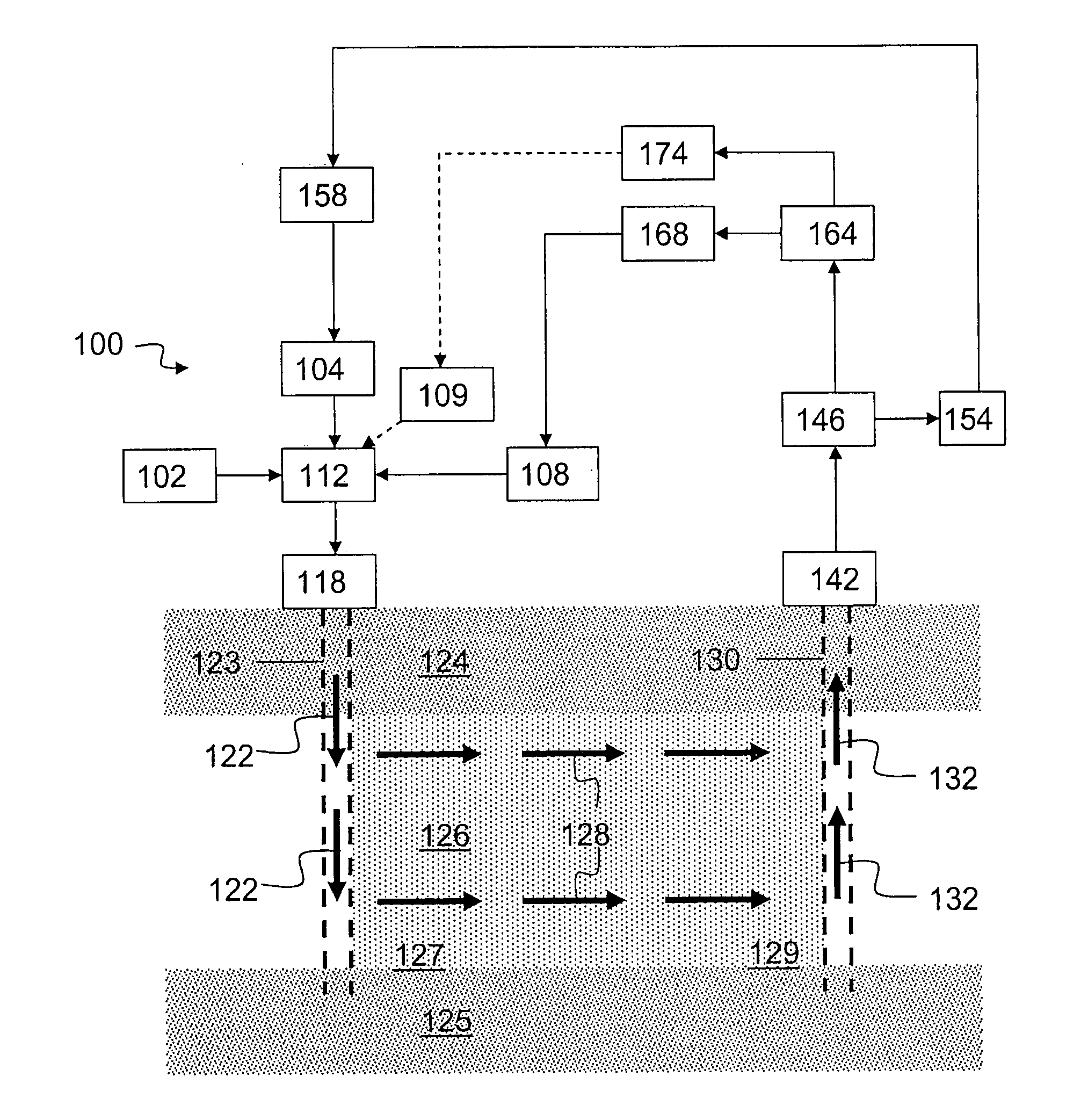
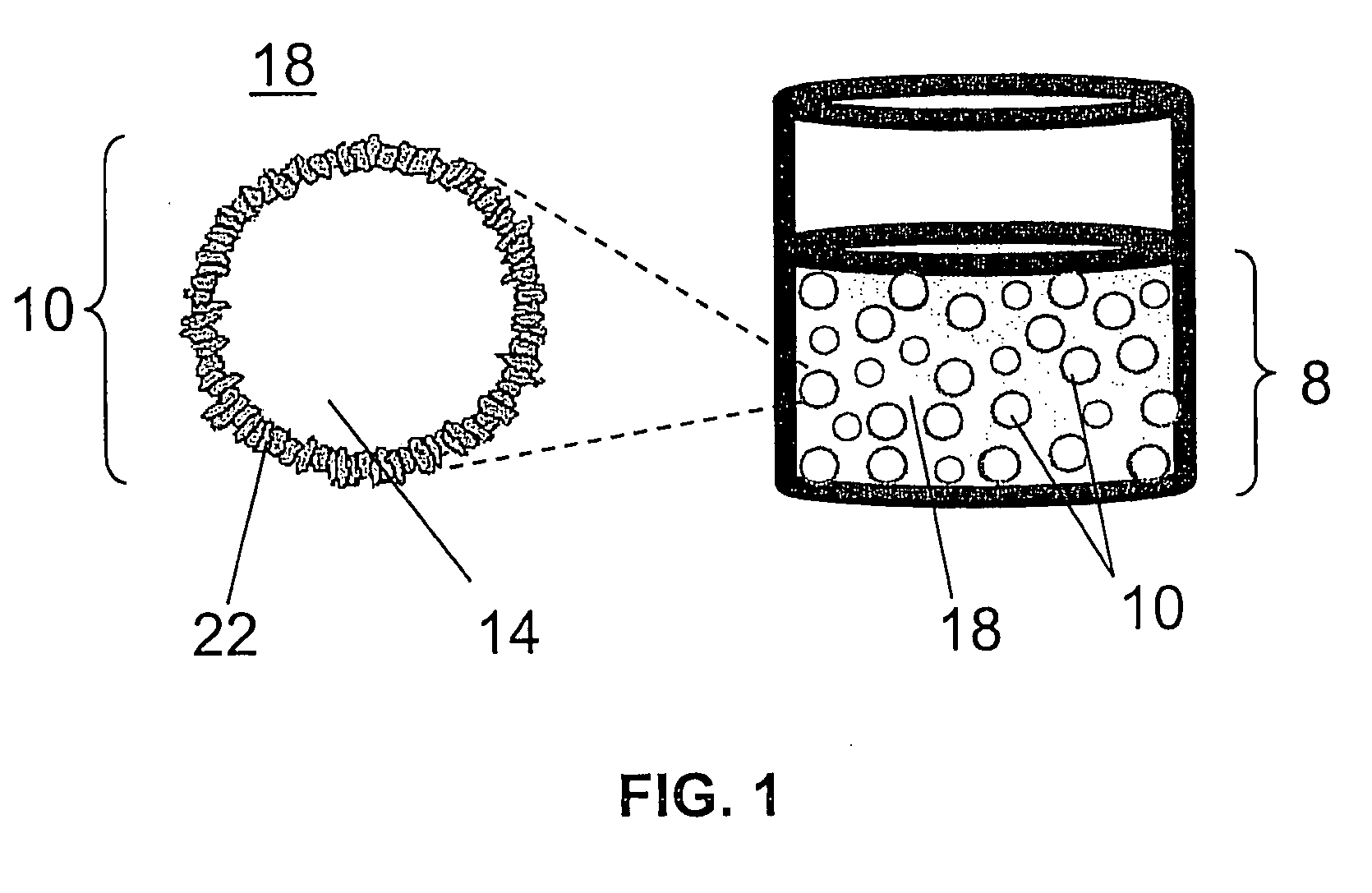
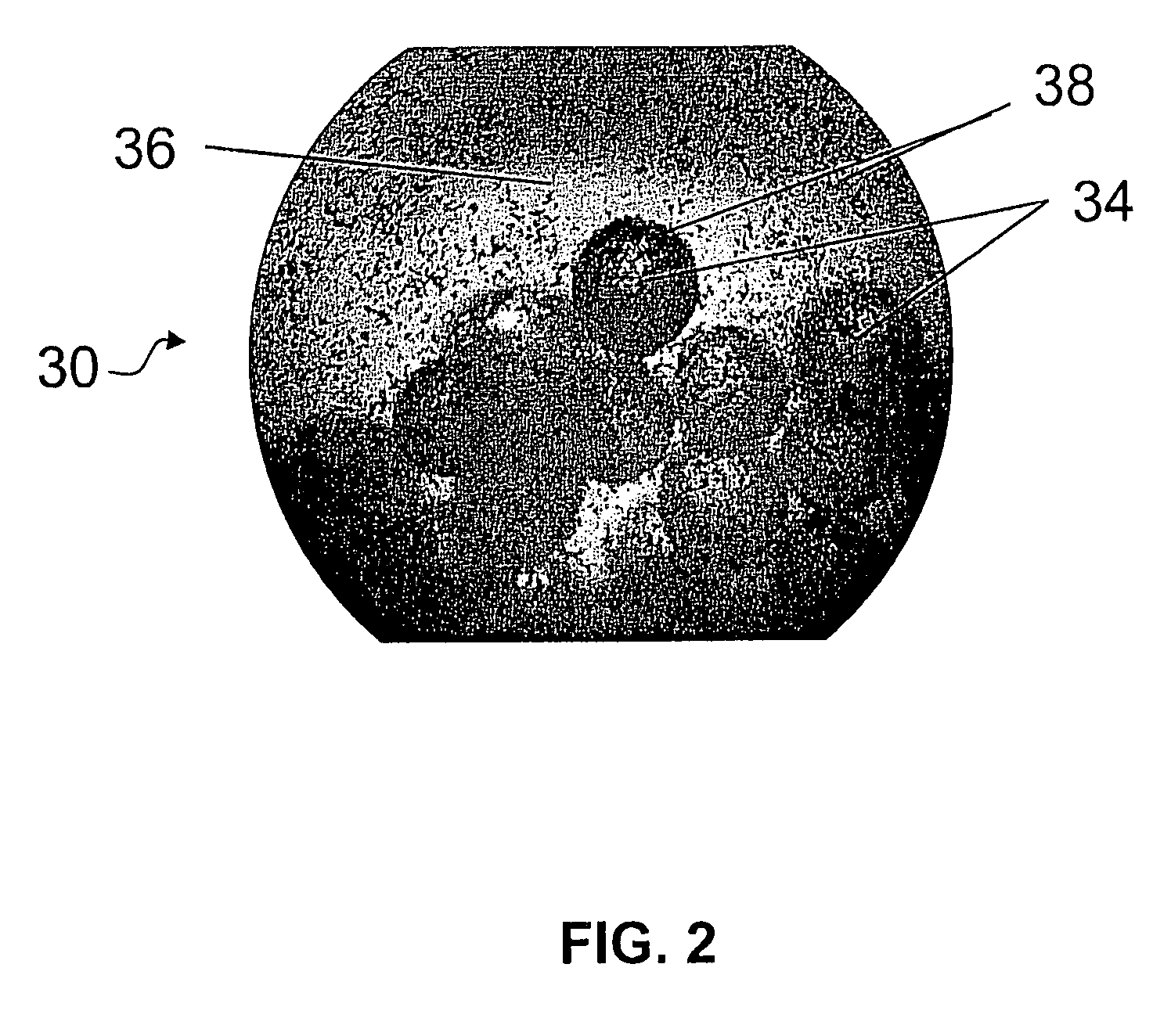
Particle Stabilized Emulsions for Enhanced Hydrocarbon Recovery
a technology of hydrocarbon recovery and stabilized emulsions, which is applied in the direction of carbon-dioxide storage, chemistry apparatuses and processes, and well accessories. it can solve the problems of invariably contaminated water, more oil being recovered, and waste-related concerns
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1a
[0115]Particles-stabilized CO2-in-aqueous liquid (C / A) and aqueous liquid-in-CO2 (A / C) macroemulsions were formed in a high-pressure batch reactor (HPBR) with view windows using an apparatus similar to the one shown in FIG. 4. The reactor included a stainless steel pressure cell of 85 mL internal volume equipped with tempered glass windows (PresSure Products G03XC01B). The windows were placed 180° apart, with one illuminated with a 20 W, 12 V compact halogen bulb and the other allowing observation with a video camera. The view window diameter was 25 mm. The window diameter was used as a scale for determining droplet diameter sizes. The reactor was equipped with a pressure-relief valve (Swagelok R3− A), a thermocouple (Omega KMQSS-125G-6), a pressure gauge (Swagelok PGI-63B), a bleed valve (Swagelok SS-BVM2), and a 3.2 mm port for admitting CO2. A cylindrical magnetic stir bar with a cross shape on top (VWR Spinplus) was utilized for internal mixing. Unless otherwise indicated, the s...
example 1b
[0116]For preparation of C / A macroemulsions, the following procedure was carried out: a slurry of the hydrophilic particles in water was prepared, a measured volume of the slurry was added to the HPBR through an opening, the opening was closed, and a measured volume of liquid or supercritical CO2 was added by means of a syringe pump. Unless otherwise indicated, the proportions of the ingredients were as follows: 10 g of particulate matter suspended in 65 mL of water and ˜18-20 mL (balance) of liquid CO2. The pressure in the HPBR was 17.2 MPa and the temperature was 15° C.
example 1c
[0117]For preparation of A / C macroemulsions, the preceding procedure was reversed. First, the dry matter was added to the HPBR, followed by injection of liquid CO2. After agitation, a high-pressure syringe pump was used to inject water to a set pressure of 17.2 MPa. For the A / C emulsions, a proportion of ˜65 mL of CO2 / (20 mL of H2O) was used.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com