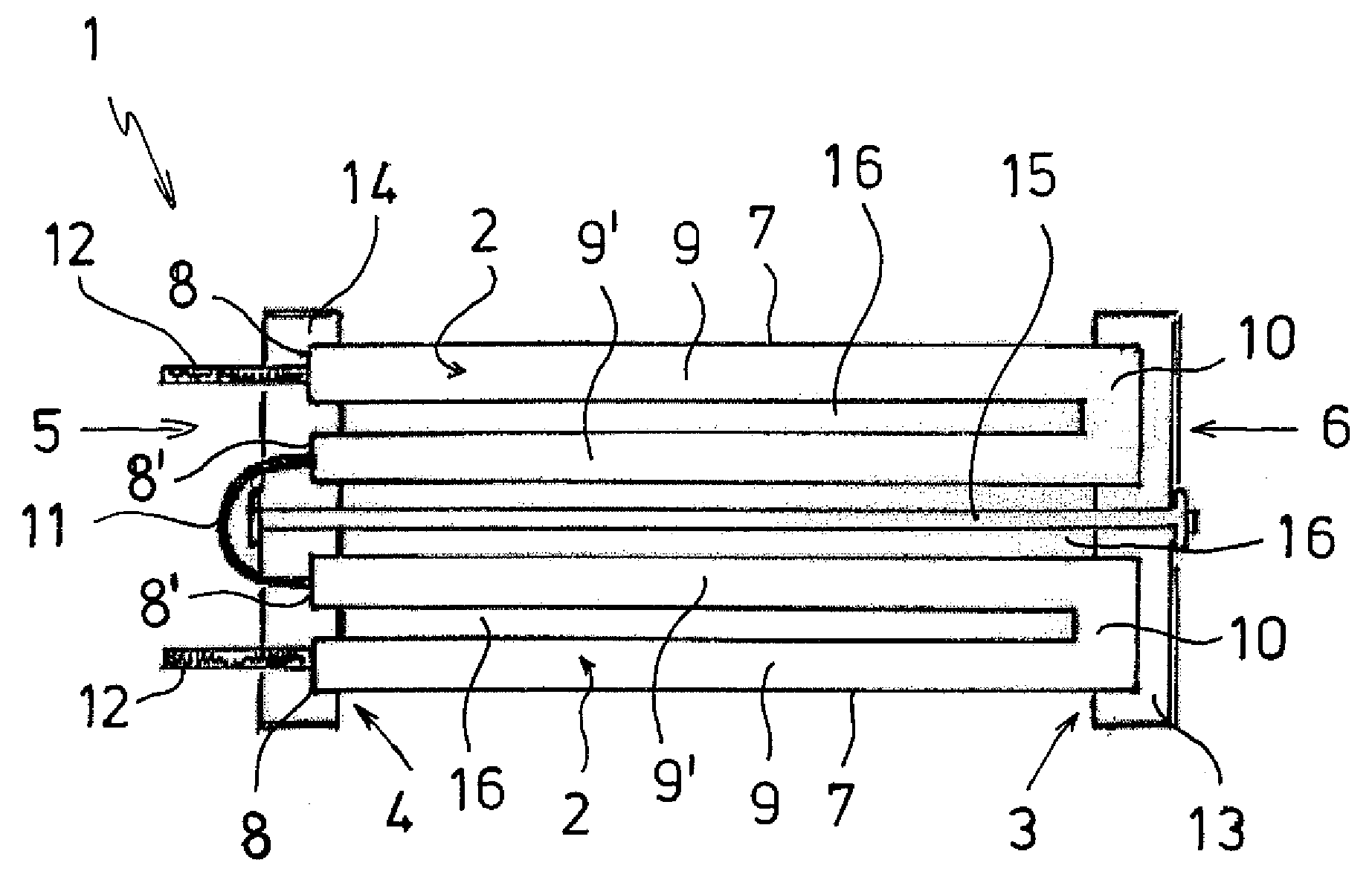
Electrical resistance heating element for a heating device for heating a flowing gaseous medium
a heating element and electric resistance technology, which is applied in the direction of electric heating, fluid heaters, air heaters, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient flow of air and unusable heating elements, and achieve the effect of improving electrical resistance heating elements and reducing the danger of overheating
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
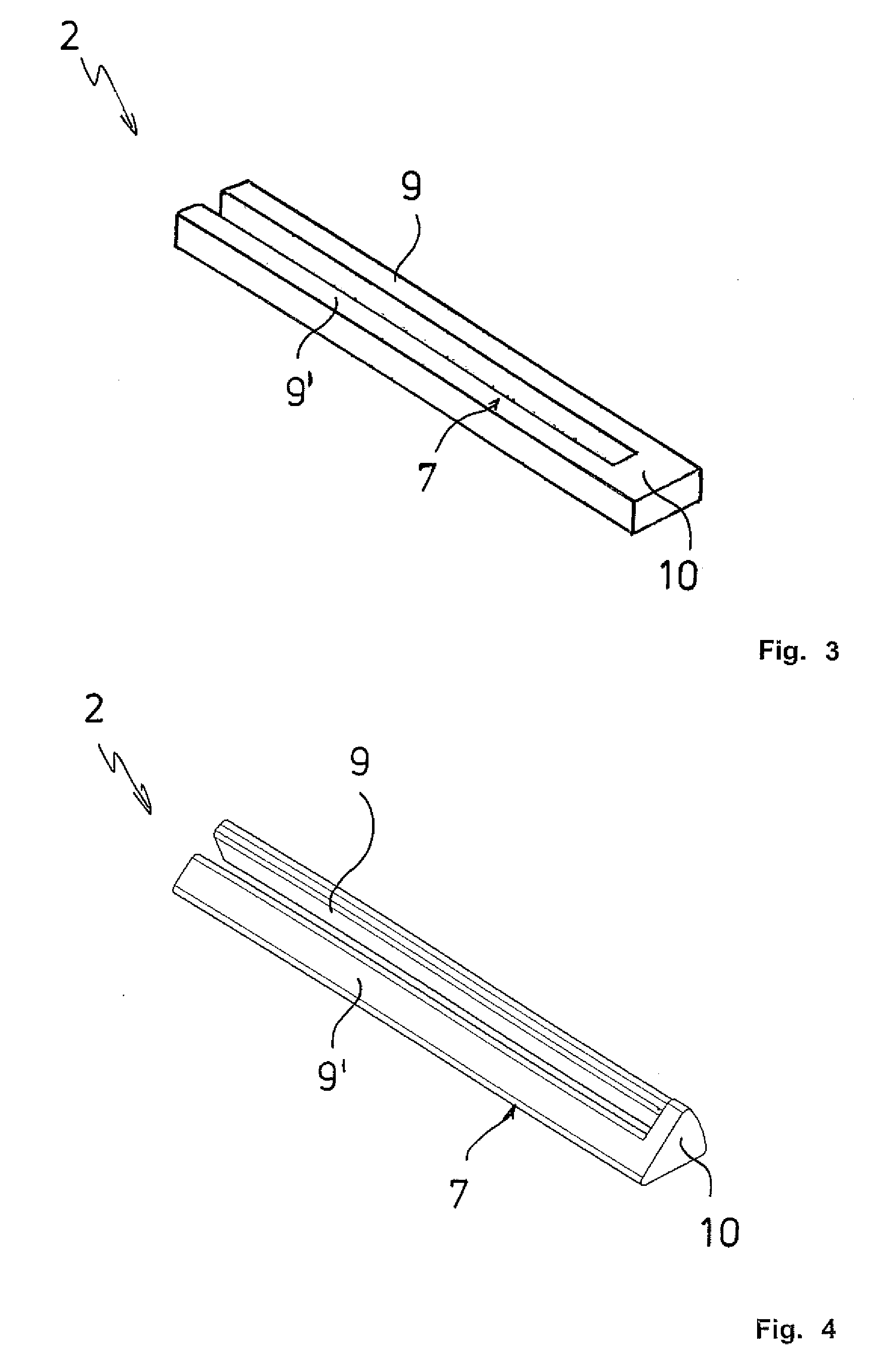
[0040]FIG. 3 shows the U-shaped heating resistor 2 made of an electrically conductive ceramic material. The limbs 9, 9′ and the base 10 have a square cross-section and are located on one plane. The surface 7 is flat.
[0041]FIG. 4 shows a second variant of the heating resistor 2 shown in FIG. 3 where the limb 9 has a rectangular cross-section and the limb 9′ and the base 10 have a triangular cross-section, all together forming a cylinder segment that corresponds to one eighth of a straight circular cylinder. The surfaces 7 of the limbs 9, 9′ are flat and inclined towards each other.
third embodiment
[0042]FIG. 5 shows the U-shaped heating resistor 2. The limbs 9, 9′ and the base 10 have an essentially triangular cross-section. They are designed so that together they form a cylinder segment that corresponds to one quarter of a circular cylinder. The surface 7 of the limbs 9, 9′ is structured. It has indentations 21 and raised areas 22 in order to enlarge the surface 7 for its contact with the flow of air. In addition, the structured surface 7 has the advantageous effect of creating turbulence of the flow of air, and thereby ensuring uniform heating thereof.
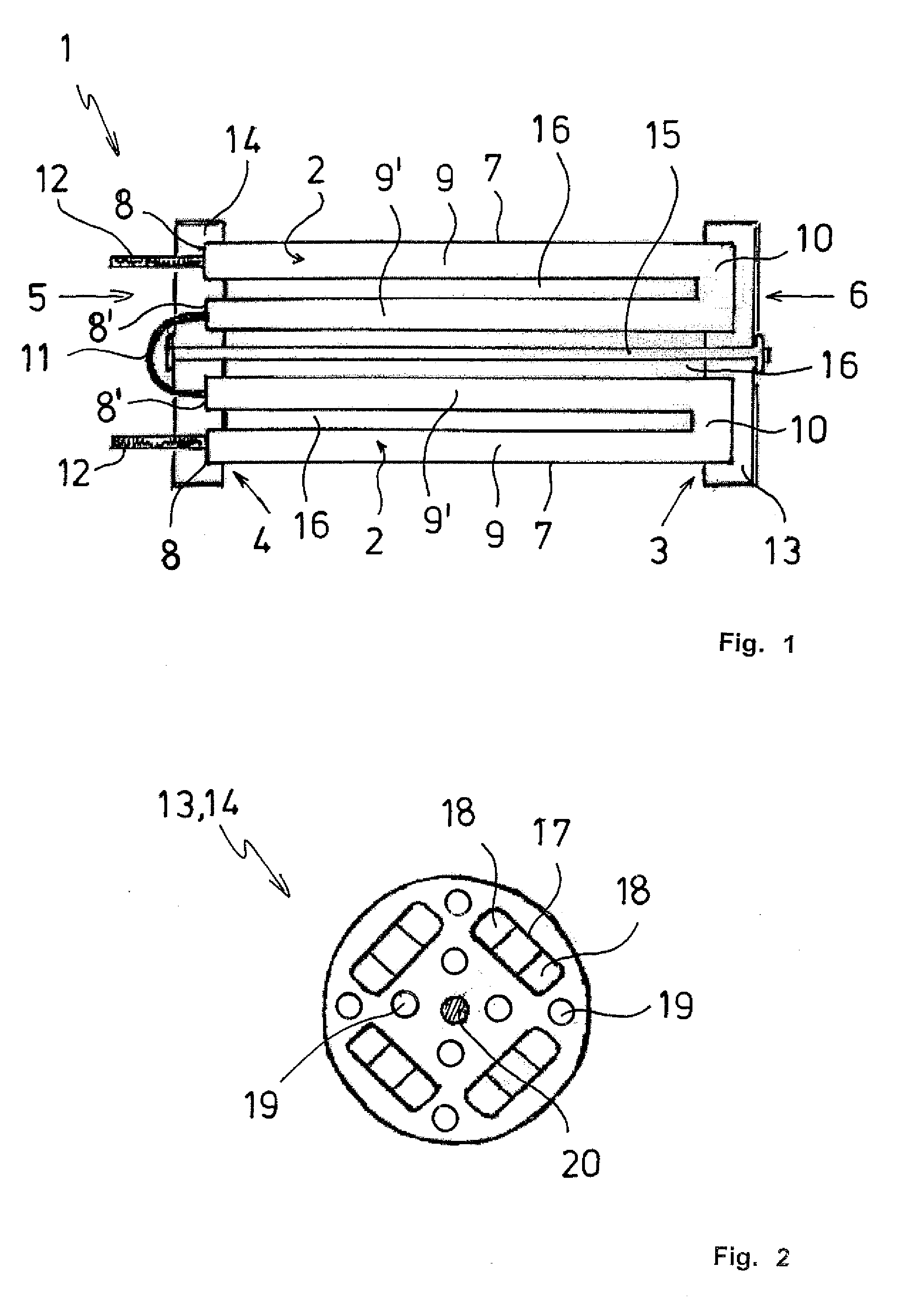
[0043]FIG. 6 shows the carrier plates 13, 14 that match the heating resistor 2 shown in FIG. 5. The carrier plates 13, 14 have a ring-shaped, essentially rectangular recess 17 and are suitable for a positive connection to the heating resistors 2. For this purpose, the heating resistors 2 are positioned in the corners 23 of the recess 17. In addition, the carrier plates 13, 14 have passages 19 for the flow of air, and the reces...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com