Cleavage of VEGF and VEGF receptor by wildtype and mutant MT-SP1
a technology of vegf receptor and vegf protein, which is applied in the field of vegf and vegf protein cleavage by wildtype and mutant mtsp1 and can solve the problems that no natural proteases are known to function, and achieves enhanced specificity toward target substrates, little to no activity, and reduced toxicity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Methods of Cloning and Characterizing Engineered MT-SP1 Protease with Altered Substrate Specificity Based on Well Understood Starting Scaffolds
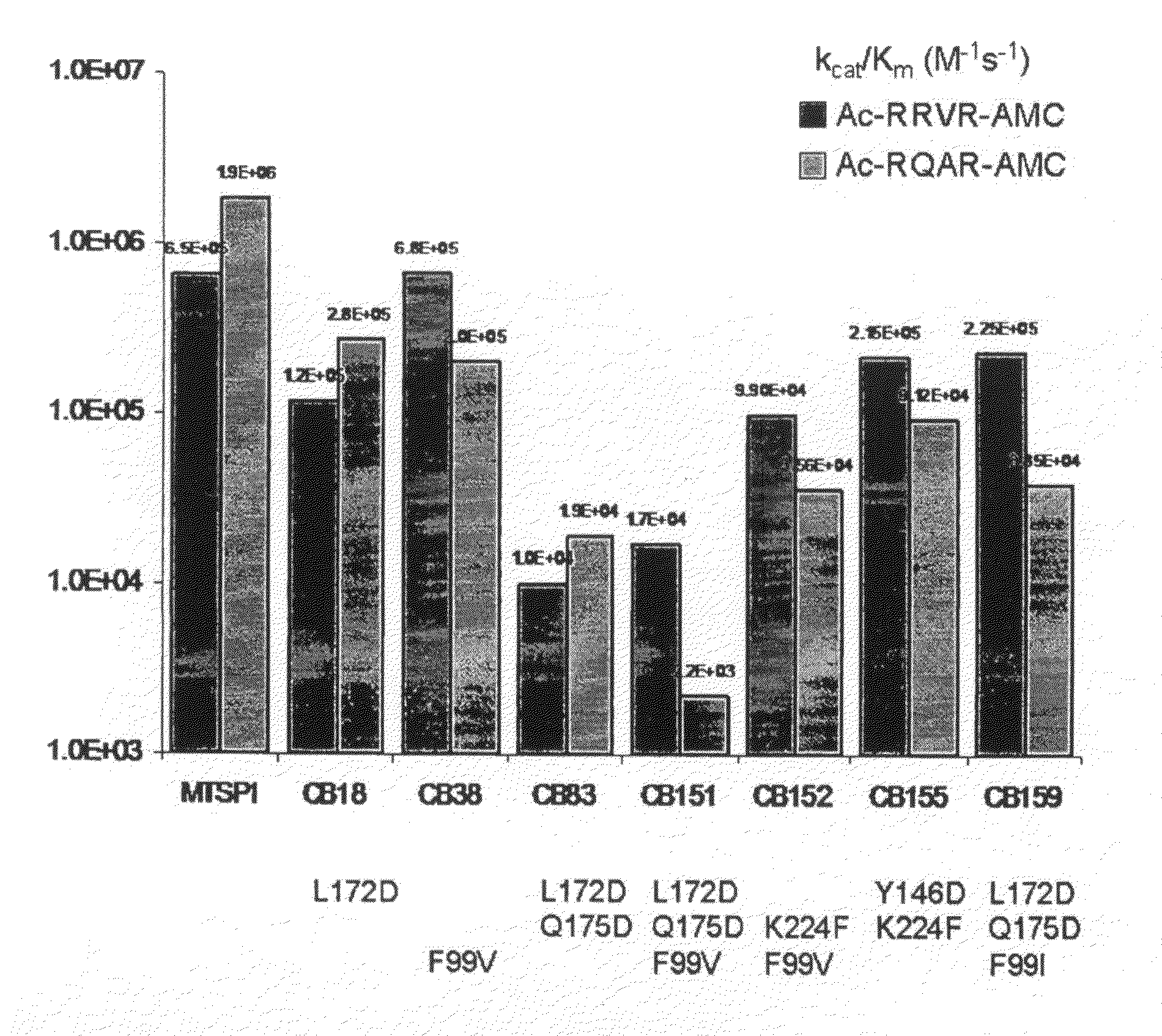
[0191]The serine protease MT-SP1 has been chosen as scaffold protease for mutagenesis towards specific proteolysis of VEGF and VEGFR in part because it has been well characterized with biochemical and structural techniques [Harris, Recent Results Cancer Res. 1998; 152:341-52].
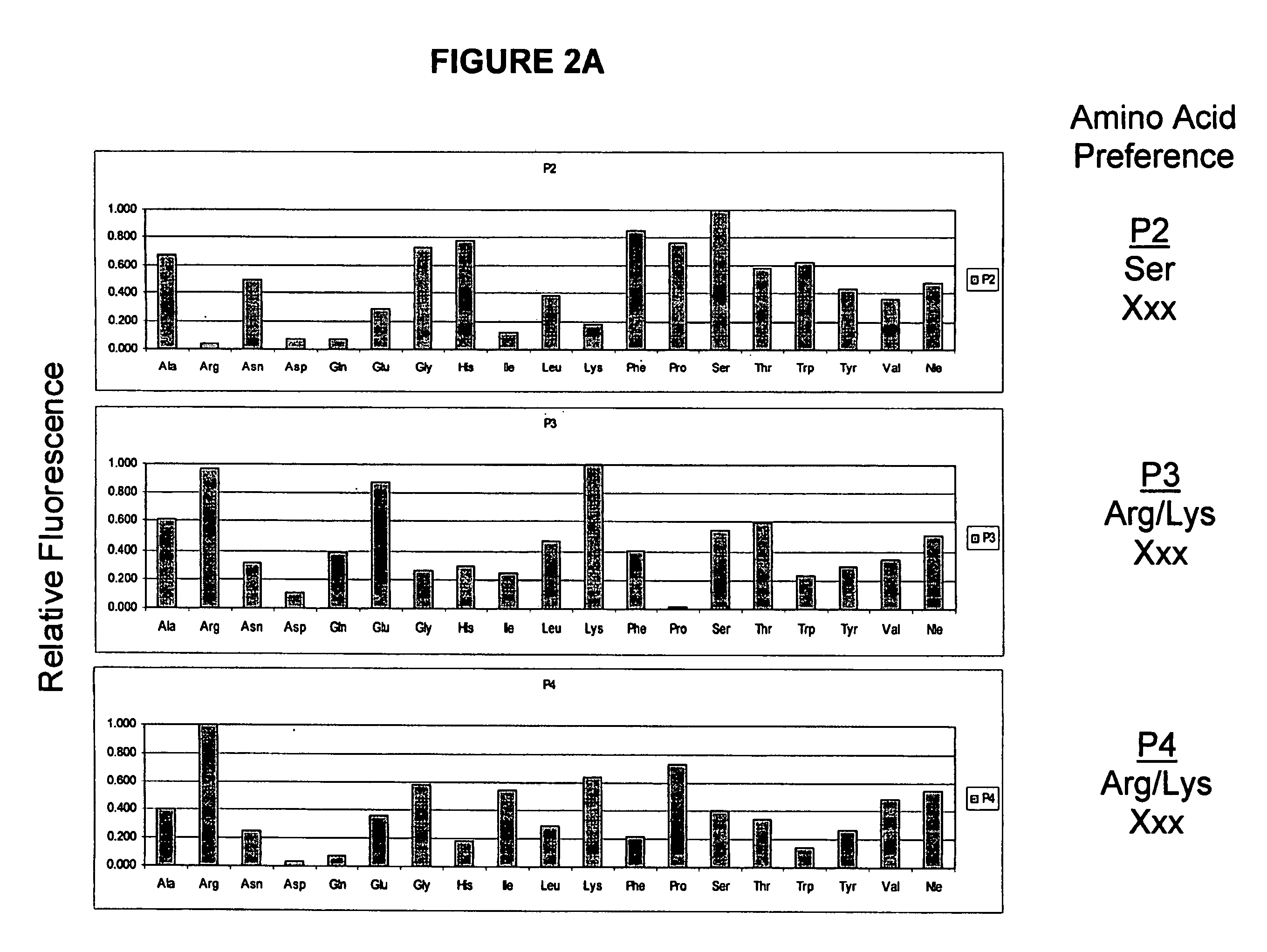
[0192]MT-SP1 is a membrane bound serine protease with multiple extracellular protein-protein interaction domains. The protease domain alone has been profiled using the totally diverse and P1-Lys PSSCL (FIG. 4A-4C) revealing an extended specificity of (basic)-(non-basic)-Ser-Arg or (non-basic)-(basic)-Ser-Arg / Lys. The X-ray crystallographic structure of MT-SP1 reveals components proposed to regulate activity and a nine amino acid insertion in the 60's loop that may determine P2 specificity
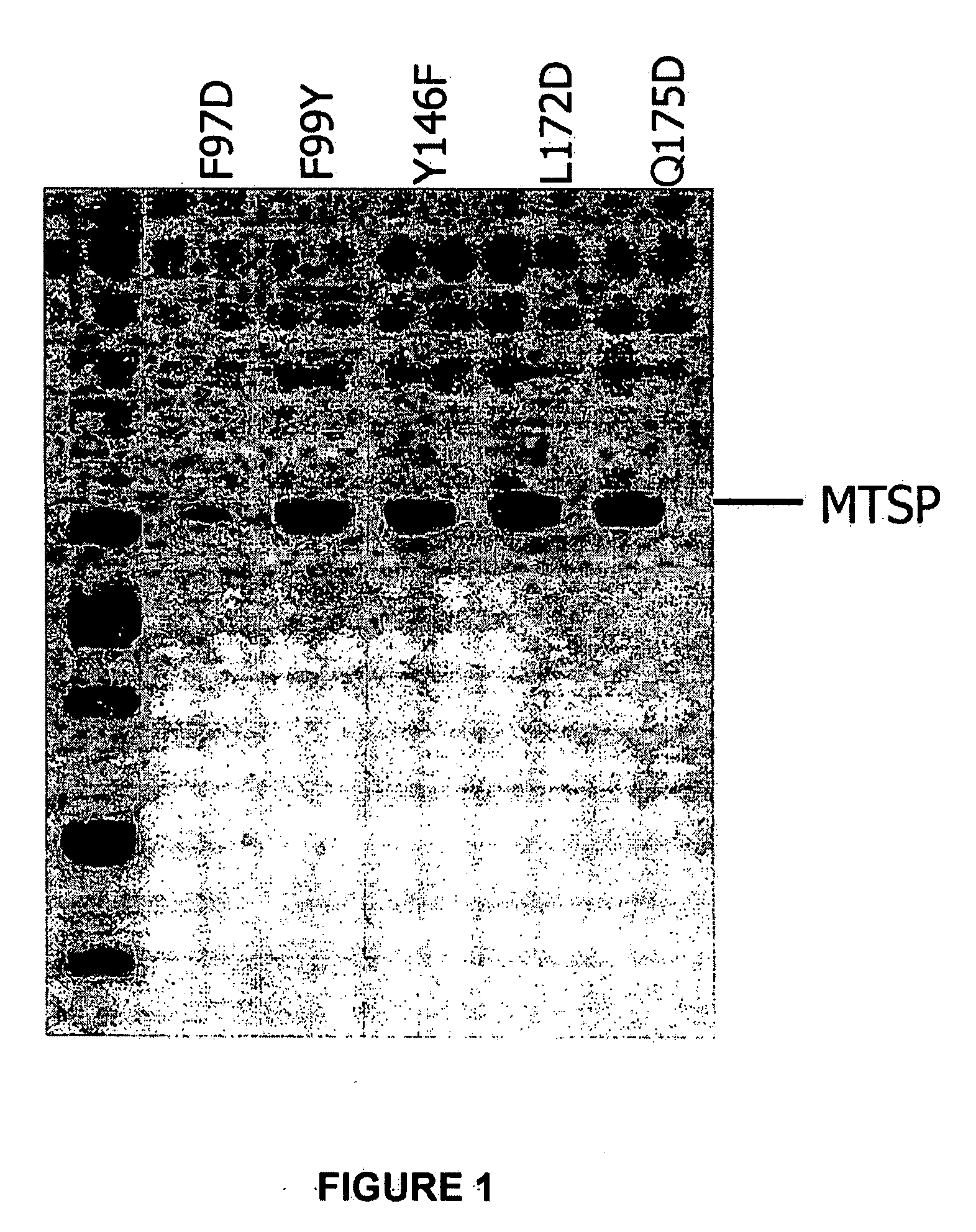
[0193]Variants of MT-SP1 have been created and characterized. Various protease mutei...
example 2
Expression and Purification of MT-SP1
[0194]A mutated MT-SP1 polypeptide (“mutein”) may contain a single mutation per polypeptide, or may contain two or more mutated residues in any combination, as illustrated in Table 11.
[0195]Wild-type and mutant MT-SP1 are cloned into the pQE bacterial expression vector (Qiagen) containing an N-terminal 6 histidine tag, prodomain, and protease domain and the resulting constructs transformed into BL21 E. coli cells. Cells are grown in 100 mL cultures to an OD of 0.6, and expression of the protease in inclusion bodies is induced by adding IPTG to a final concentration of 1 mM. After 4-6 hours, the bacteria are pelleted by centrifugation and the pellet resuspended in 50 mM Tris pH 8, 500 mM KCl, and 10% glycerol (buffer A). Cells are lysed by sonication and pelleted by centrifugation at 6000×g. Pellets are resuspended in 50 mM Tris pH 8, 6 M urea, 100 mM NaCl and 1% 2-mercaptoethanol (buffer B). Membrane and organelles are pelleted by centrifugation ...
example 3
Synthesis and Screening of Combinatorial Libraries for Characterization of MT-SP1 Wild-Type and Muteins
Fixed P1 Amino Acid Method
[0197]Individual P1-substituted Fmoc-amino acid ACC-resin (ca. 25 mg, 0.013 mmol) was added to wells of a Multi-Chem 96-well reaction apparatus. The resin-containing wells were solvated with DMF (0.5 mL). A 20% piperidine in DMF solution (0.5 mL) was added followed by agitation for 30 min. The wells of the reaction block were filtered and washed with DMF (3×0.5 mL). In order to introduce the randomized P2 position, an isokinetic mixture (Ostresh, J. M., et al., (1994) Biopolymers 34:1681-9) of Fmoc-amino acids (4.8 mmol, 10 equiv / well; Fmoc-amino acid, mol %: Fmoc-Ala-OH, 3.4; Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-OH, 6.5; Fmoc-Asn(Trt)-OH, 5.3; Fmoc-Asp(O-t-Bu)-OH, 3.5; Fmoc-Glu(O-t-Bu)-OH, 3.6; Fmoc-Gln(Trt)-OH, 5.3; Fmoc-Gly-OH, 2.9; Fmoc-His(Trt)-OH, 3.5; Fmoc-Ile-OH, 17.4; Fmoc-Leu-OH, 4.9; Fmoc-Lys(Boc)-OH, 6.2; Fmoc-Nle-OH, 3.8; Fmoc-Phe-OH, 2.5; Fmoc-Pro-OH, 4.3; Fmoc-Ser...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com