Vehicle communication systems and methods for electric vehicle power management
a technology for communication systems and electric vehicles, applied in the field of electric vehicles, can solve the problems of inability to quickly replace other devices, inability to communicate with each other, and inability to quickly deploy both devices, so as to reduce the power consumption of the vehicle and facilitate the electrical load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Reference will now be made in detail to the embodiments of the present invention, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings.
Overview
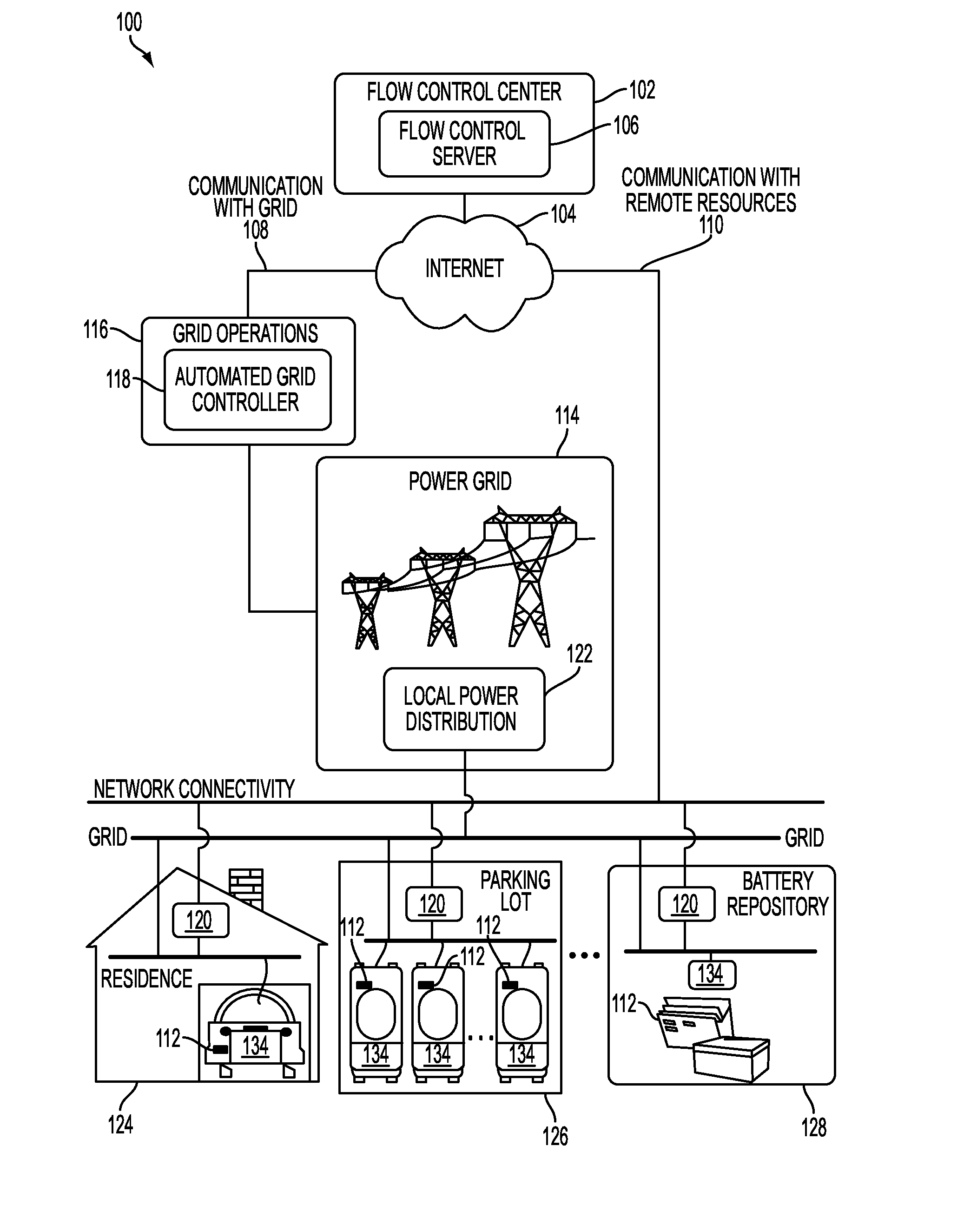
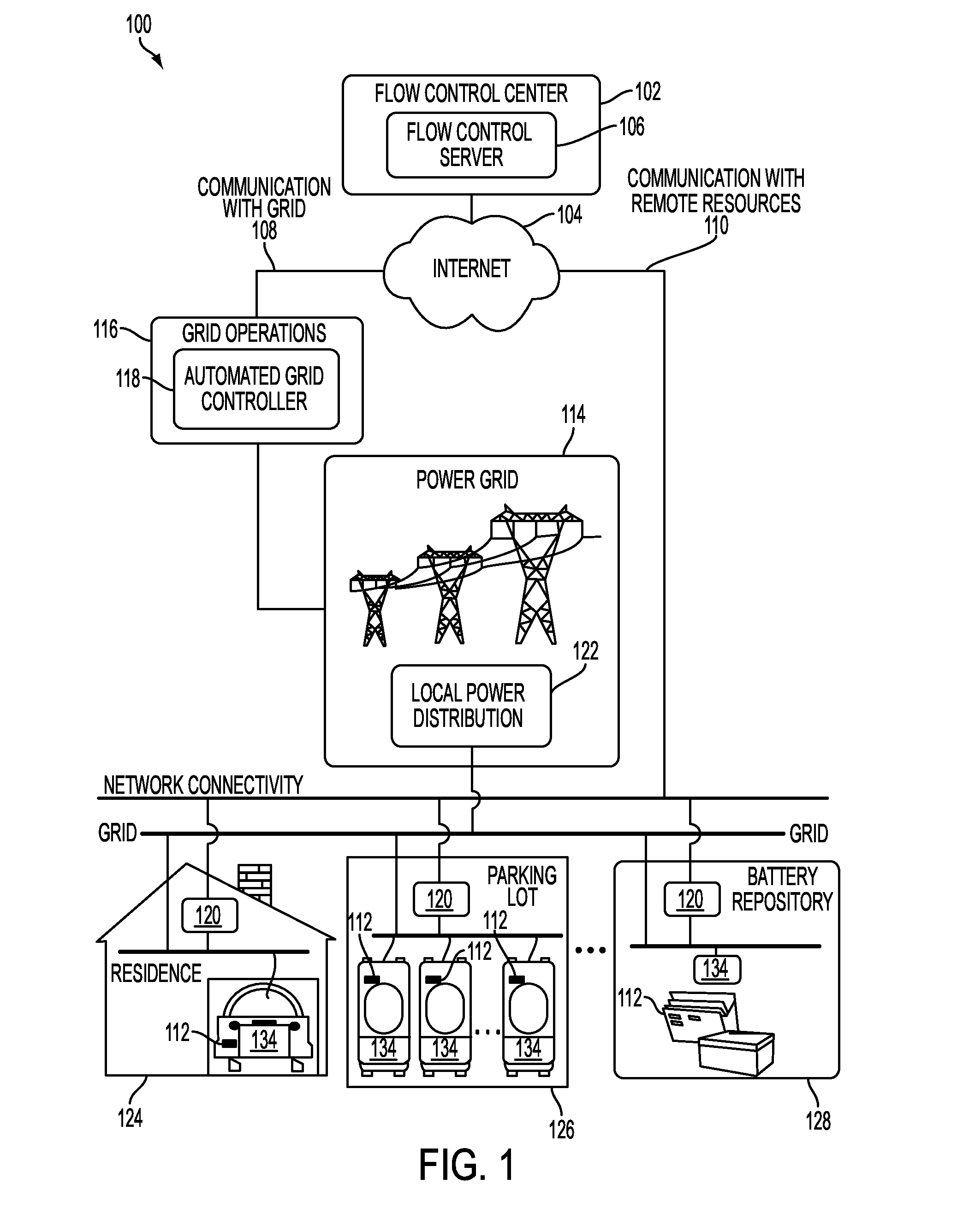
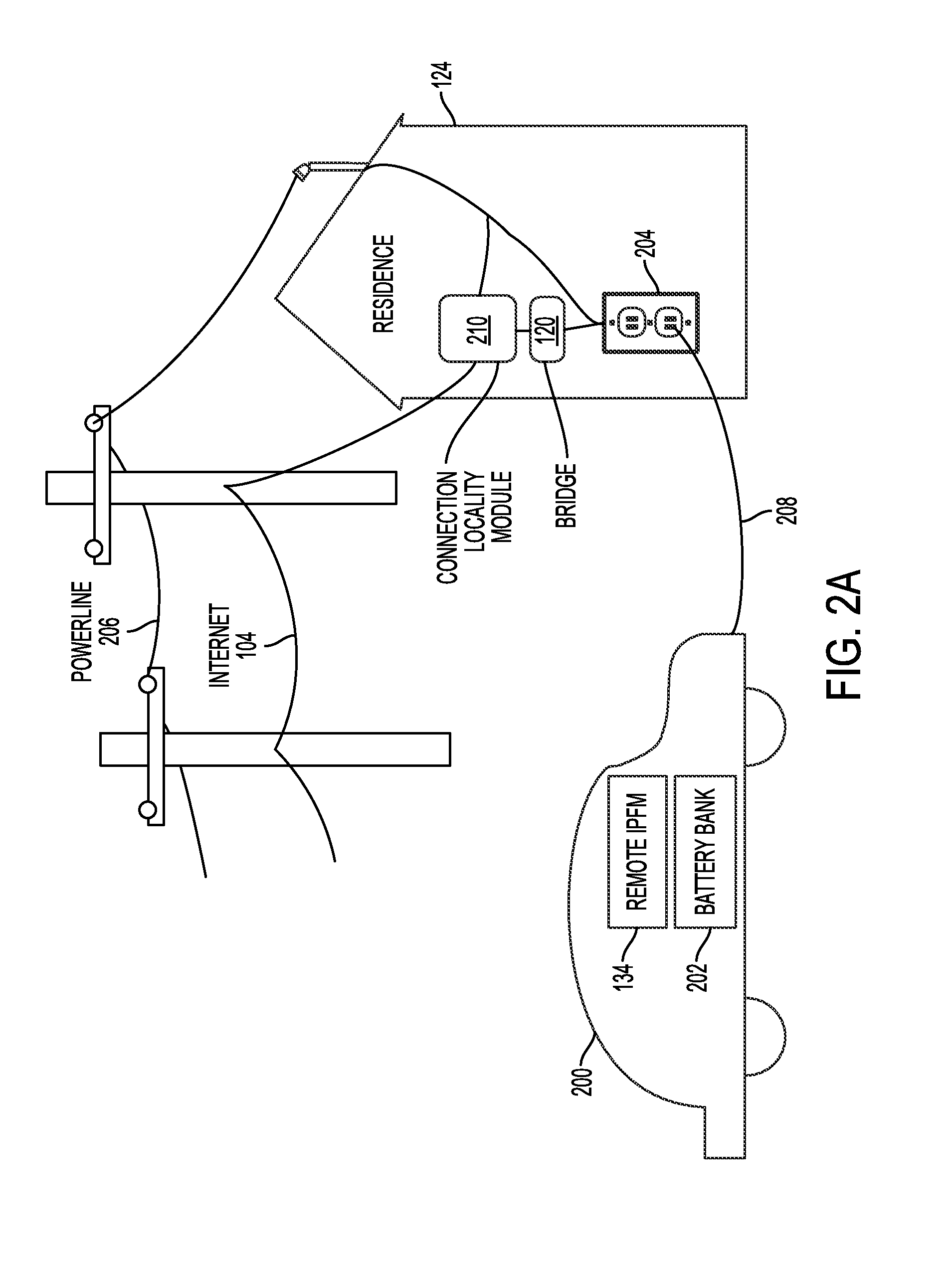
Described herein is a power aggregation system for distributed electric resources, and associated methods. In one implementation, a system communicates over the Internet and / or some other public or private networks with numerous individual electric resources connected to a power grid (hereinafter, “grid”). By communicating, the system can dynamically aggregate these electric resources to provide power services to grid operators (e.g. utilities, Independent System Operators (ISO), etc).
“Power services” as used herein, refers to energy delivery as well as other ancillary services including demand response, regulation, spinning reserves, non-spinning reserves, energy imbalance, reactive power, and similar products.
“Aggregation” as used herein refers to the ability to control power flows into and out of a set of spatially distributed el...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com