Capacity-variable type swash plate compressor
a compressor and variable type technology, applied in the direction of machines/engines, mechanical equipment, positive displacement liquid engines, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the durability, generating abnormal sounds, and impairment of capacity controllability, so as to reduce manufacturing costs and facilitate the operation of link mechanisms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
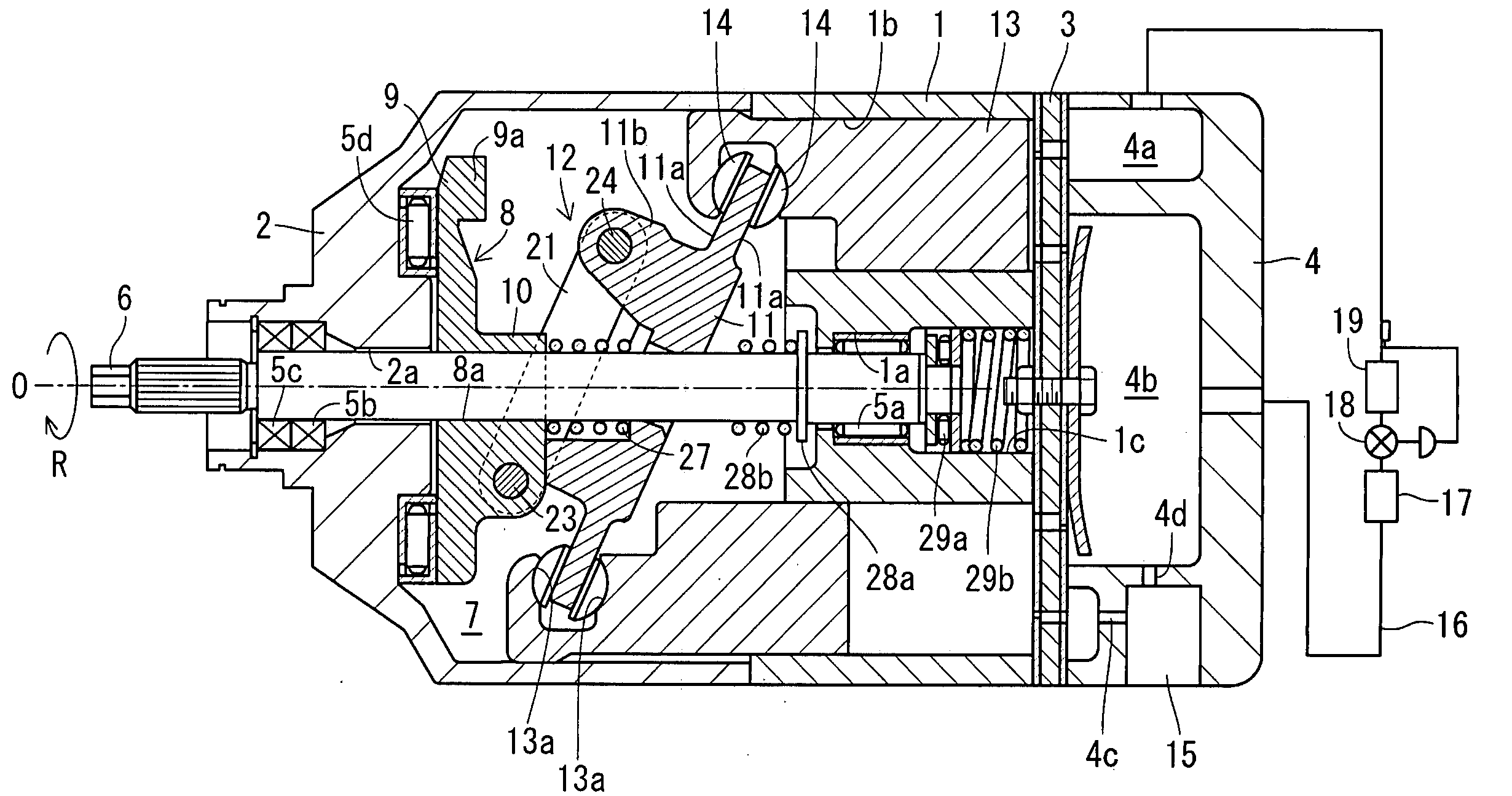
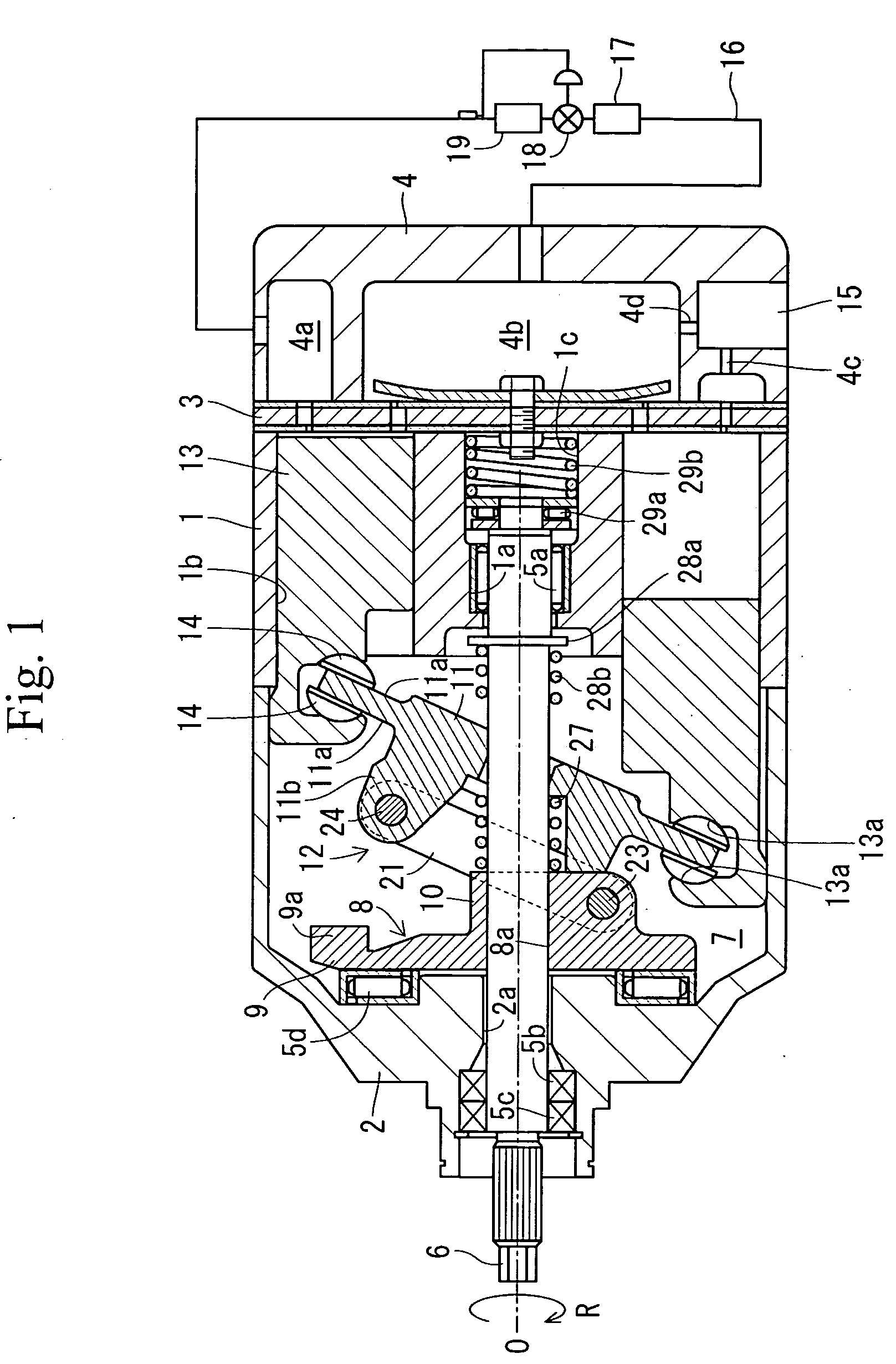
[0058]According to a capacity-variable type swash plate compressor in Embodiment 1, as shown in FIG. 1, a housing includes a cylinder block 1, the front housing 2, and a rear housing 4, a front housing 2 is joined to the front end of the cylinder block 1, and the rear housing 4 is joined to the rear end of the cylinder block 1 via a valve unit 3. The cylinder block 1 and the front housing 2 are formed with shaft holes 1a and 2a extending in the axial direction so as to penetrate therethrough, and a drive shaft 6 is rotatably supported in the shaft holes 1a and 2a via the radial bearings 5a and 5b and a shaft seal device 5c. The left side in FIG. 1 corresponds to the front side, and the right side thereof corresponds to the rear side.
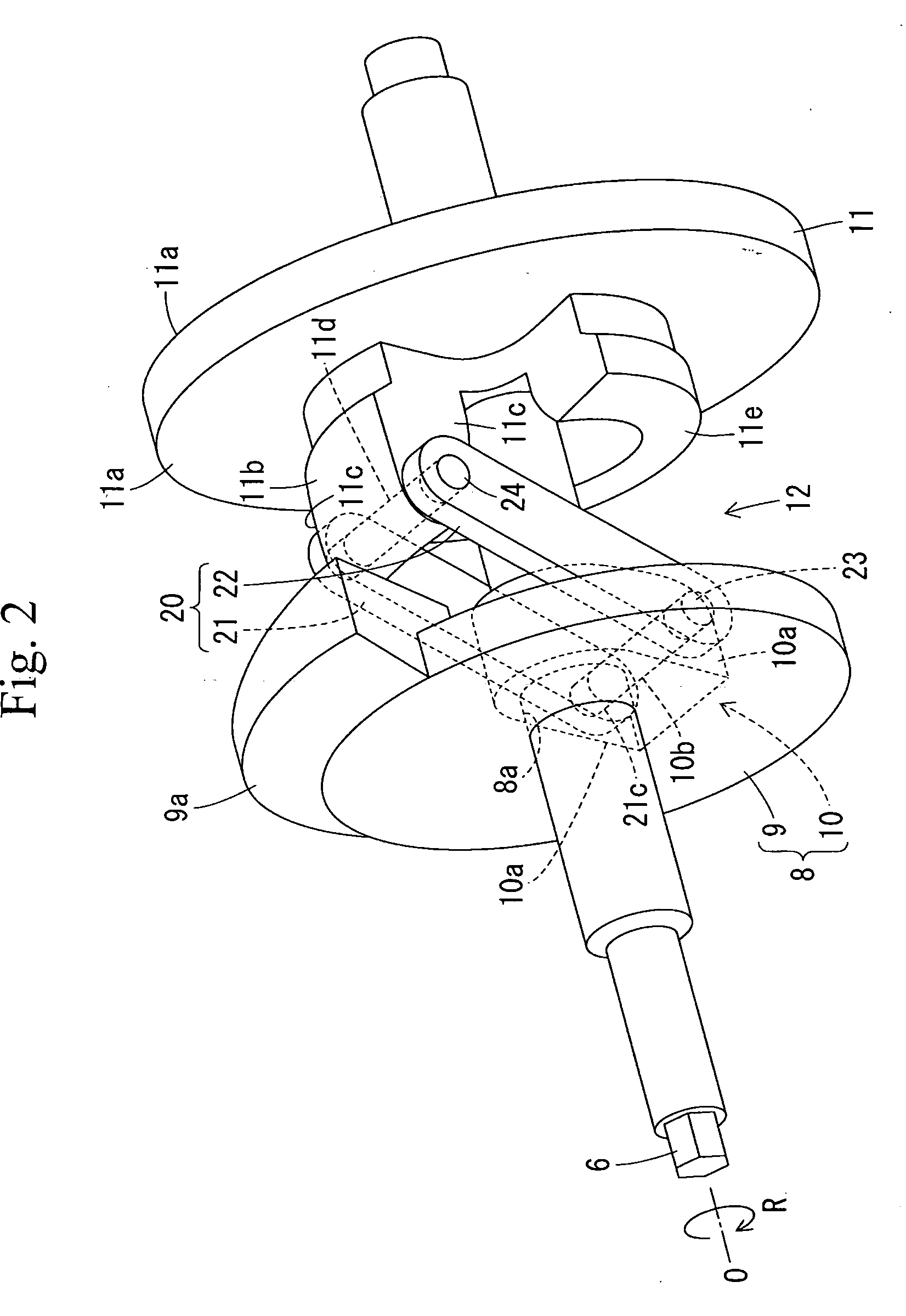
[0059]The front housing 2 and the cylinder block 1 define a crank chamber 7. A lug plate 8 is fixed to the drive shaft 6 in the crank chamber 7. As shown in FIGS. 2 to 4 as well, the lug plate 8 is formed with a press-fitting hole 8a, and the drive shaft...
embodiment 2
[0084]The compressor in Embodiment 2 employs a link mechanism 30 as shown in FIG. 5 and FIG. 6. In the link mechanism 30, an outer spline 31a is formed on a drive shaft 31, and an inner spline 32a is formed on a thrust plate 32, and the outer spline 31a and the inner spline 32a are fitted to each other. In this manner, the thrust plate 32 is clearance-fitted to the drive shaft 31.
[0085]The thrust plate 32 is formed of vibration-control metal alloy. The lug member 33 is formed separately from the thrust plate 32, and comes into abutment with the thrust plate 32. A lug member 33 is formed with a press-fitting hole 33a, and the drive shaft 31 is press-fitted into the press-fitting hole 33a. Other configurations are the same as in Embodiment 1.
[0086]In this compressor, the thrust plate 32 and the lug member 33 are formed separately, and the thrust plate 32 comes into abutment with the lug member 33. Therefore, the thrust plate 32 does not have a function to rotate the swash plate 11 syn...
embodiment 3
[0089]The compressor in Embodiment 3 employs a link mechanism 40 shown in FIG. 7. In the link mechanism 40, part of a drive shaft 41 is used as a lug member 41a. Other configurations are the same as in Embodiment 2.
[0090]In this compressor, control of the press-fitting margin required for press-fitting the lug member 41a into the drive shaft 41 is eliminated. In this compressor, a labor to machine the seat of the thrust plate 32 after having assembled the sub-assembly including the drive shaft 41 (lug member 41a), the thrust plate 32, the link mechanism 40, and the swash plate is eliminated. Other effects and advantages are the same as in Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com