Tissue Engineering of Lung
a tissue engineering and lung technology, applied in the field of lung tissue engineering, can solve the problems of lung being difficult to engineer in the laboratory, affecting the quality of lung tissue, and wide range of problems,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experimental examples
[0221]The invention is further described in detail by reference to the following experimental examples. These examples are provided for purposes of illustration only, and are not intended to be limiting unless otherwise specified. Thus, the invention should in no way be construed as being limited to the following examples, but rather, should be construed to encompass any and all variations which become evident as a result of the teaching provided herein.
example 1
Decellularization of Rat Lung and Morphological Characterization of Decellularized Scaffolds
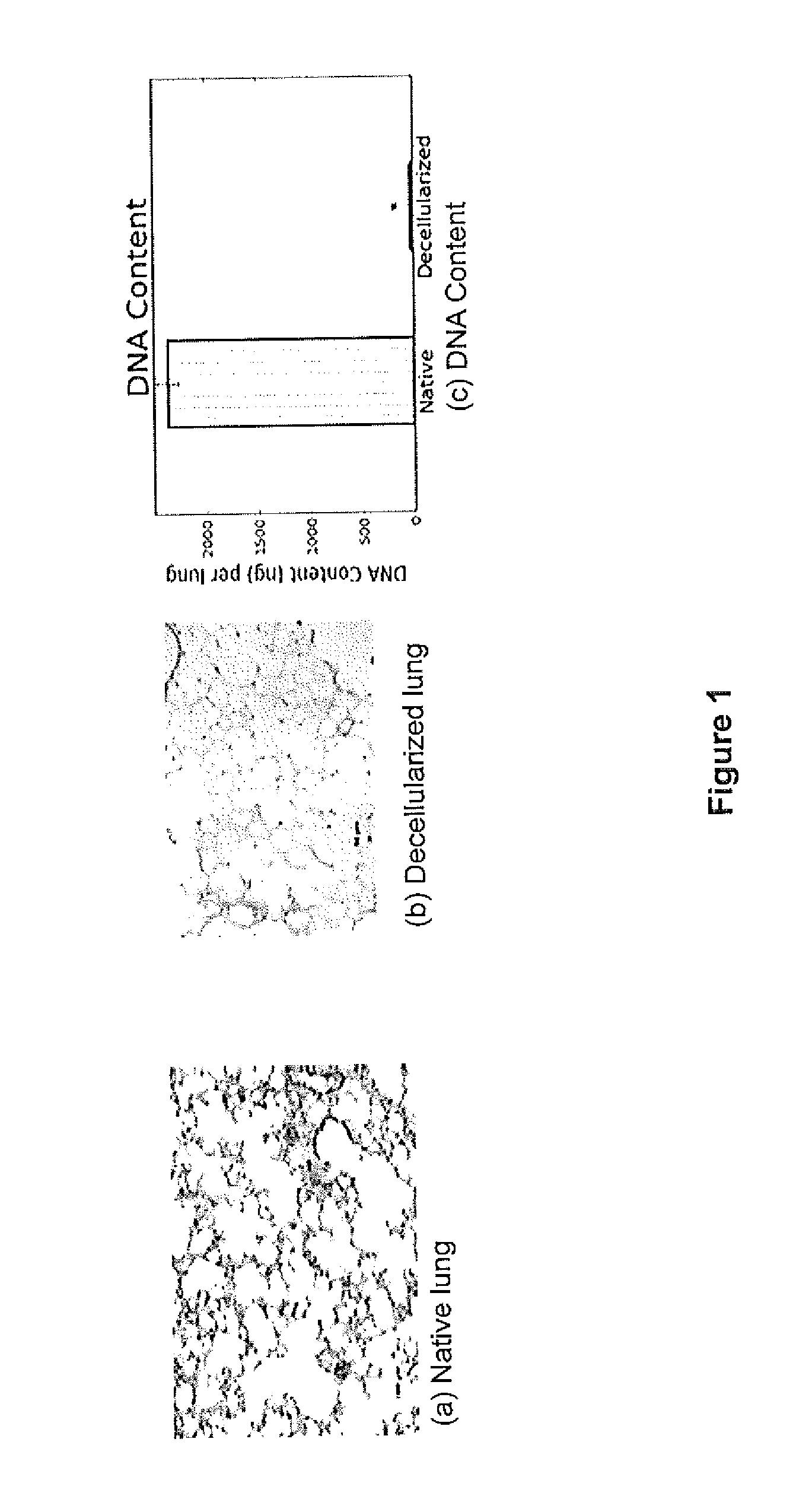
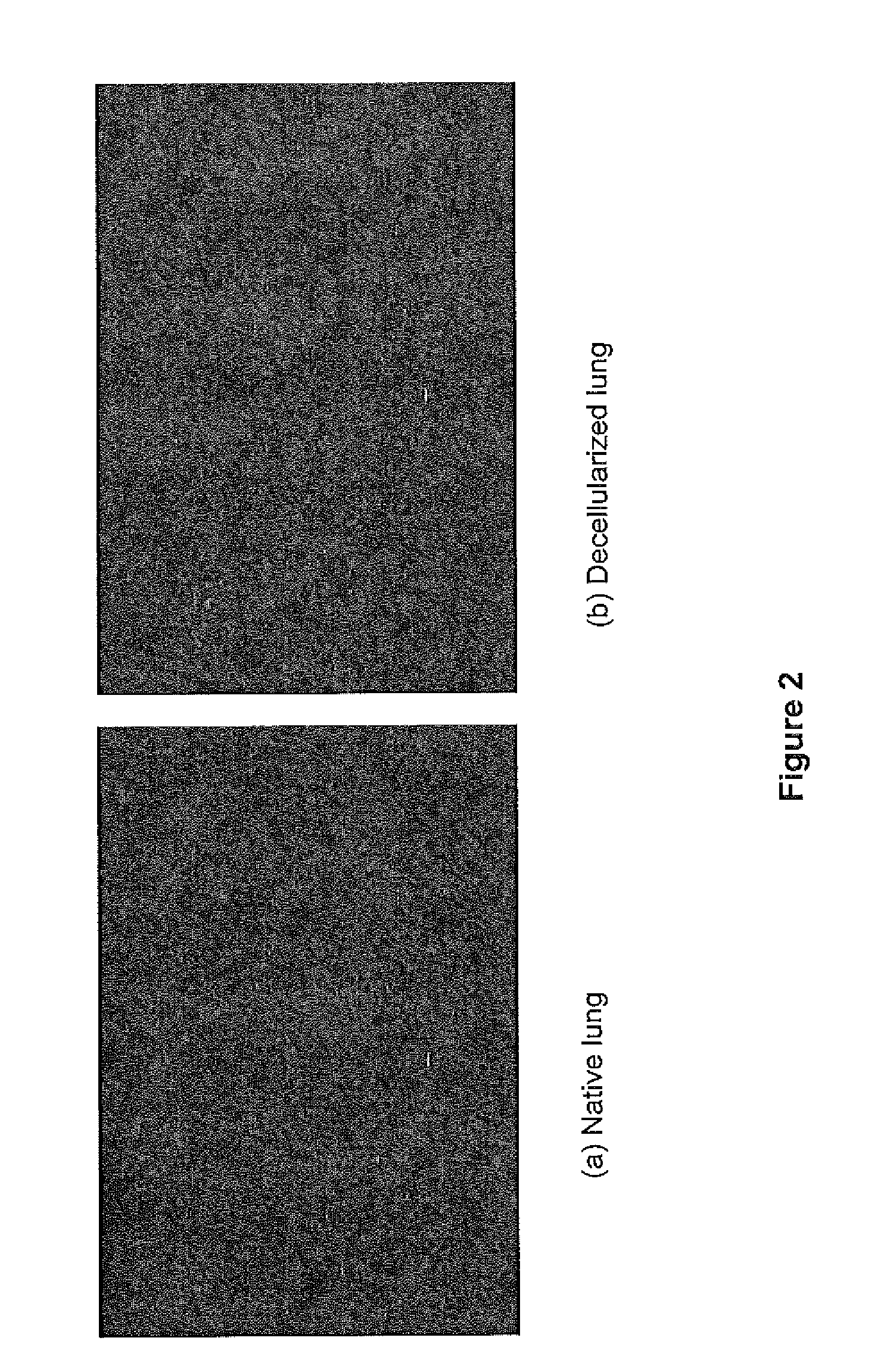
[0222]A decellularized organ offers several advantages for use as a tissue engineering scaffold. In one aspect, the decellularized scaffold contains the appropriate 3-dimensional organization required for tissue function, including a vascular system and airway network in the case of lung. In addition, extracellular matrix (ECM) components are widely conserved across species, thus reducing the likelihood of a decellularized scaffold inducing an immune response upon xenogeneic implantation [Bernard et al., 1983, Biochemistry 1983; 22:5213-23]. In another aspect, native ECM offers the optimal substrate for cell attachment, spreading, growth and differentiation.
[0223]The goal of the decellularization process of the present invention is to remove cellular and nuclear material while retaining key aspects of and minimizing any damage to the ECM of the lung. The results presented herein demonstrate t...
example 2
Contribution of Extracellular Matrix Components to the Mechanical Integrity of Decellularized Lung Tissue
[0269]The following experiments were designed to evaluate the composition of the decellularized scaffolds in more detail with a focus on the mechanical properties of the scaffolds. Without wishing to be bound by any particular theory, it is believed that that decellularized lung scaffolds retain salient mechanical features of native lung, due principally to contributions from collagen and elastin. The results presented herein demonstrate the utility of the decellularized lung tissue as a platform to study lung mechanics independent of cellular contributions.
[0270]The results presented herein demonstrate that collagen content is retained, elastin content is retained at ˜40% of native levels, while glycosaminoglycans are largely lost from the decellularized scaffolds.
[0271]The materials and methods employed in these experiments are now described.
Materials and Methods
[0272]Organ Har...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com