High-strength martensite heat resisting cast steel, method of producing the steel, and applications of the steel
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
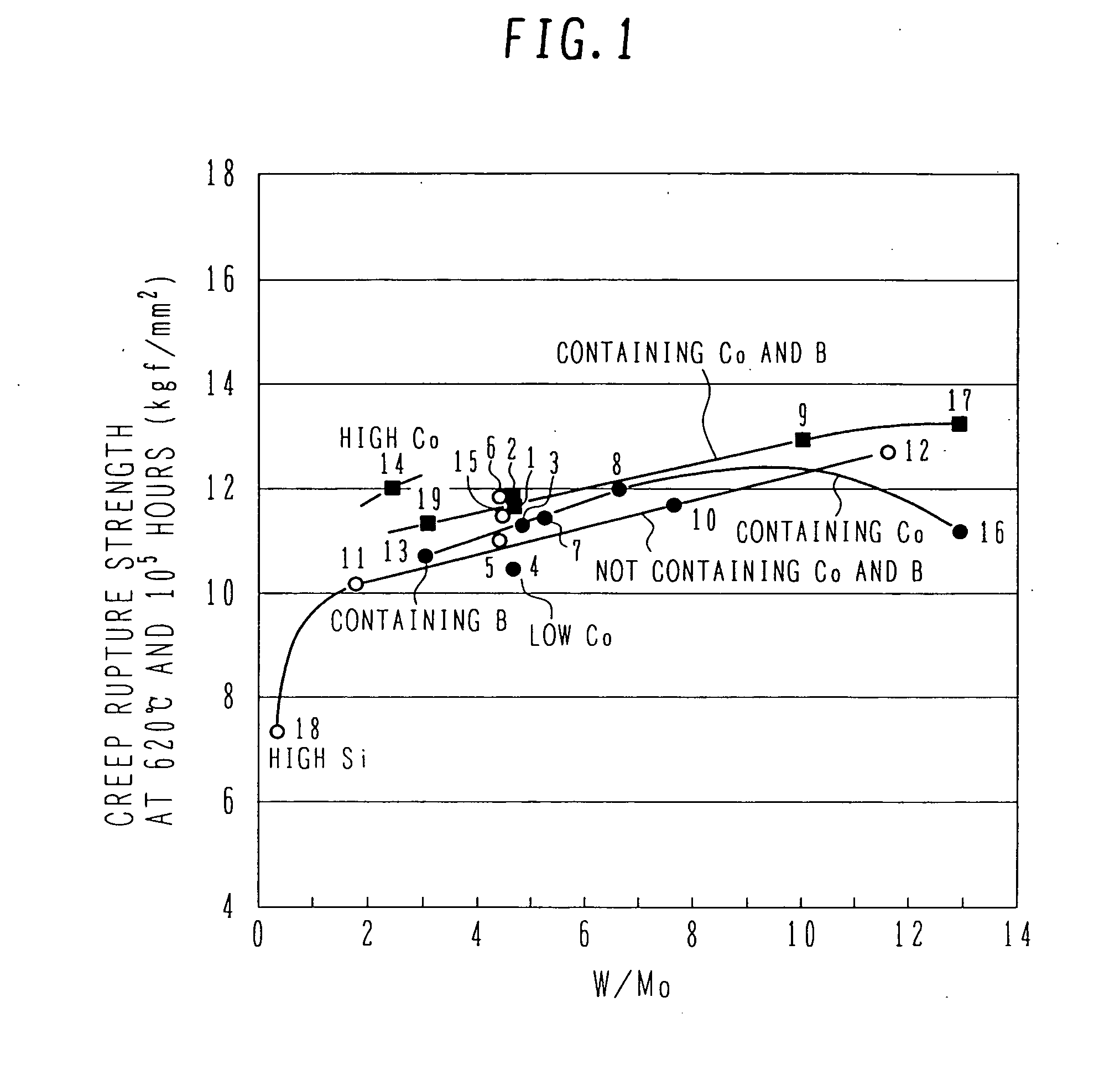
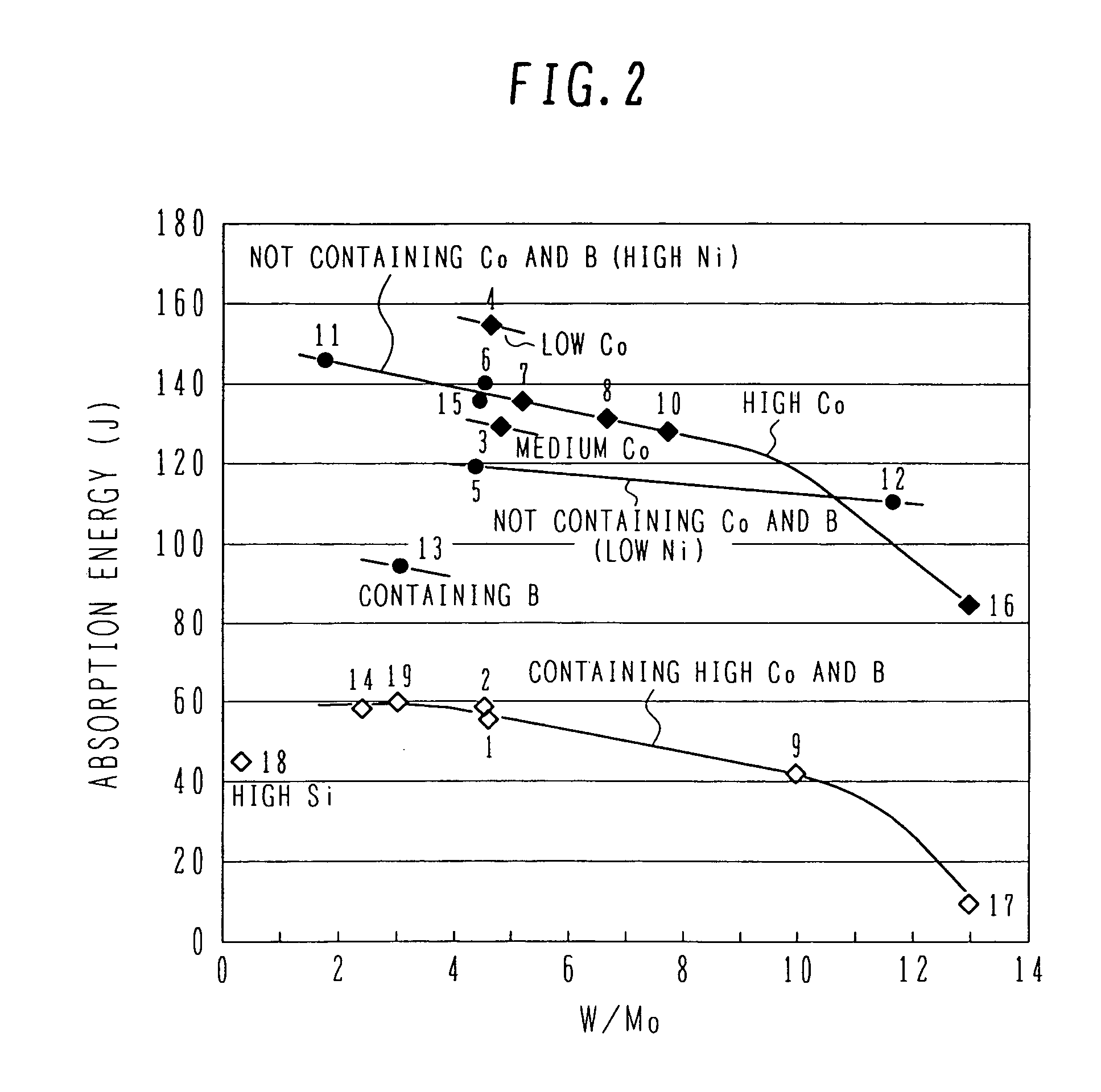
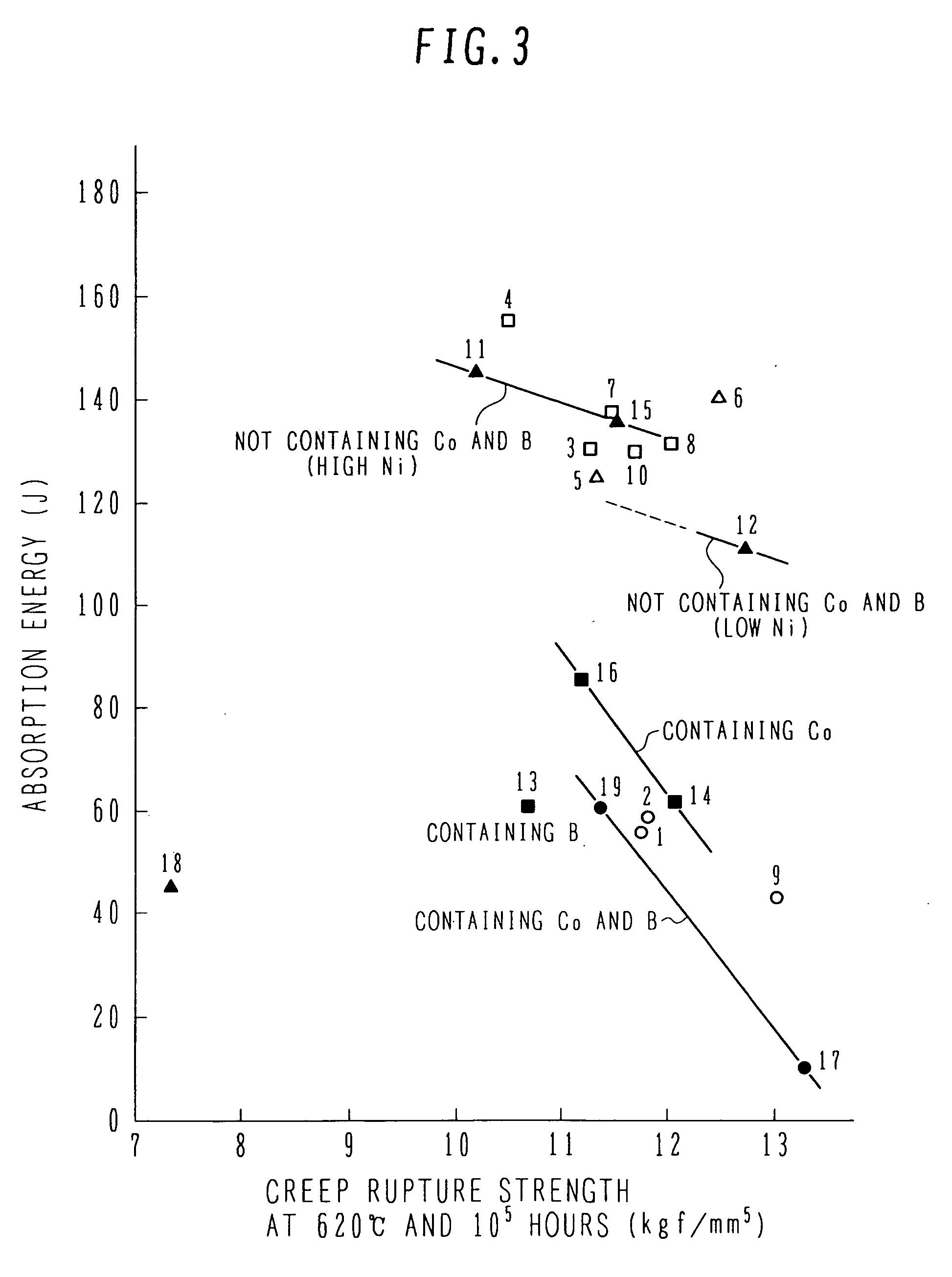
[0050]Table 1, given below, shows chemical composition (% by mass) of the steel of the present invention and comparative steels which are used in this embodiment for comparative studies. In Table 1, samples No. 1-10 represent the steel of the present invention, samples No. 11-13 represent the comparative steels, and samples No. 14-19 represent the known steels (corresponding to Patent Documents 1 and 3). As seen from Table 1, in the samples No. 1-10 representing the steel of the present invention, the (W / Mo) ratio is 4.0-10.0.
[0051]Each of the steel samples shown in Table 1 was prepared by producing an ingot of 50 kg in a vacuum high-frequency induction melting furnace, and forming a plate of 30 mm (t)×90 mm (w)×L by hot forging. The hot forging was performed under heating conditions of temperature 1150° C.×3 hours and at the forging temperature of 1150-950° C. while the heating was repeated six times.
[0052]Simulating a central portion of a large-sized steam turbine rotor shaft, hea...
second embodiment
[0061]FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view of a high-pressure steam turbine (HP) using the high-strength martensite heat resisting steel according to the present invention as a rotor shaft material. FIG. 5 is a cross-sectional view of an intermediate-pressure steam turbine (IP) using the high-strength martensite heat resisting steel according to the present invention as a rotor shaft material. In this second embodiment, the HP and the IP are connected in tandem to constitute a steam turbine power plant having steam temperature of 625° C. and output capacity of 1050 MW. A low-pressure steam turbine is of the cross-compound four-flow exhaust type, and the blade height in the last stage thereof is 43 inches. More specifically, the steam turbine power plant can be constituted by a set of (HP)-(IP)-generator and a set of two low-pressure steam turbines (LP)-generator, each set operating at the rotation speed of 3000 rpm, or by a set of (HP)-(LP)-generator and a set of (IP)-(LP)-generator, ea...
third embodiment
[0080]FIG. 6 is a cross-sectional view of a high- and intermediate-pressure integral steam turbine. This third embodiment relates to a steam turbine power plant with steam temperature of 620° C. and output capacity of 600 MW. The power plant of this third embodiment is of the tandem compound double-flow type, and the last-stage blade height in the LP is 43 inches. A rotation speed of 3000 rpm is obtained by the high- and intermediate-pressure integral steam turbine (HP-IP) and one LP (C) or two LPs (D). The steam temperature and pressure in the high-pressure section (HP) are 600° C. and 250 kgf / cm2. In the intermediate-pressure section (IP), the steam temperature is heated to 600° C. by a reheater and operation is performed at pressure of 45-65 kgf / cm2. The steam temperature in the low-pressure section (LP) is 400° C., and steam in the LP is sent to a condenser under vacuum of 722 mmHg at 100° C. or below.
[0081]The high-pressure side steam turbine (HP) includes an inner compartment ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com