Water-based resin compositon and articles made therefrom
a water-based resin and composition technology, applied in the field of new products, can solve the problems of limited performance of articles prepared from a conventional elastomer dispersion, the nature of components that may be used, and the use of a conventional water-based resin dispersion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
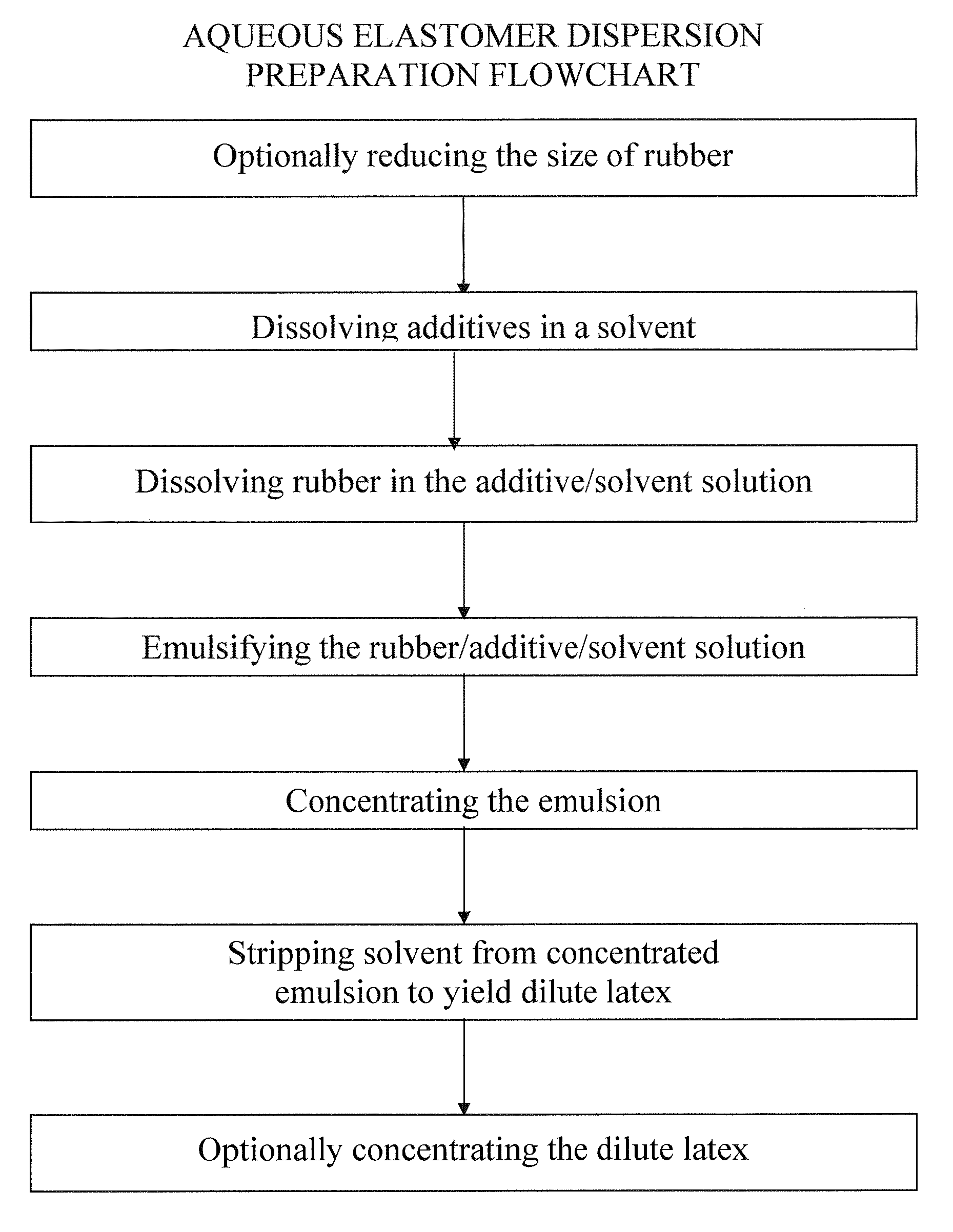
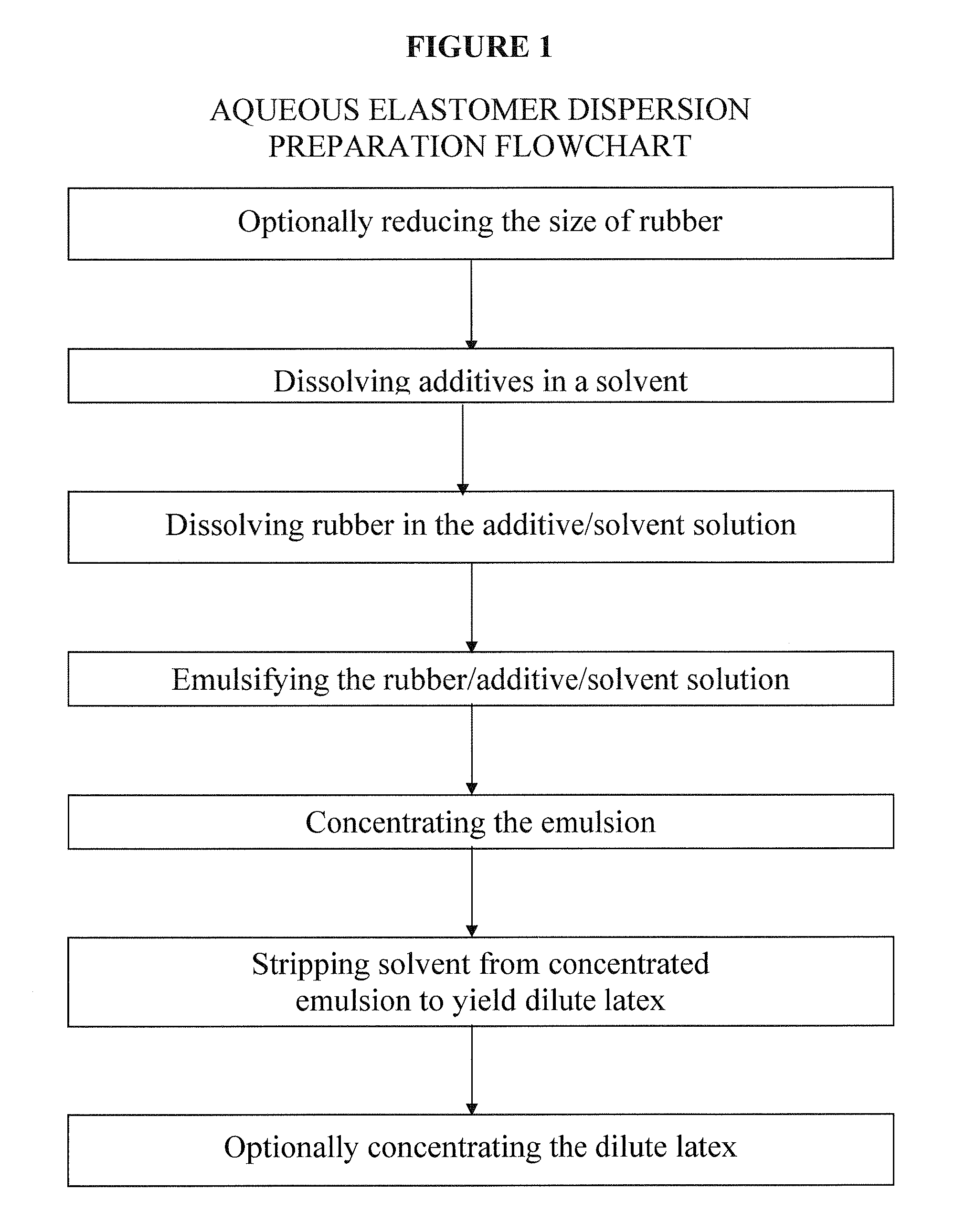
Image
Examples
example 1
Polyisoprene Latex with Additives Wingstay L, ZDEC and DPG
[0071]In this example, the additives Wingstay L, an antioxidant (obtained from Goodyear), and zinc diethyl dithiocarbamate (ZDEC) and diphenyl guanidine (DPG), vulcanization accelerators (both obtained from Flexsys), are first dissolved in solvents. The solutions are prepared by dissolving 0.4 g Wingstay L in 60 mL DCM, dissolving 0.2 g DPG in 10 mL DCM and dissolving 0.1 g ZDEC in 10 mL DCM and then adding these into 600 mL of pentane (obtained from Merck) in a 1 liter beaker.
[0072]20 g of polyisoprene rubber (Kraton IR) is cut into small pieces and slowly added into a beaker that is continuously stirred and contains the additive solution which includes 600 mL pentane and 80 mL DCM solvent that contains predissolved 2 phr Wingstay L, 1 phr DPG and 0.5 phr ZDEC. The concentration in Example 1 is about 2.9 weight polyisoprene / volume solvent. A higher concentration of about 6% weight / volume should be feasible.
[0073]The beaker i...
example 2
Polyisoprene Latex with Additives Wingstay L, ZDEC, DPG and MBT
[0081]A solution containing four additives is prepared by dissolving 0.44 g Wingstay L (obtained from Goodyear, 2 phr) in 60 mL DCM (obtained from Merck), dissolving 0.22 g DPG (obtained from Flexsys, 1 phr) in 20 mL DCM, dissolving 0.11 g ZDEC (obtained from Flexsys, 0.5 phr) in 20 mL DCM, dissolving 0.11 g MBT (obtained from Merck, 0.5 phr) in 50 mL acetone (obtained from Merck) and then adding the solutions one at a time to 600 mL pentane (obtained from Merck, solvent for polyisoprene) in a 1 liter beaker.
[0082]22 g of polyisoprene rubber (Kraton IR) is cut into small pieces and slowly added into the continuously stirred solvent mixture containing the four predissolved additives described above. The beaker is tightly covered with a piece of polyethylene sheet to minimize evaporation and the rubber / additives / pentane / DCM / acetone mixture is stirred until the rubber is completely dissolved. The temperature of the solvent ...
examples 3-5
And Control Polyisoprene Latex with Varying Amounts of Additives Wingstay L, ZDEC, DPG and ZMBT
[0090]In Examples 3-5, varying amounts of Wingstay L, ZDEC, and DPG, as shown in Table 3 below, are incorporated with polyisoprene latex into a single dispersion following the method described above in reference to FIG. 1. Example Control has the same formulation as Example 3, as shown in Table 3, but is not prepared according to the methods of the present invention. Instead, Example Control is prepared according to the method described in Example 1 of U.S. Pat. No. 6,828,387 (see col. 7, line 45 to col. 8, line 67). In U.S. Pat. No. 6,828,387, each of the accelerators was formulated into a separate dispersion and was added individually to a solution containing latex in water. In Example Control, accelerators ZDEC, DPG, and ZMBT and Wingstay L that were already in dispersion form were added to latex in an aqueous solution and were then mixed together.
[0091]The latex particle sizes for Exam...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| sizes | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com