Methods for detection and quantification of analytes in complex mixtures
a technology of complex mixtures and analytes, applied in the field ofgenomics, can solve the problems of insufficient supply of biological samples, method still requires significant amounts of biological samples, and the kinetics of hybridization on the surface of a microarray are less efficient than hybridization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
Generation of Unique Labels Using Two Different Labels
[0115]In this example, ten unique labels are made from two different fluorescent labels. First, ten unique templates of a 220-base pair single-stranded DNA are synthesized. The templates consist of a pre-determined ratio of the following 20-base pair repeats:
5′ (ACTCTCTCTCTCTCTCTCTC)n(GCTCTCTCTCTCTCTCTCTC)m3′
where n=1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, m=1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, and n+m=11.
[0116]The second strand is synthesized using the primer GAGAGAGAGA, Klenow polymerase, DNA ligase, dGTP, dATP, dUTP-fluorescein and dCTP-rhodamine. After the reaction is complete the product is treated with S1 nuclease to digest the DNA with gaps, and the remaining full length DNA is then purified. The labeled nucleotides will be incorporated into the DNA in a unique ratio determined by the ratio of the two repeats. The end result is ten uniquely labeled nucleic acids where the set ratio of fluorescein to rhodamine is 1:10, 2:9, 3:8, 4:7, 5:6, ...
example ii
Generation of a Labeled Specifier
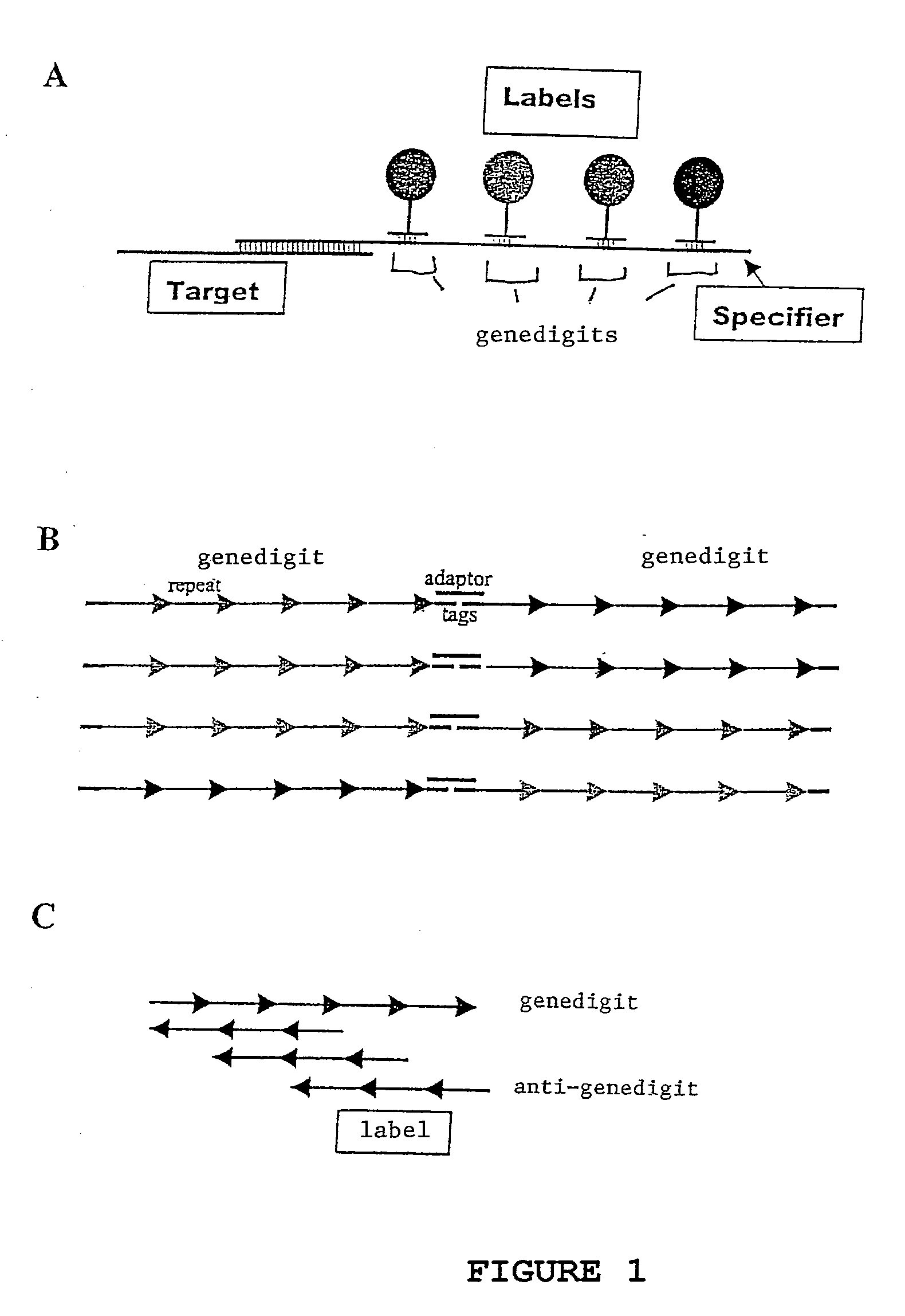
[0118]The specifiers are synthesized by ligating together one target specific sequence (synthetic oligonucleotide, peptide-nucleic acid (PNA), PCR product, or linked-nucleic acid (LNA)), and several “genedigits” (see FIG. 1A). In this example, each specifier contains a unique combination of 4 different genedigits. This results in the generation of 10,000 possible unique specifiers.
[0119]The genedigits are synthetic oligonucleotides that contain only two of the natural bases, plus two bases that not found in nature: isocytidine and isoguanine. Such base composition ensures that the genedigits will not non-specifically hybridize with analytes in a complex mixture. The sequence of each genedigit is composed of 5 repeats of an 8-base pair core sequence (see FIG. 1B). Each core sequence unit differs from the others by at least two bases.
[0120]In order to make 10,000 unique specifiers, forty different genedigits are synthesized and split into 4 groups cont...
example iii
Gene Expression Analysis Using Specifiers
[0123]In order to determine differences in gene expression between astrocytes and LPS-activated astrocytes, RNA is isolated from both populations of astrocytes using cell lysis in guanidine isothiocynine or phenol / chloroform. A population of specifiers is added to each RNA sample under conditions suitable for hybridization. The mRNA-specifier complexes are isolated with oligo dT beads and washed extensively to remove excess specifiers. The specifiers are eluted from the mRNA by digesting the mRNA with RNAse A. The specifiers are then are processed for labeling as described in Examples I and II and these labels are detected using a CCD camera. The number of specifiers corresponding to specific mRNAs from un-treated astrocytes is then compared to the specifier pattern from LPS-treated astrocytes. Since the sequence of the target specific region of the specifier is known, this identifies the genes that are differentially expressed between the tw...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com