Computerized identification of normal and abnormal diurnal cortisol secretion patterns and levels of testosterone from human saliva samples
a technology of which is applied in the field of computerized identification of normal and abnormal diurnal cortisol secretion pattern and human saliva sample levels, can solve the problems of increased risk of cardiovascular disease, increased risk of heart disease, increased insulin resistance, etc., and achieves high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
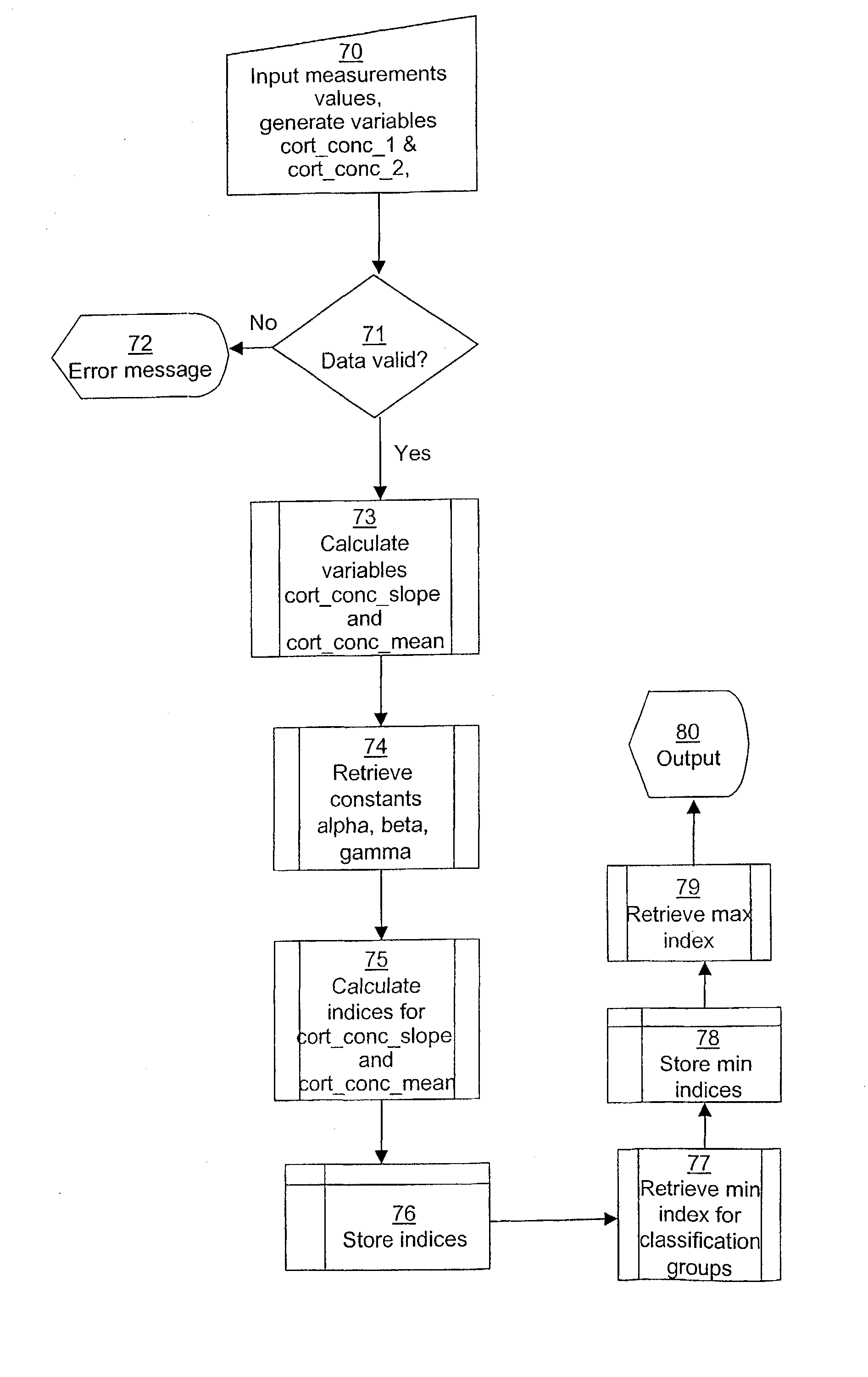
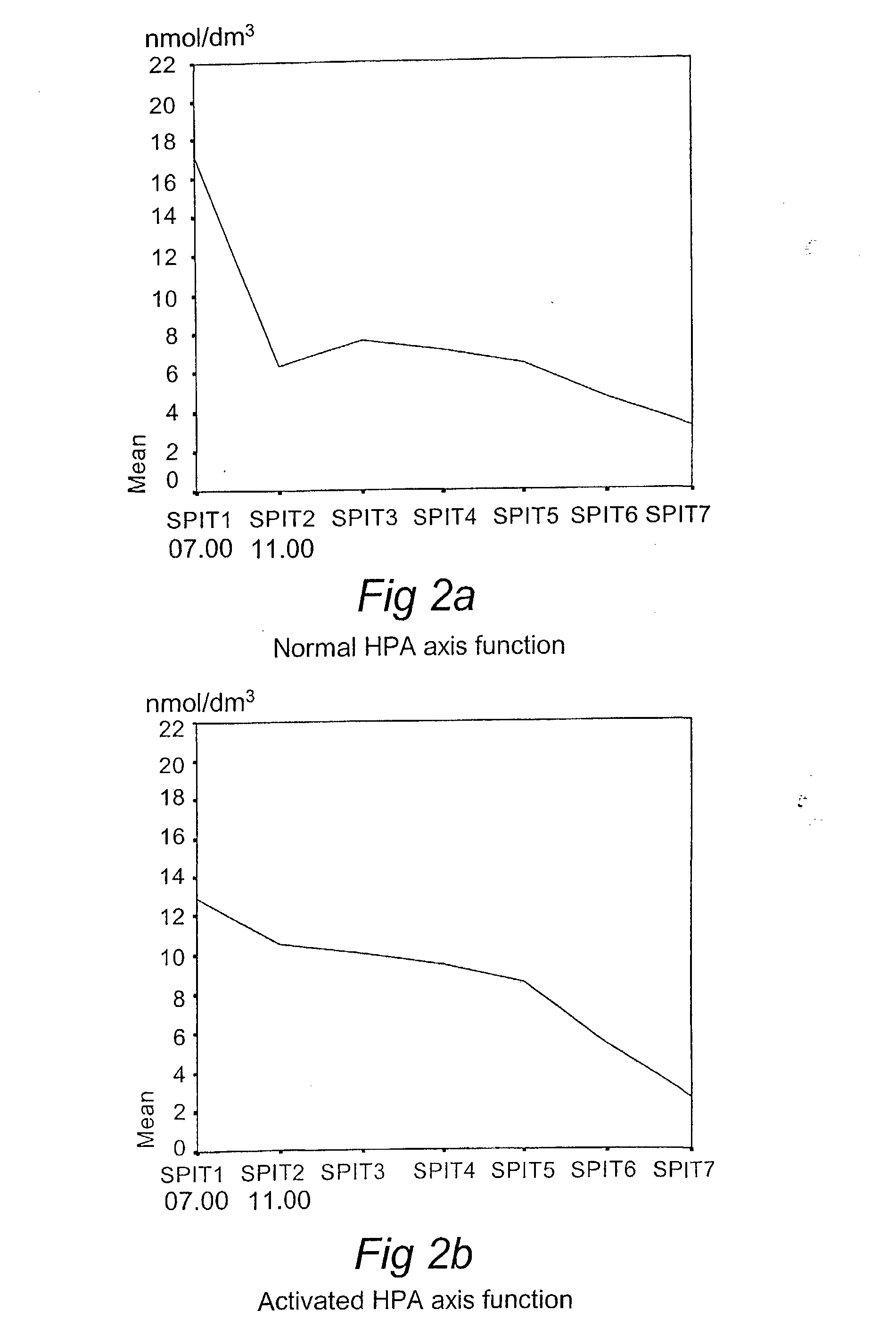
[0058] In a normal subject, the value of cort_conc_slope should be high and the value of cort_conc_mean may be either high or low. This appears from the leftmost portion of the graph in FIG. 2a.
[0059] The corresponding indices for a subject could then be as follows:
[0060] The high_index for cort_conc_slope might be 1.00 (corresponds to a high test value in the morning sample at 07.00 am and a low test value in the second sample at 11.00).
[0061] The high_ind for cort_conc_mean might be 0.6.
[0062] This subject belongs to the group with normal HPA axis (group A in the group definition matrix) with a membership value of 0.6 (i.e. the minimum of 1.00 and 0.6). The membership value of any other group would be less than this value.
[0063] Borderline cases, i.e. two classification groups with identical membership indices, may occur. These subjects are labeled as borderline normal / activated, borderline normal / -blunted or borderline activated / blunted as appropriate with regard to the indi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com