Detection of fragments of nectin-1 for the diagnosis of alzheimer's disease
a technology of nectin-1 and detection of fragments, applied in the field of detection and diagnosis of alzheimer's disease, can solve the problems of increased onset of ad symptoms, wasting of the brain, and no reliable method for pre-mortem physiological detection of ad
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0056]Nectin-1 is expressed in hippocampal neurons and localized to the excitatory synapses.
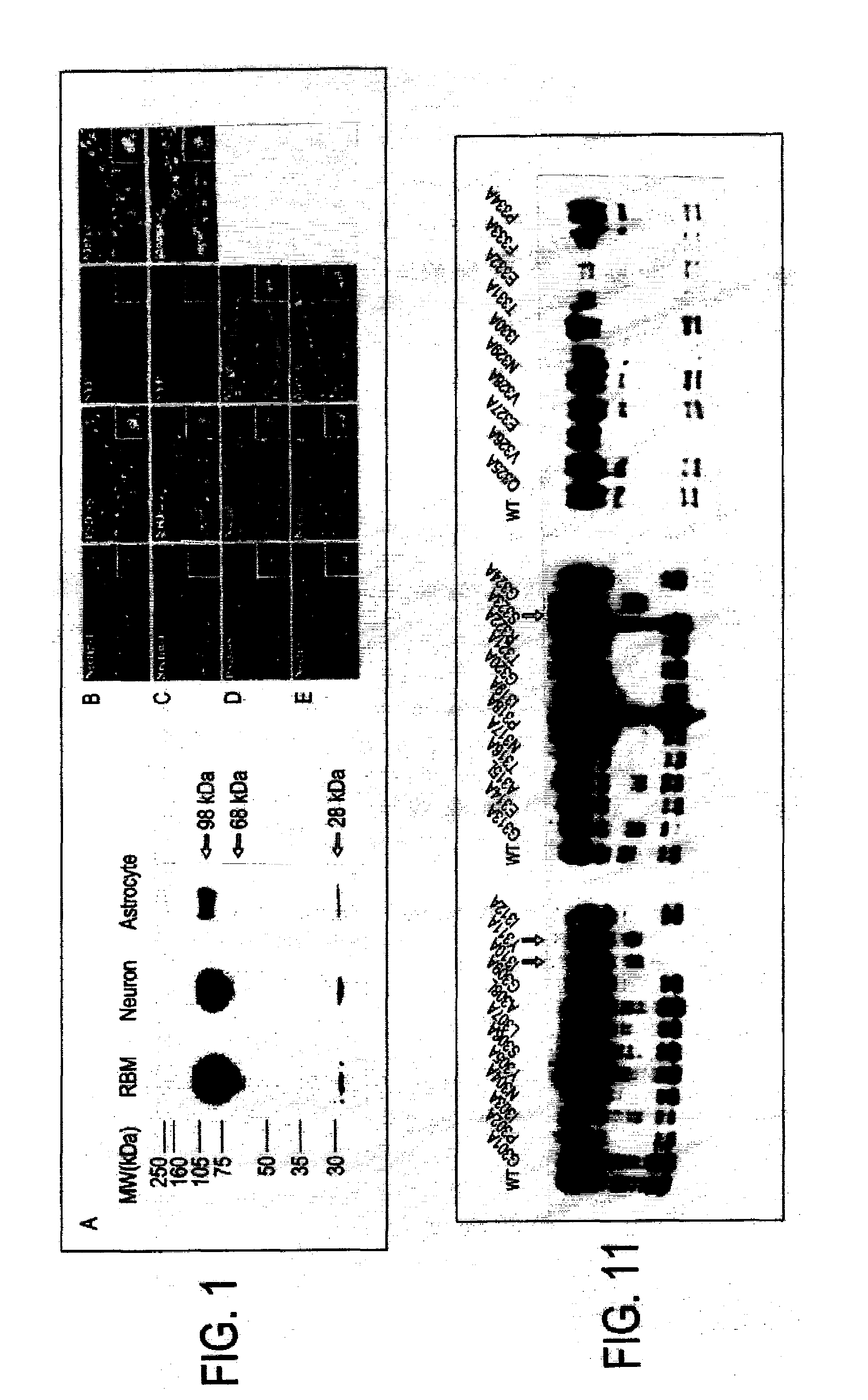
[0057]FIG. 1A shows a Western blot of lysates from rat brain membrane, DIV14 cultured hippocampal neurons, and primary astrocytes, incubated with polyclonal antibody against nectin-1. Three distinct bands are shown (98, 68 and 28 kDa). Neurons at 28 DIV were methanol fixed and labeled with synaptic markers. In FIG. 1B, neurons were triple stained with nectin-1 (red), PSD-95 (green) and synaptophysin (blue). Immunofluorescence images show nectin-1, PSD-95 and synaptophysin immunostaining separately and overlaid in which regions of colocalization that appear white in the superimposed image. One synaptic complex is represented at high magnification in each insert. In FIG. 1C, neurons are also triple stained with nectin-1 (red), NMDA receptor 1 (NR1, green) and synaptophysin (blue). Colocalization between nectin-1 and NR1 indicates that nectin-1 localizes to glutamatergic synapses. In FIG. 1D, th...
example 2
The Ectodomain of Nectin-1 Undergoes Shedding
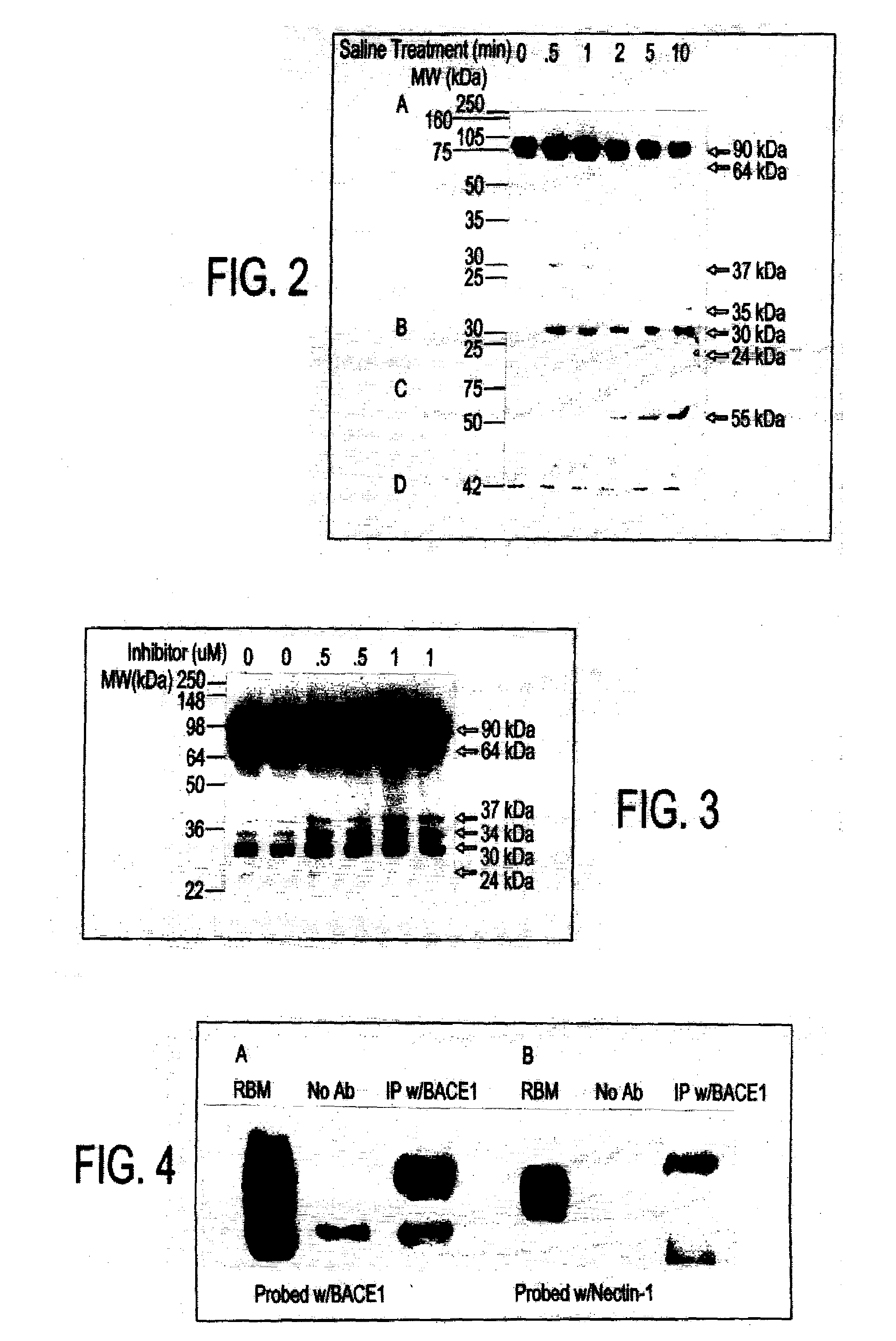
[0059]FIG. 2 shows a Western blot of the shedding of nectin-1. Neurons at 21 DIV were treated with physiological saline for 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, and 10 minutes, followed by collection of media and cell lysates and analysis on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel. The membranes from cell lysates (FIG. 2A) and media (FIG. 2C) were probed with polyclonal nectin-1 antibody and ectodomain specific monoclonal nectin-1 antibody, respectively. The membrane from FIG. 1A was stripped and treated with calf intestinal phosphatase (CIP) for 30 min. at 37° C. and reprobed with polyclonal nectin-1 antibody (FIG. 2B). The membrane from the cell lysate was also probed with β-actin antibody (FIG. 2D).
[0060]The ectodomain of nectin-1 is cleaved and released from Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells and 5-day old mouse cortical neurons in a soluble form. It was discovered that nectin-1 shedding also occurs in rat hippocampal neurons by short term treatment with physiological saline....
example 3
Three C-Terminal Nectin-1 Derived Fragments Accumulate in Hippocampal Neurons
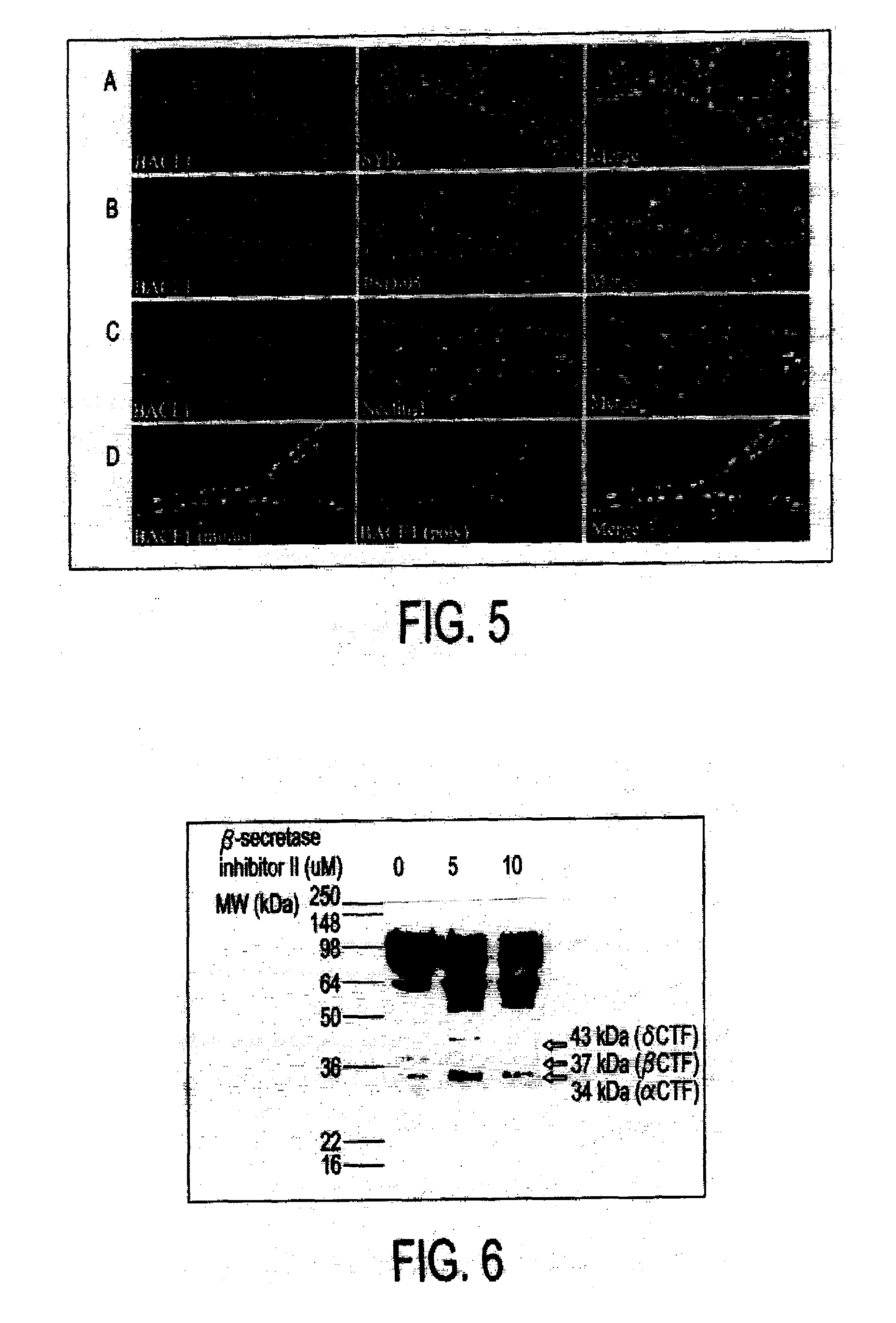
[0061]Hippocampal neurons were plated at a density of 1.3×105 cells. The neurons at 21 DIV were transduced with an adenovirus vector expressing a C-terminal flag tagged nectin-1 for 24 hrs at a MOI of 50. Neurons were treated without (FIG. 3, lanes 1 and 2) or with 0.5 μM (FIG. 3, lanes 3 and 4) and 1 μM γ-secretase inhibitor X (FIG. 3, lanes 5 and 6) for 24 hrs. These cells were harvested in reducing sample buffer and analyzed on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel.
[0062]Technical difficulties preclude detection of endogenous C-terminal fragments, particularly the 35 and 24 kDa forms due to low expression levels in neurons. To circumvent this, C-terminal Flag tagged nectin-1 was over expressed in neurons as described above. The Western blot exhibits six distinct molecular weight bands, 90, 64, 37, 34, 30 and 24 kDa bands. The presence of four small fragments likely indicates that there are alternative cleavage sites reveal...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Cell angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com