Negative electrode for non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery, method for producing the same, and non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery
a secondary battery and non-aqueous electrolyte technology, applied in the manufacturing process of electrodes, cell components, electrochemical generators, etc., can solve the problems of large volume change, large stress, and limitation of the active material of the negative electrode of elements, so as to suppress the deformation of the negative electrode, reduce the stress, and reduce the effect of stress
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0179]A layered-type lithium secondary battery as illustrated in FIG. 11 was produced in the following manner.
(i) Preparation of Positive Electrode
[0180]A positive electrode mixture paste was prepared by sufficiently mixing 10 g of lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) powder with a mean particle size of approximately 10 μm, serving as a positive electrode active material, 0.3 g of acetylene black, serving as a conductive agent, 0.8 g of polyvinylidene fluoride powder, serving as a binder, and a suitable amount of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP).
[0181]The resultant paste was applied onto one face of a positive electrode current collector 75a made of a 20-μm thick aluminum foil, dried and rolled to form a positive electrode active material layer 75b. This was then cut into a predetermined shape to obtain a positive electrode. The positive electrode active material layer carried on one side of the aluminum foil of the positive electrode thus obtained had a thickness of 70 μm and a size of 30 mm×...
example 2
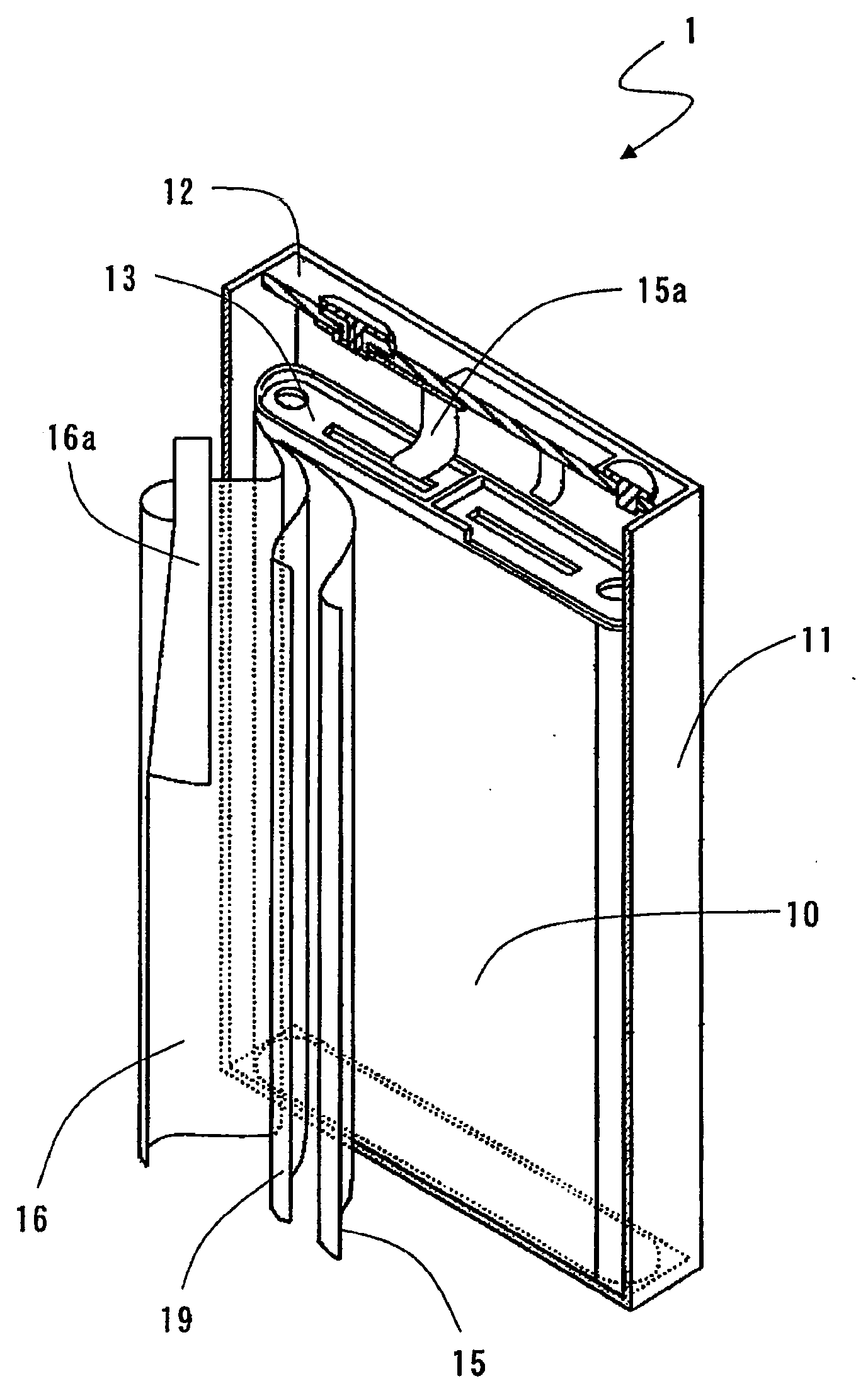
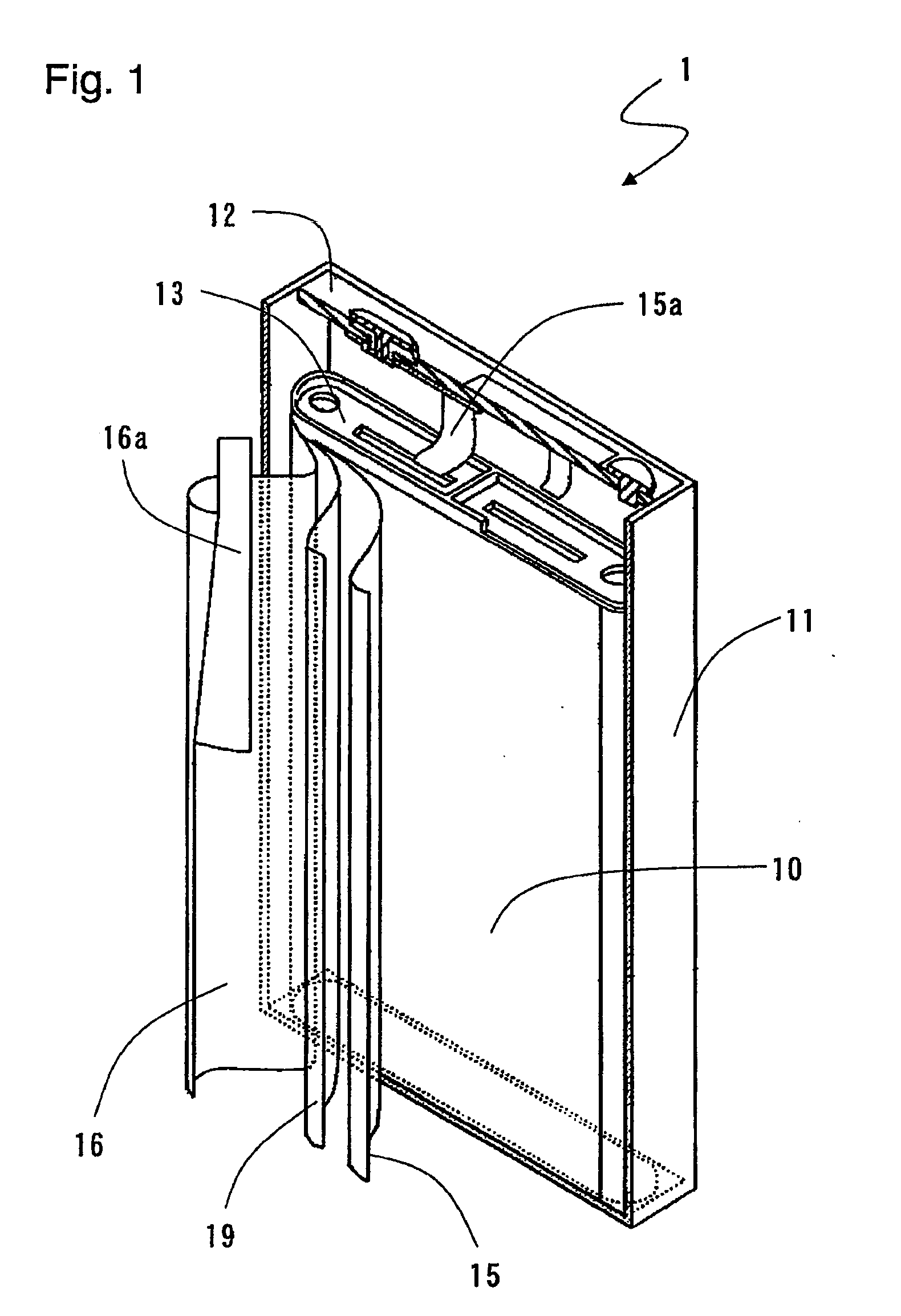
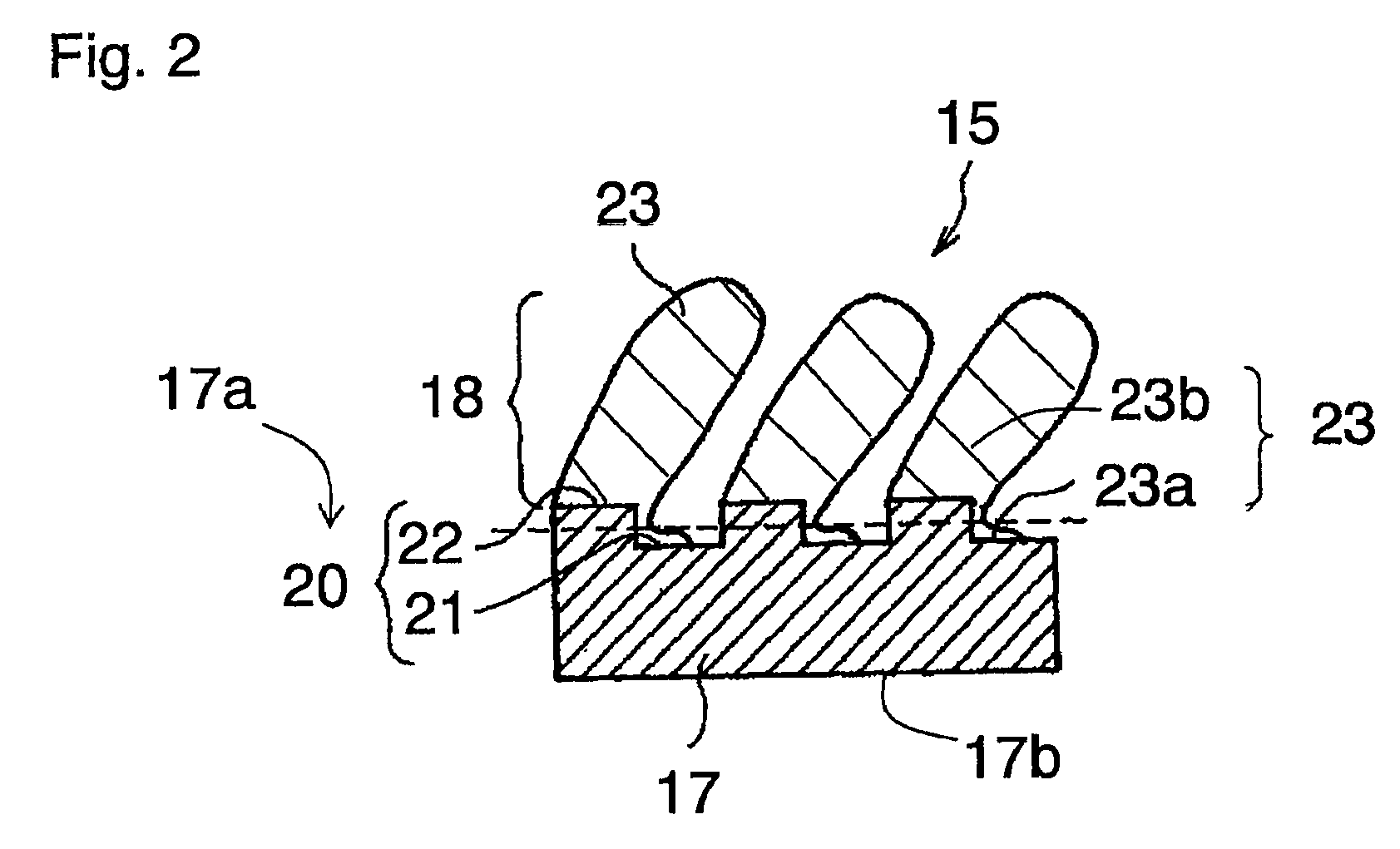
[0224]With reference to FIG. 16, a device for producing columns of a negative electrode is briefly described. FIG. 16 is a schematic sectional view of the structure of a device for producing columns that grow inclined relative to the direction perpendicular to the surface of a current collector. FIG. 17 is a schematic sectional view of the structure of a device for producing columns that grow in the direction perpendicular to the surface of a current collector.
[0225]As illustrated in FIG. 16, a production device 70 has a vacuum vessel 71, which contains an unwinding roll 72, masks 73, deposition sources 74, film-forming rolls 75a and 75b, a rewinding roll 77, a vacuum pump 78, and oxygen nozzles 79a and 79b, and the pressure thereof is reduced by the vacuum pump 78. A current collector 17 is rewound by the rewinding roll 77 via the unwinding roll 72 and the film-forming rolls 75a and 75b. On the route thereto, when a deposition substance having evaporated from the deposition sources...
example 3
[0234]First, silicon (Si) was used as the negative electrode active material capable of absorbing and releasing lithium ions. An oxygen gas with a purity of 99.7% was introduced into the vacuum vessel of the oblique deposition device 70 illustrated in FIG. 16 from the oxygen nozzles 79b placed near the deposition source, to form columns made of SiO0.5.
[0235]Except for the use of this negative electrode, in the same manner as in Example 1, a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery was produced.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com