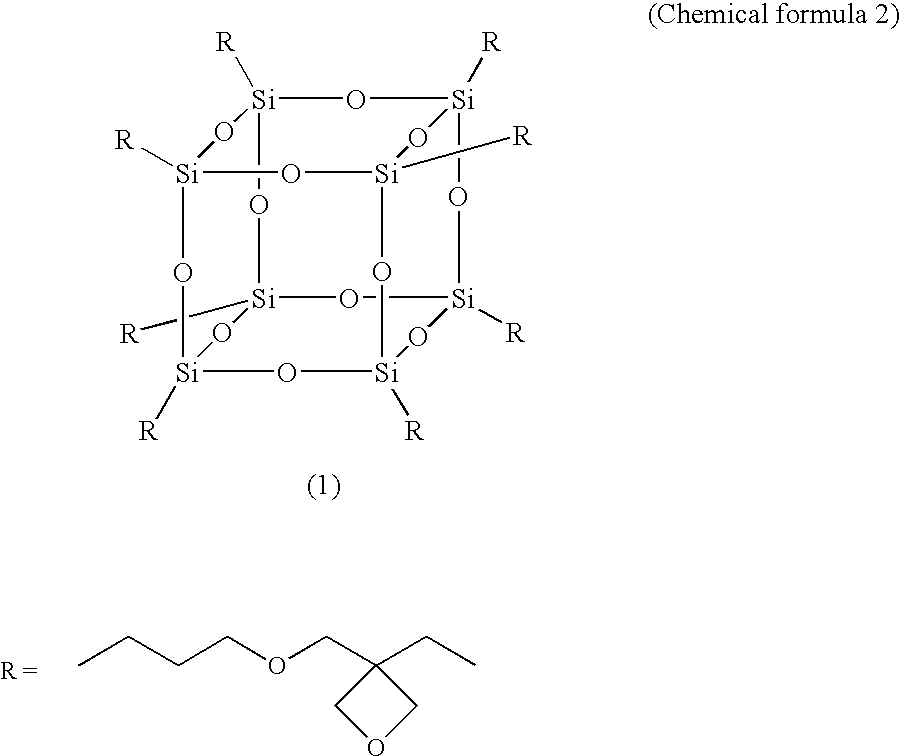
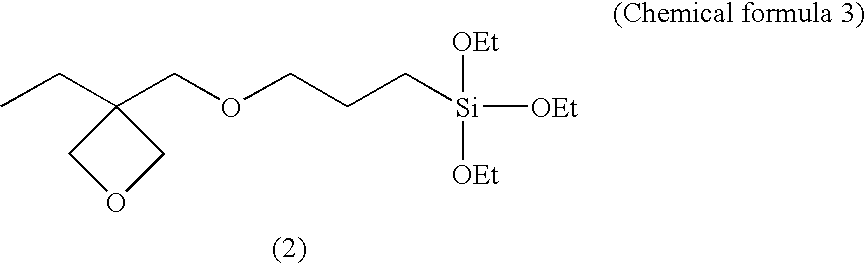
[0054]Into a three necked flask made of Teflon (registered trademark) and equipped with a cooling tube were charged 159.7 g of kerosene, 10 g of a 10% ethyl acetate solution of ethyl cellulose, 9.1 g of a 66% toluene solution of an aluminum chelate agent (ethylacetoacetate aluminum diisopropylate; ALCH, Kawaken Fine Chemicals Co., Ltd.), 21.2 g of a 66% toluene solution of a silsesquioxane type oxetane derivative (OX-SQ-H, TOAGOSEI CO., LTD.), and 0.04 g of a silane coupling agent (A-187, Nippon Unicar Company Limited). The mixture was heated using a mantle heater, and the heating was terminated when the temperature of the reaction mixture reached 120° C. Then, the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature by use of an ice bath. As a result, a precipitate was formed. Subsequently, the reaction mixture was filtrated to collect the precipitate. The precipitate was washed with hexane three times and was dried under reduced pressure, thereby obtaining 9.9 g of a white solid as an ...
example a2
[0055]Example A1 was repeated except that the silane coupling agent was not employed, thereby obtaining 10.0 g of a white solid as an aluminum chelate-based latent curing agent.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com