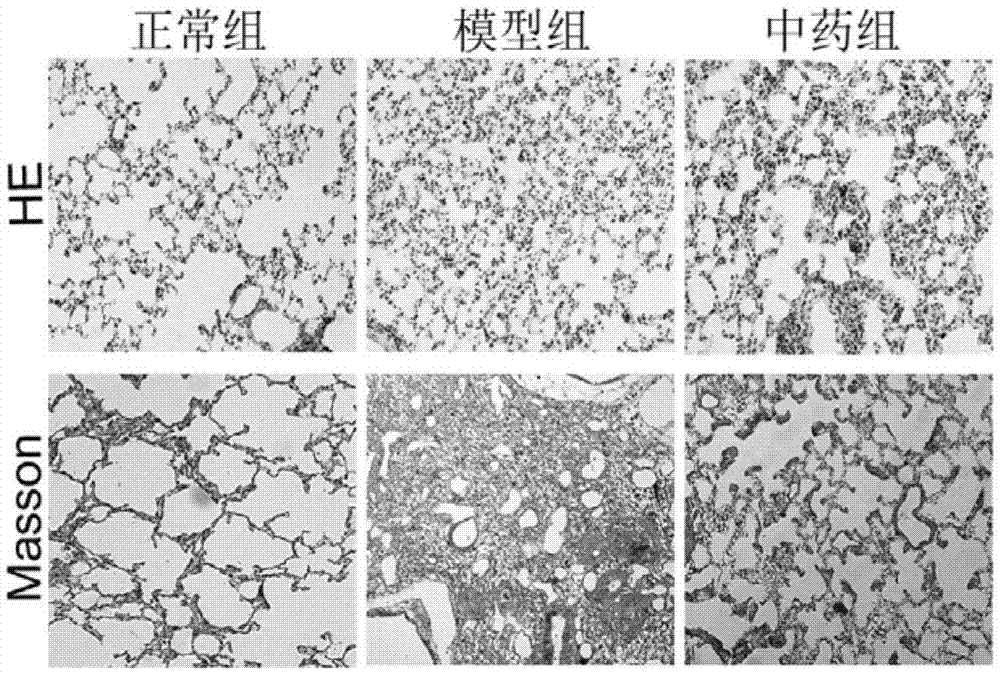
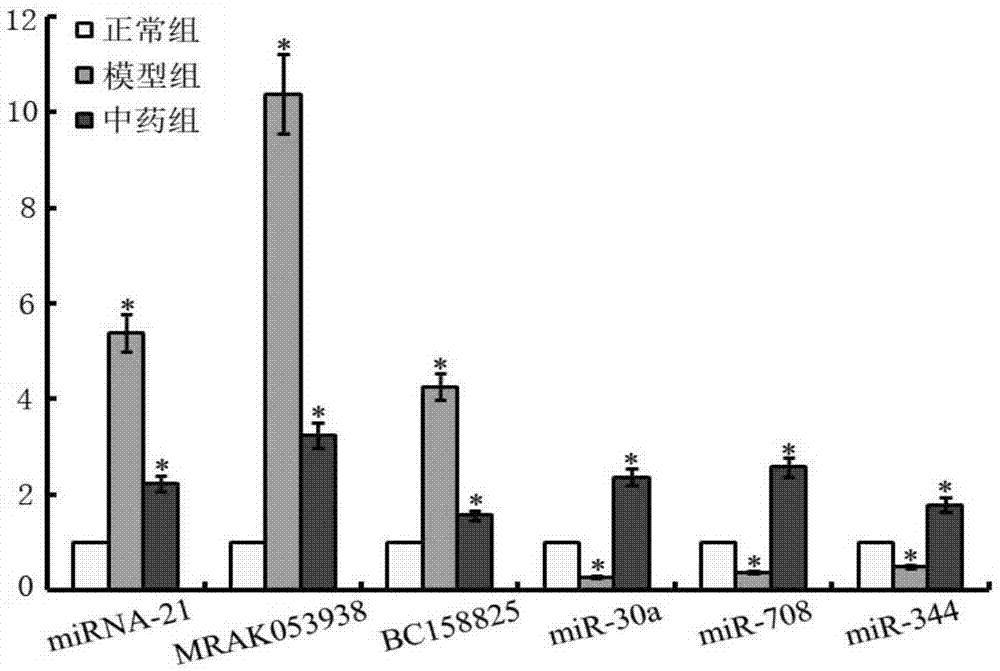
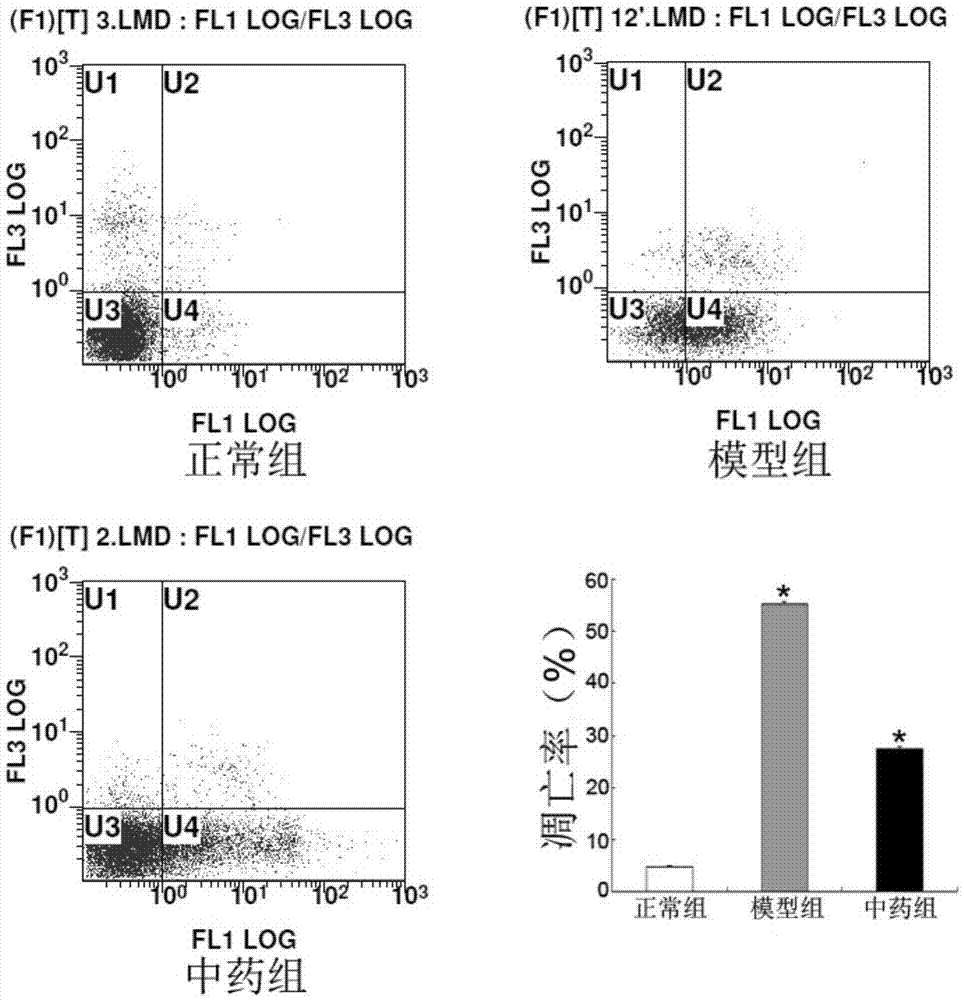
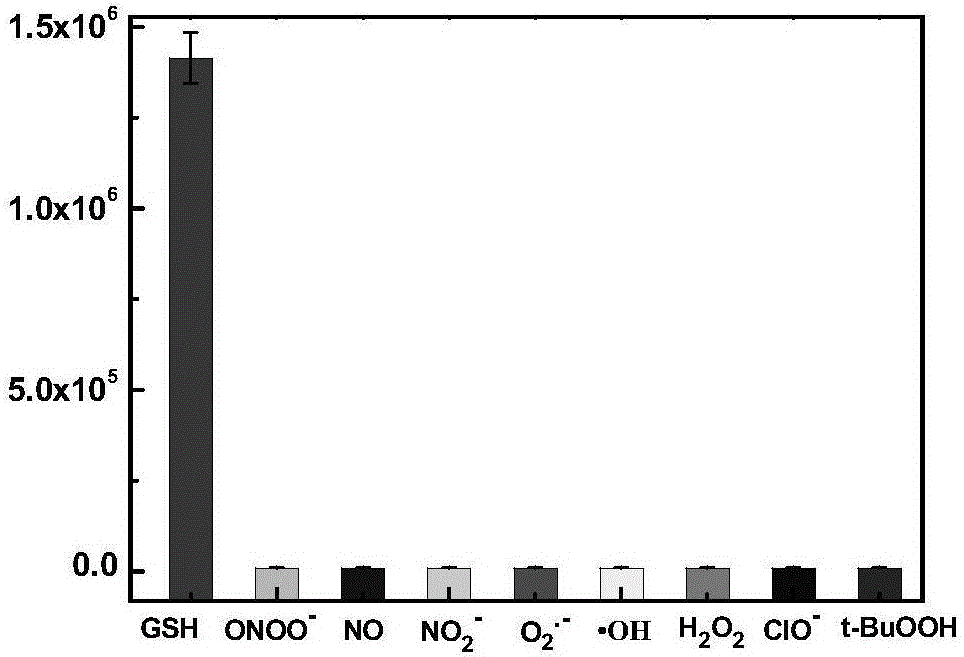
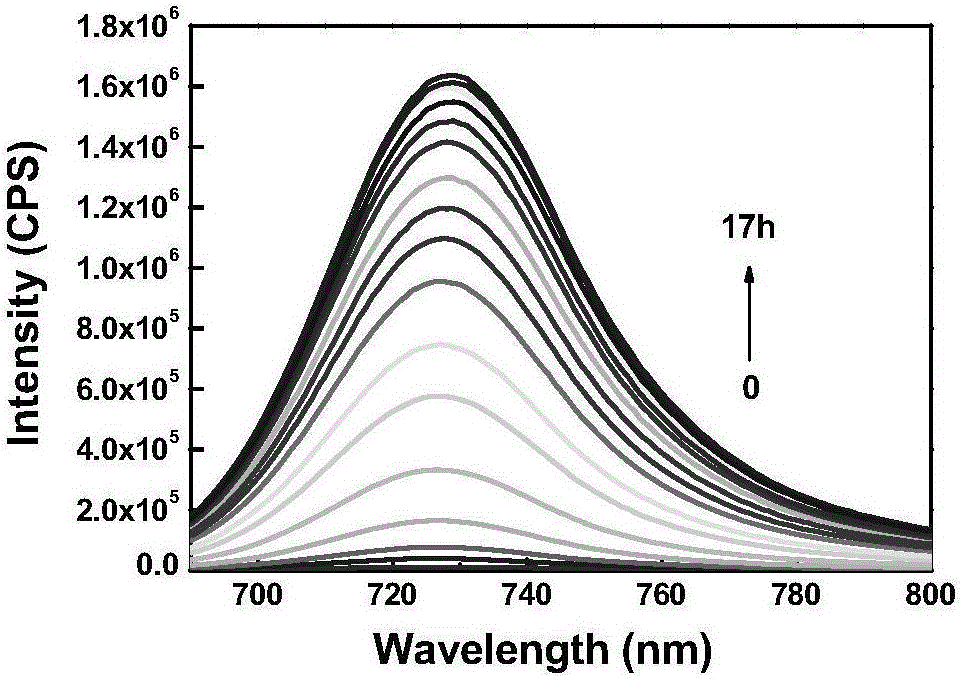
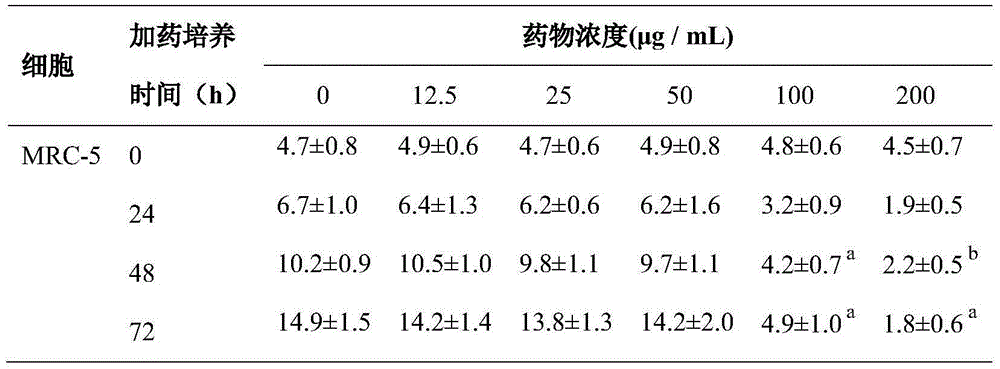
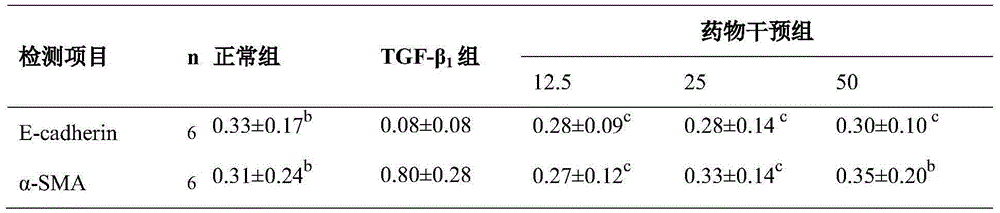
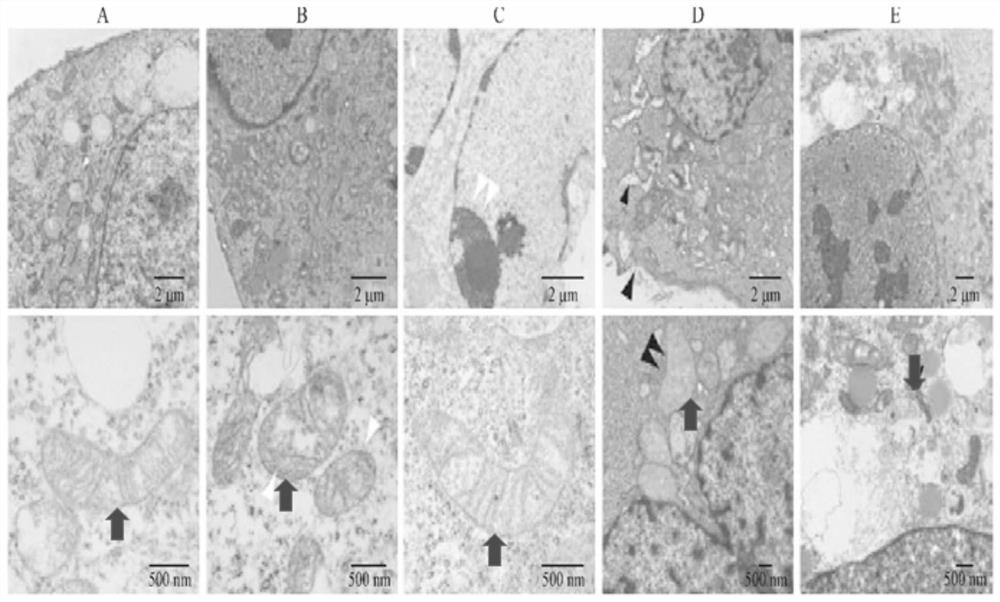
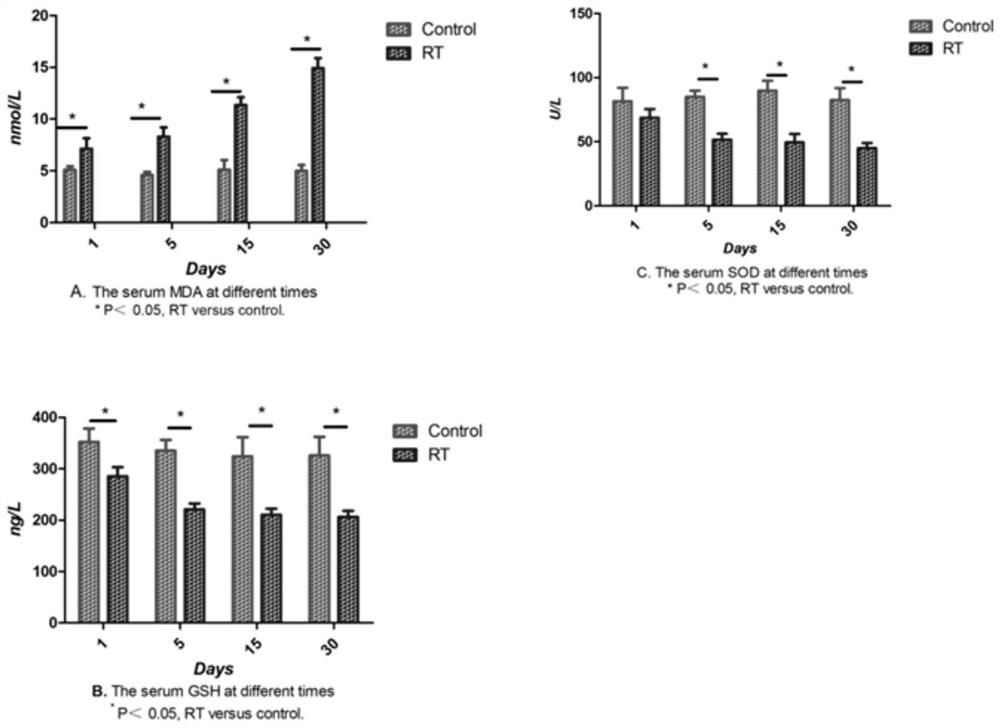
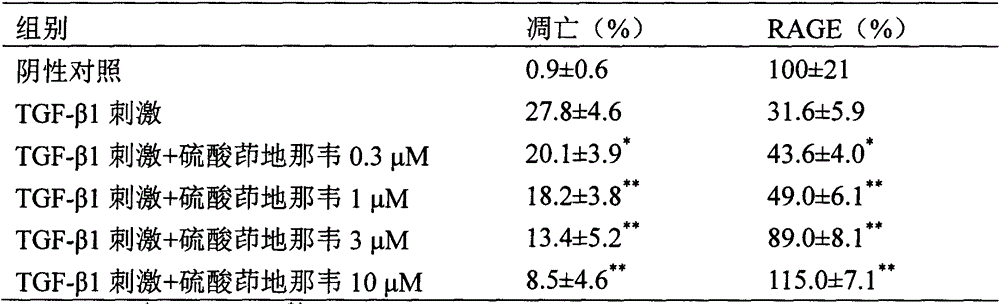
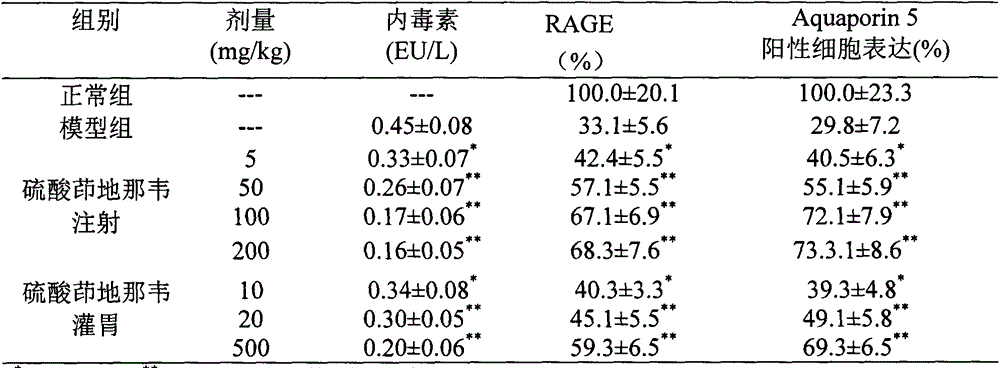
Patents
Literature
65 results about "Alveolar epithelial cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells (PAEpiC), comprised of alveolar type I and type II epithelial cells, line more than 99% of the internal surface area of the lung [1]. Type I cells are large squamous cells whose thin cytoplasmic extensions cover >95% of the internal surface area.
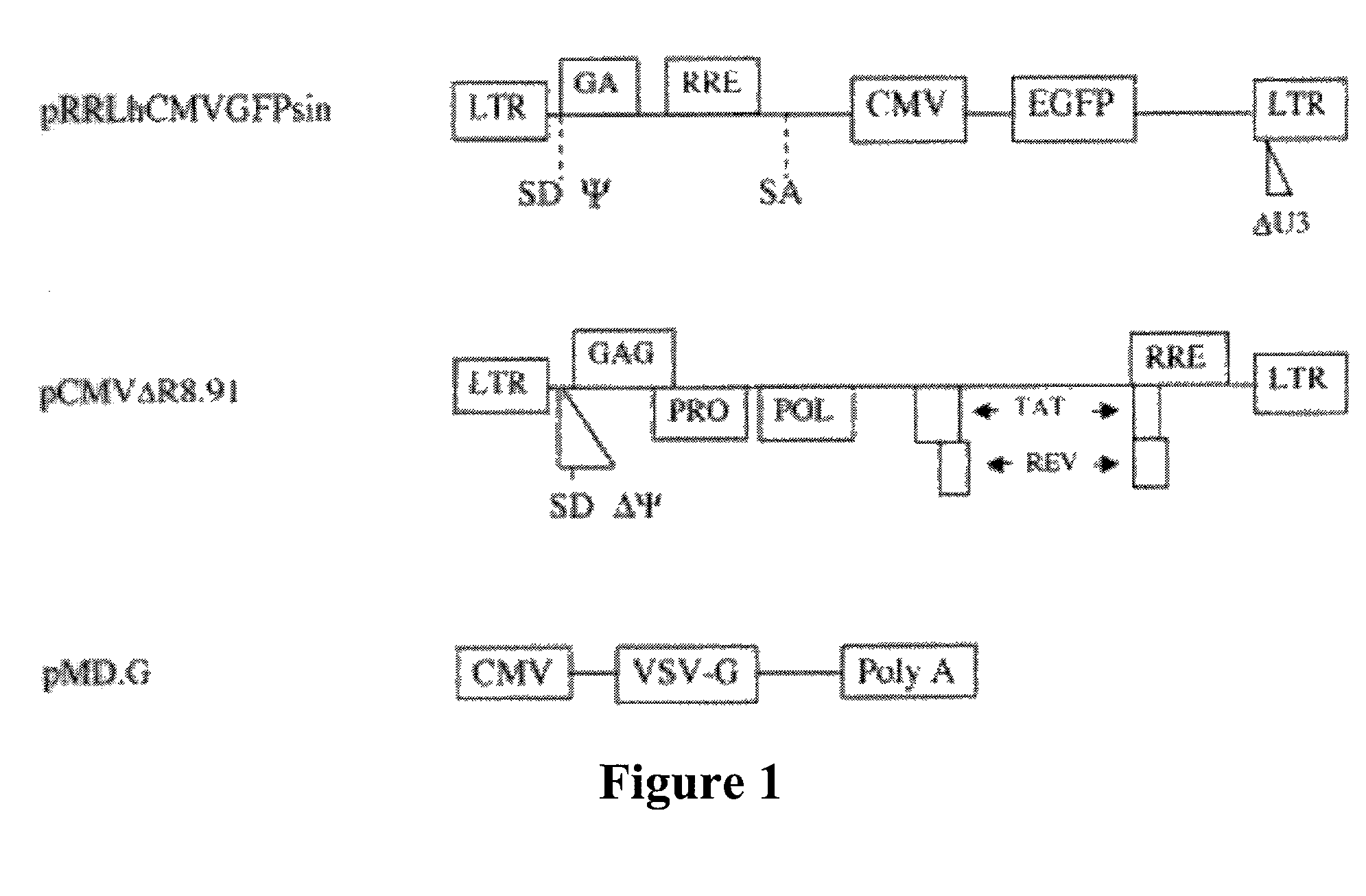
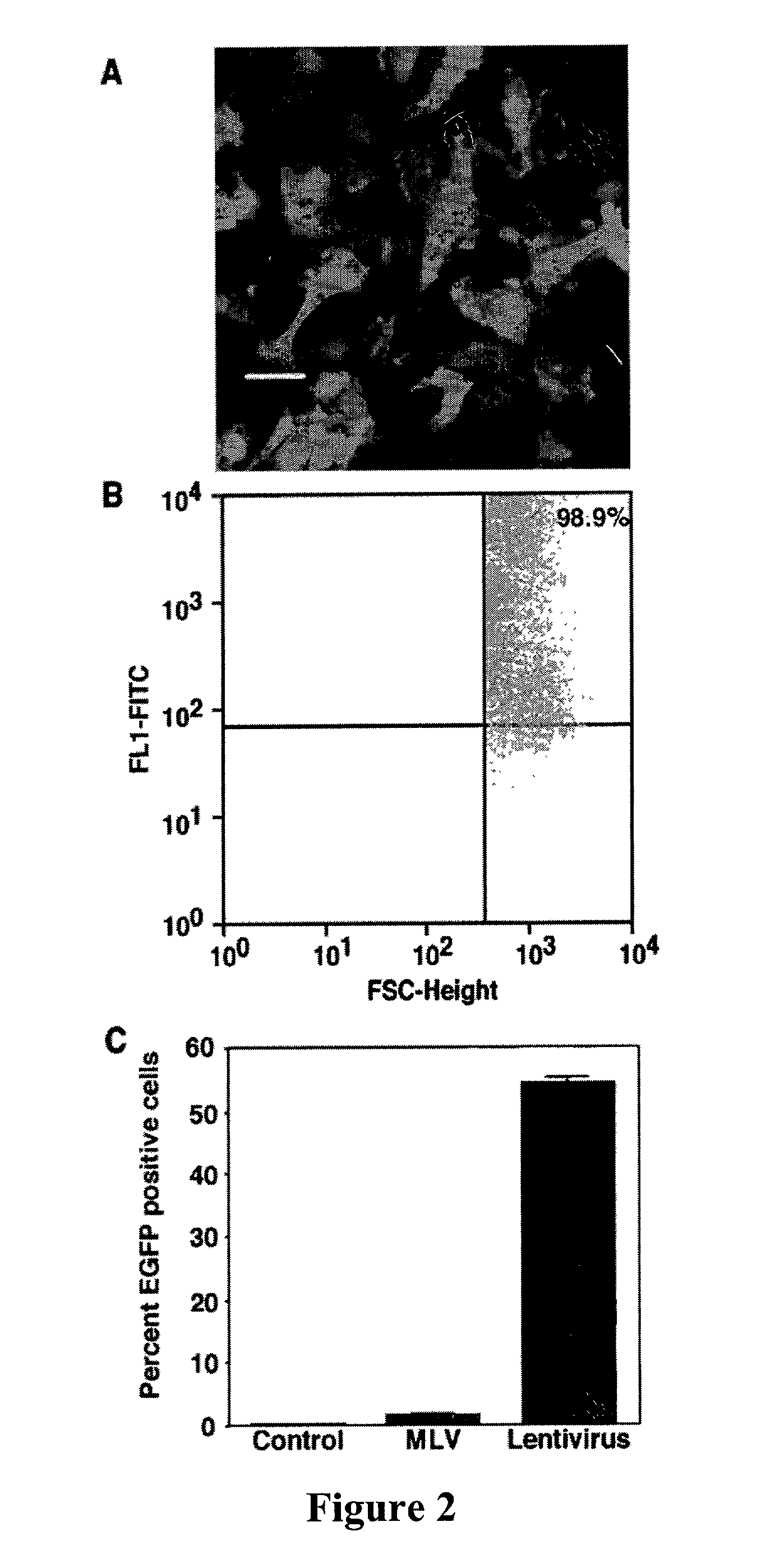
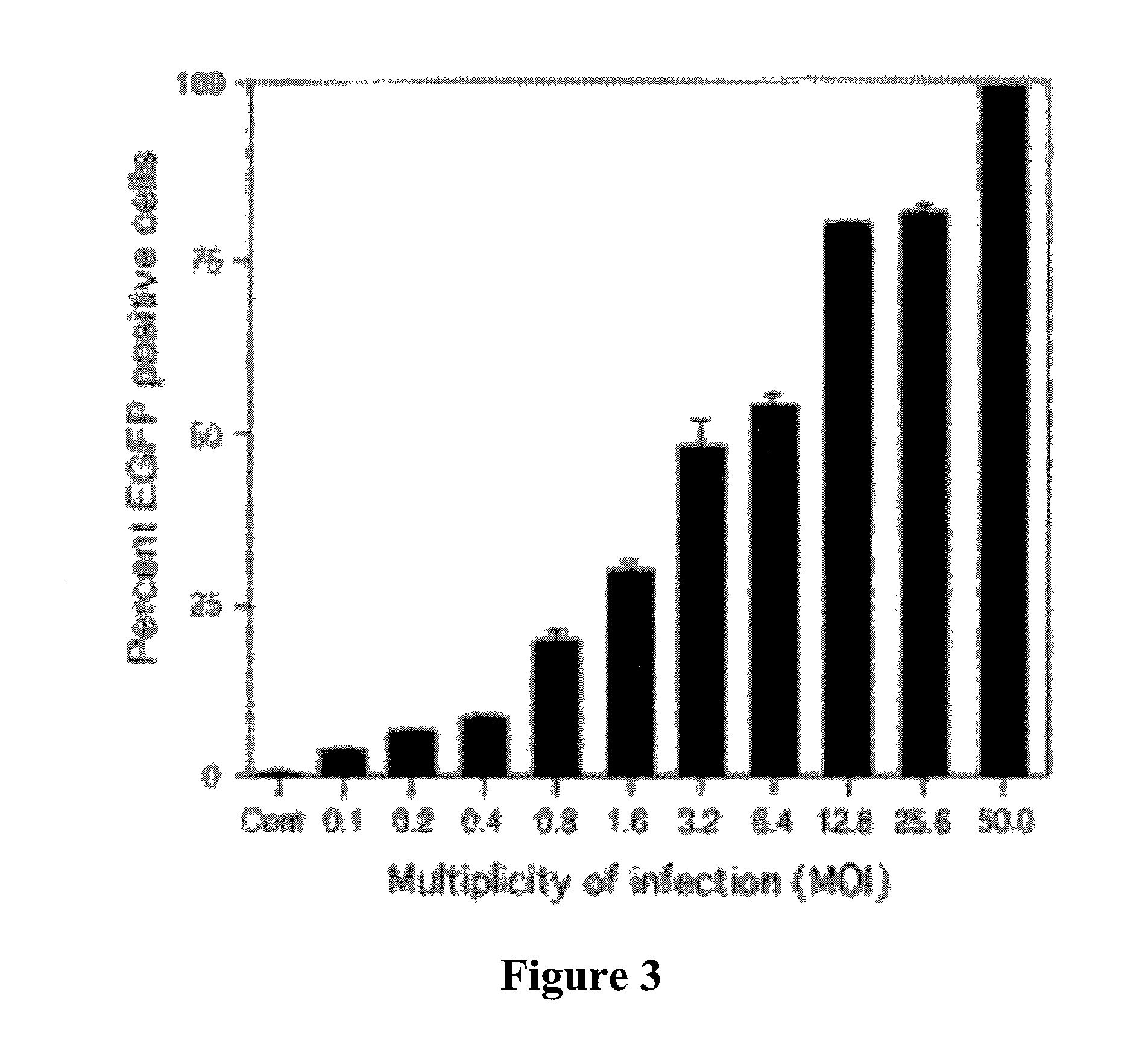
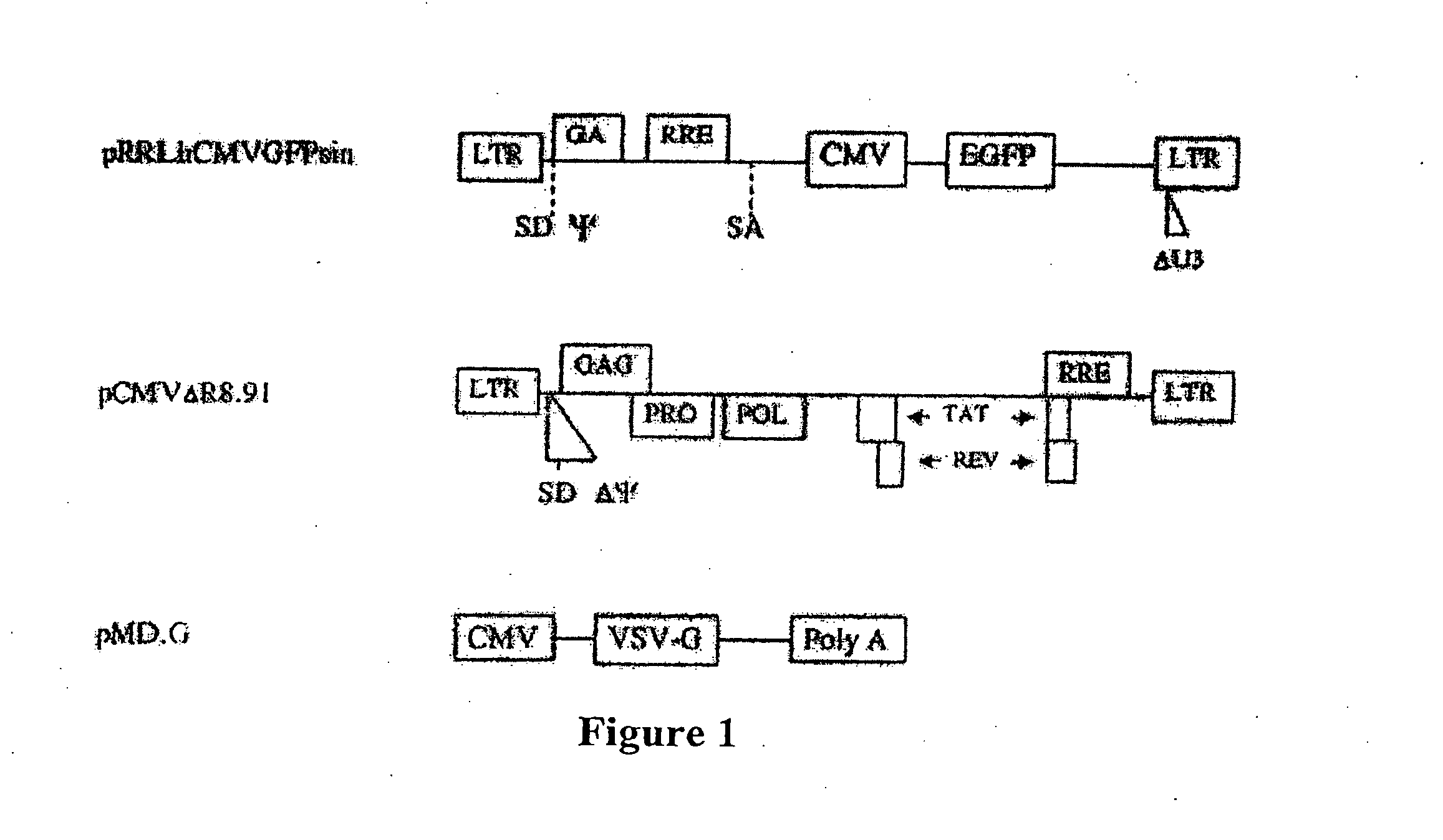
Lentivirus vectors for gene transfer to alveolar epithelial cells
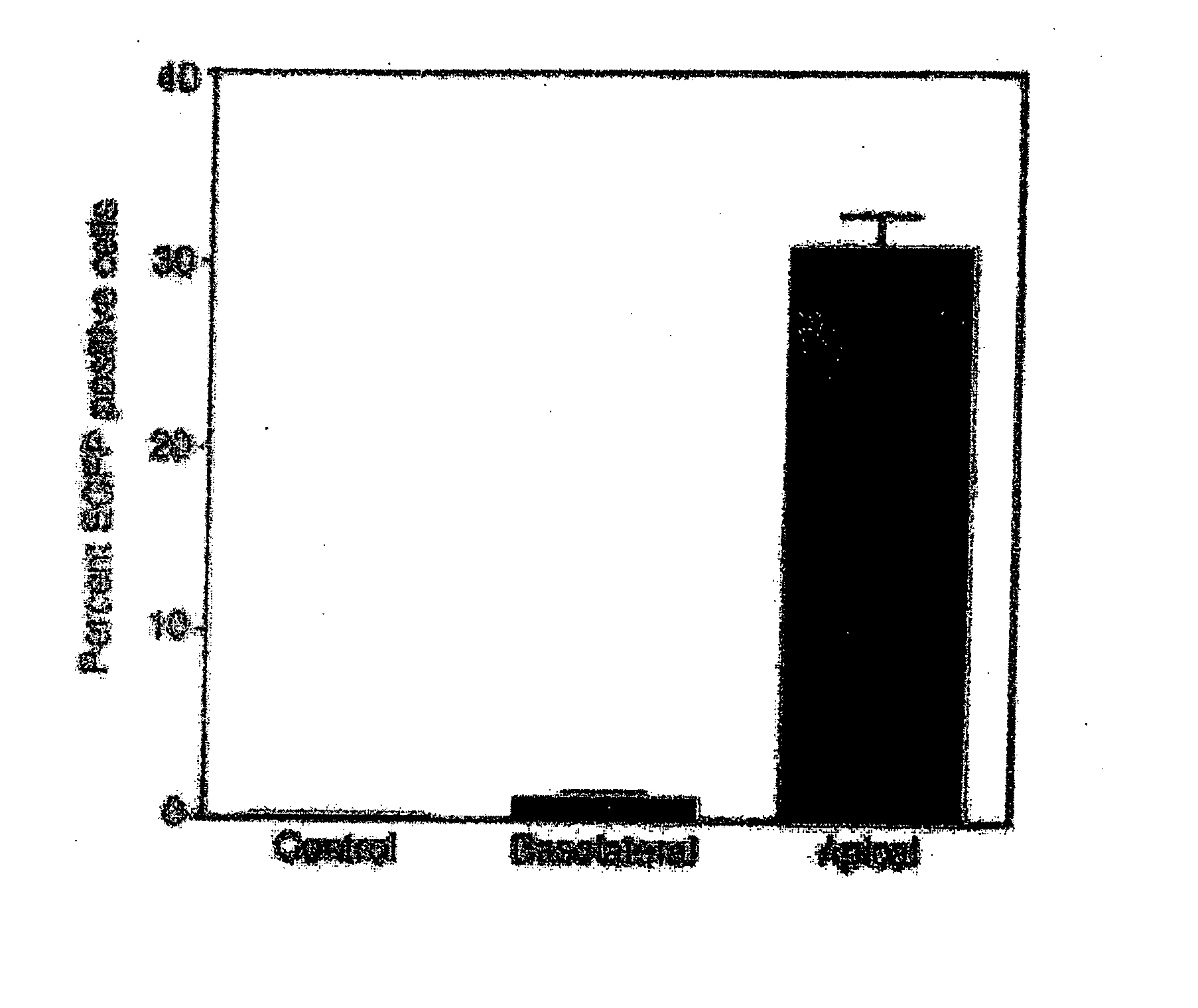
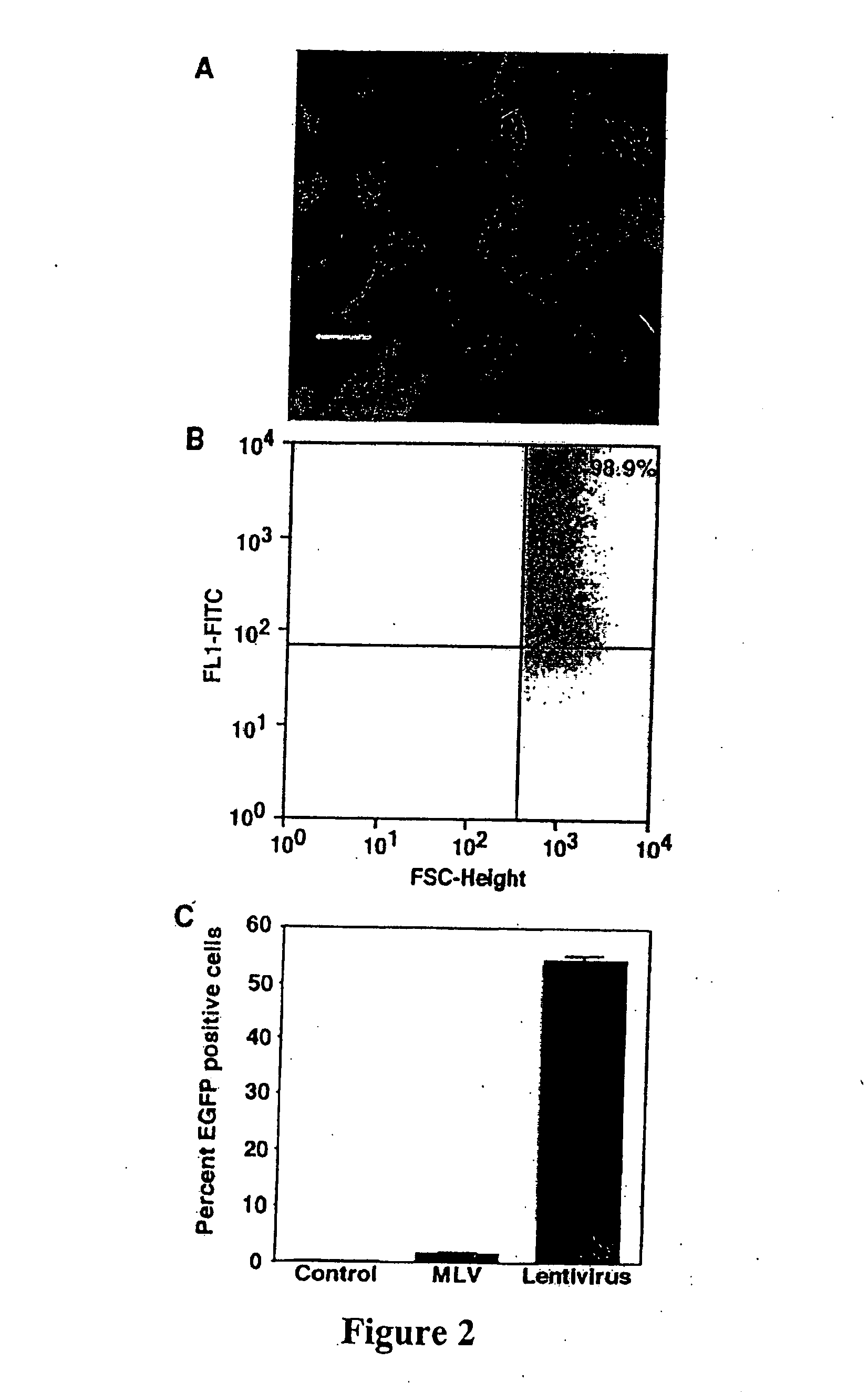
The present invention demonstrates that VSV-G-pseudotyped lentivirus vectors efficiently transduce AEC in primary culture and in vivo with transduction favored by virus application from the apical side. Transduction efficiency in AEC increased with increasing MOI and greatly exceeded that achieved with a similarly pseudotyped MLV retrovirus vector. The present invention also demonstrates the successful in vivo transfer of genes through lentivirus vector transduction. Mammals injected with lentivirus vector via the trachea expressed the reporter protein in alveolar epithelial cells within 48 to 72 hours after infection.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Goat TLR4 gene knock-out vector and construction method thereof
InactiveCN106755097AThe method is simple and fastHigh knockout efficiencyNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliCompetent cell
The invention discloses a goat TLR4 gene knock-out vector and a construction method thereof. The construction method comprises the following steps: firstly, designing an sgRNA fragment of the TLR4 gene by adopting a CRISPR / cas9 system, synthesizing an sgRNA nucleotide sequence, constructing and simultaneously expressing the sgRNA and plasmid PYSY-sgRNA of Cas9 D10A, connecting and transforming to an Escherichia coli DH5 alpha competent cell, and verifying the transformant; and judging and proving by enzyme digestion and sequencing that the TLR4 gene knock-out vector is constructed correctly. The invention adopts the CRISPR / cas9 for constructing the vector, and provides a theoretical basis for subsequently acquiring a goat TLR4 gene deletion type alveolar epithelial cell system, and studying the immune response molecular mechanism of mycoplasma pneumonia infection.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY MEDICINE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
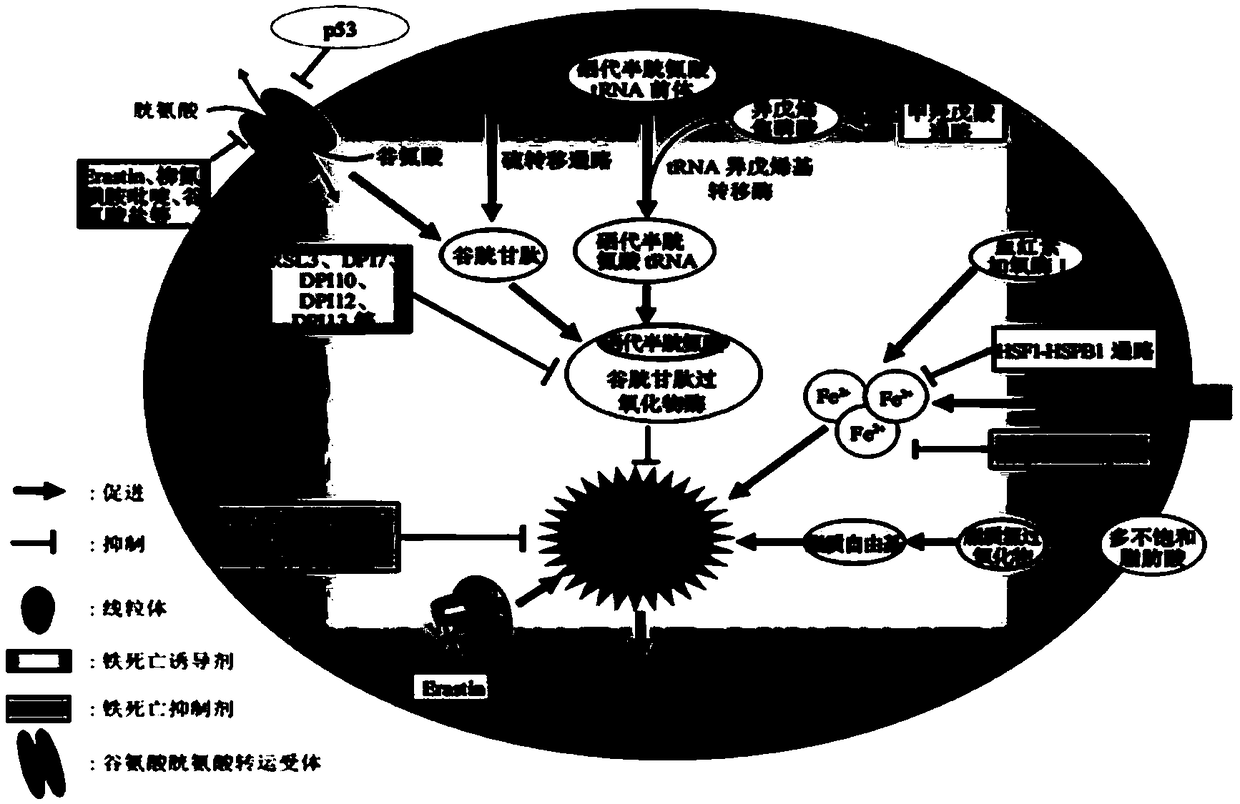
Application of ferroptosis inhibitor
The invention relates to the technical field of medical science, in particular to new application of a ferroptosis inhibitor. The ferroptosis inhibitor is prepared from Liproxstatin-1, Ferrostatin-1,rosiglitazone, pioglitazone, troglitazone and Zileuton. The new application refers to that the inhibitor is applied to treating radiation-induced pulmonary injury diseases. The application has the advantages that (1) radioactive rays trigger radiation-induced pulmonary injury by mediating pulmonary alveoli epithelial cells to have ferroptosis, the ferroptosis specificity inhibitor can be used to prevent and treat radiation-induced pulmonary injury, and has the important meaning on development of new drug for preventing and treating radiation-induced pulmonary injury; and (2) it is found that radioactive rays can cause cell death through the mode of ferroptosis, and application of the ferroptosis inhibitor also has the significant theoretical meaning on guiding research for guiding radioactive rays to treat cancer mechanism.
Owner:JINSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
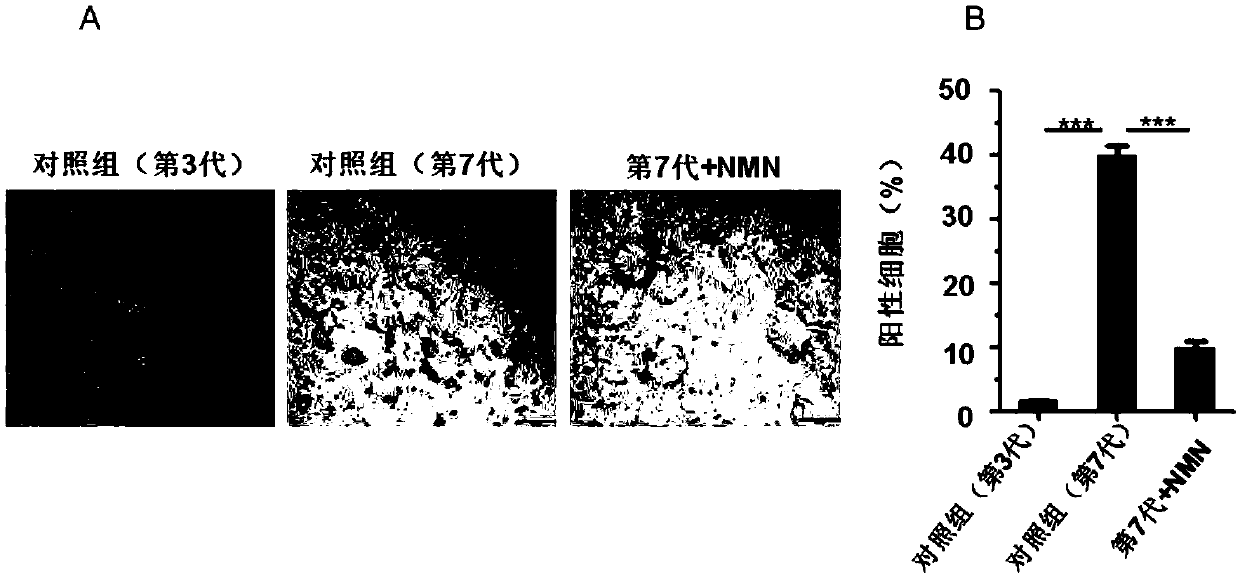
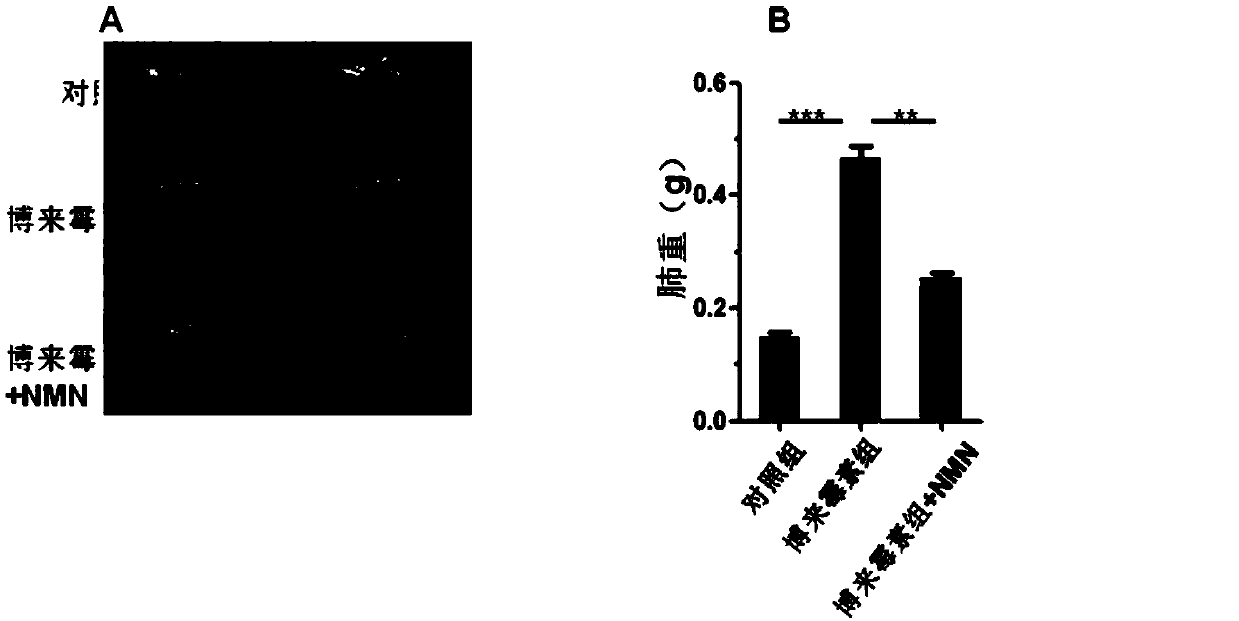
Use of beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide or precursor thereof in preparation of medicament for delaying lung aging
PendingCN109674808AAnti agingReduced lung functionOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderDiseaseNicotinamide mononucleotide
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedicine, and particularly relates to a use of a beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide or a precursor thereof in the preparation of a medicament for delaying lung aging. In the prior art, there is no study of supplementation of the beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide or the precursor thereof and reduction of an age-related lung function. In the invention,a mouse model of lung aging is constructed to find, for the first time, that lung aging, especially alveolar epithelial cell aging, can be delayed by adding the beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide or the precursor thereof, and the use of the beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide or the precursor thereof in the preparation of the medicament for delaying the lung aging is provided. The invention provides anew way for delaying the lung aging and delaying the reduction of the lung function, and provides a new treatment basis for preventing or treating related lung diseases caused by the lung aging, which has a broad prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Application of hesperidin in preparation of medicament for preventing and/or treating pulmonary fibrosis diseases
InactiveCN104906120APrevent proliferationInhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderDiseaseBiological activation
The invention discloses an application of hesperidin in preparation of a medicament for preventing and / or treating pulmonary fibrosis diseases. By virtue of experimental verification, the hesperidin can achieve an effect of preventing and treating pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting lung fibroblast proliferation, inhibiting epithelium-mesenchyme conversion of alveolar epithelial cells and inhibiting lung fibroblast activation, so that the hesperidin can achieve a new application in preparation of the medicament for preventing and / or treating the pulmonary fibrosis diseases. The application relates to various medicament dosage forms such as capsules, drop pills, aerosol preparations, spraying agents, tablets, granules and injections prepared from the hesperidin. Moreover, the application also relates to a composition, which is formed by taking the hesperidin as a main component, for preventing and treating the pulmonary fibrosis.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Application of thyroxine receptor analogues and salts or predrugs thereof to preparation of pulmonary disease treating and/or preventing drugs
InactiveCN107469086AEffective protectionPromote maturityOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderTherapeutic effectLung tissue
The invention provides a novel application of thyroxine receptor analogues and pharmaceutically acceptable salts or predrugs thereof which are used for treating and / or preventing pulmonary diseases. The thyroxine receptor analogues and the pharmaceutically acceptable salts or predrugs thereof can effectively protect alveolar epithelial cells, adjust synthesis, storage and distribution of surface proteins of the alveolar epithelial cells, promote maturation, differentiation and integrity of the alveolar epithelial cells, are beneficial to elimination of hydrops in the lung, promote recovery of damaged mitochondria in the alveolar epithelial cells and enhance bio-synthesis of the mitochondria, so that repair of damaged lung tissue is facilitated, pulmonary fibrosis is stopped and reversed, immunoreaction is regulated, a cancerization environment is changed, pulmonary diseases are prevented and treated, pulmonary functions such as gas exchange and the like are improved, and the treatment effect is realized.
Owner:深圳市润佳通科技有限公司
Traditional Chinese medicine composition and application thereof to preparation of drugs for treating pulmonary fibrosis diseases
The invention relates to a constitution and preparing method of a traditional Chinese medicine composition and application thereof to preparation of drugs for treating pulmonary fibrosis diseases. The composition is composed of radix astragali, radix codonopsis, radix ophiopogonis, fructus schizandrae, radix notoginseng, thunberg fritillary bulb, rhizoma anemarrhenae and licorice roots. The composition can regulate the expression of short-chain non-coding RNA (miRNAs) and long-chain non-coding RNA (incRNA), and can protect alveolar epithelial cells and interfere with the activity of myofibroblasts, so that the process of pulmonary fibrosis can be inhibited. Therefore, the composition is expected to be well applied to preparation of drugs for treating pulmonary fibrosis diseases.
Owner:BINZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
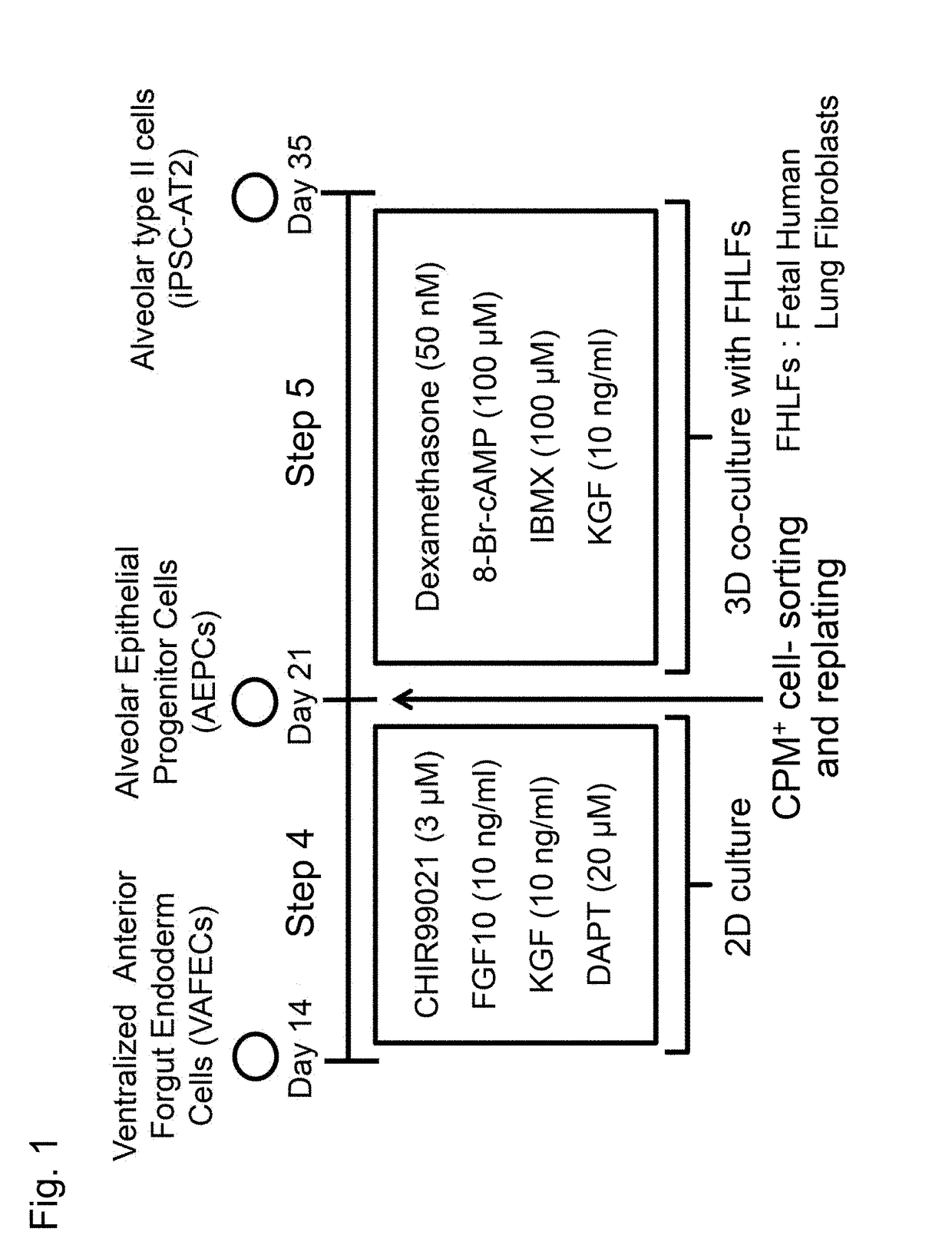
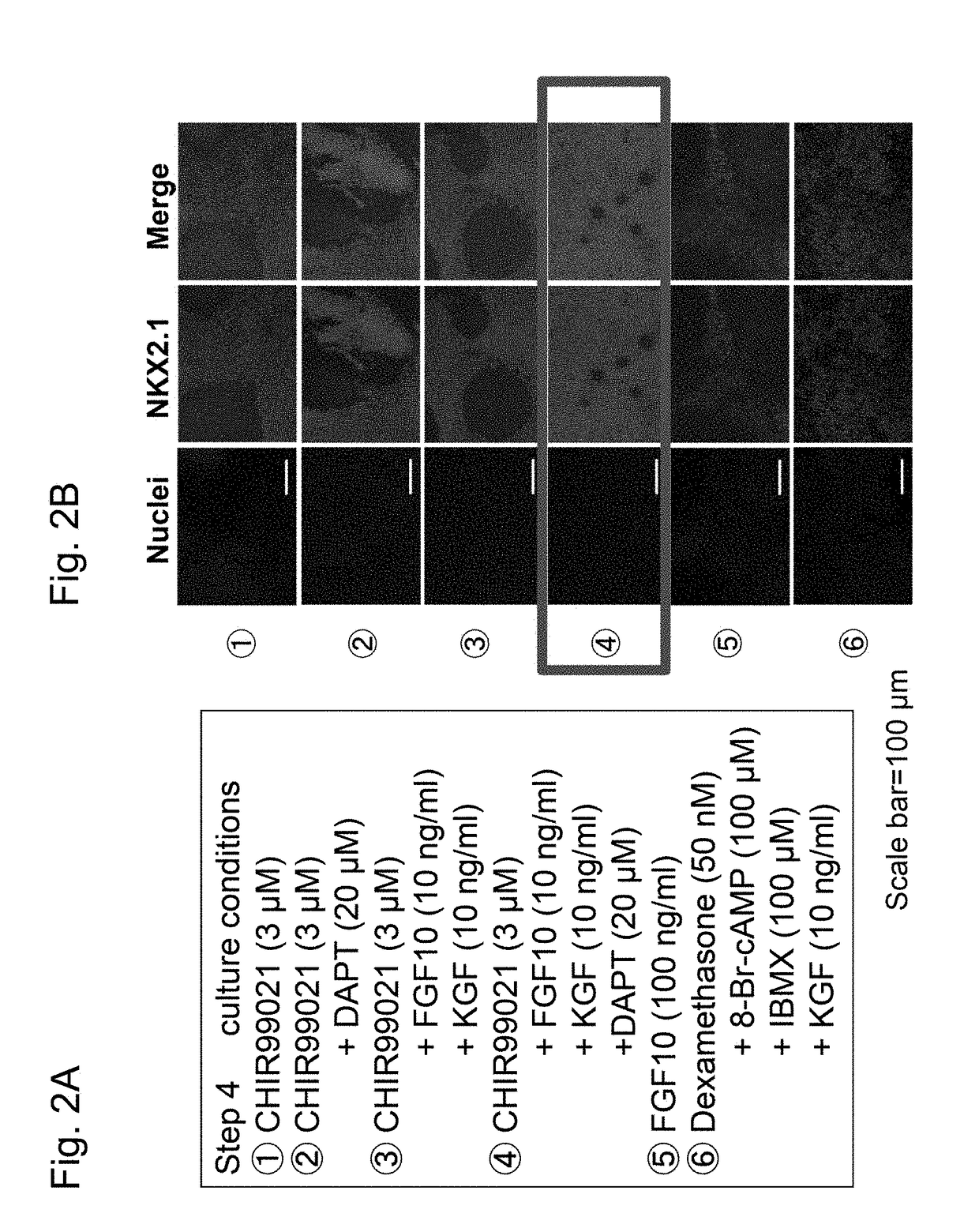
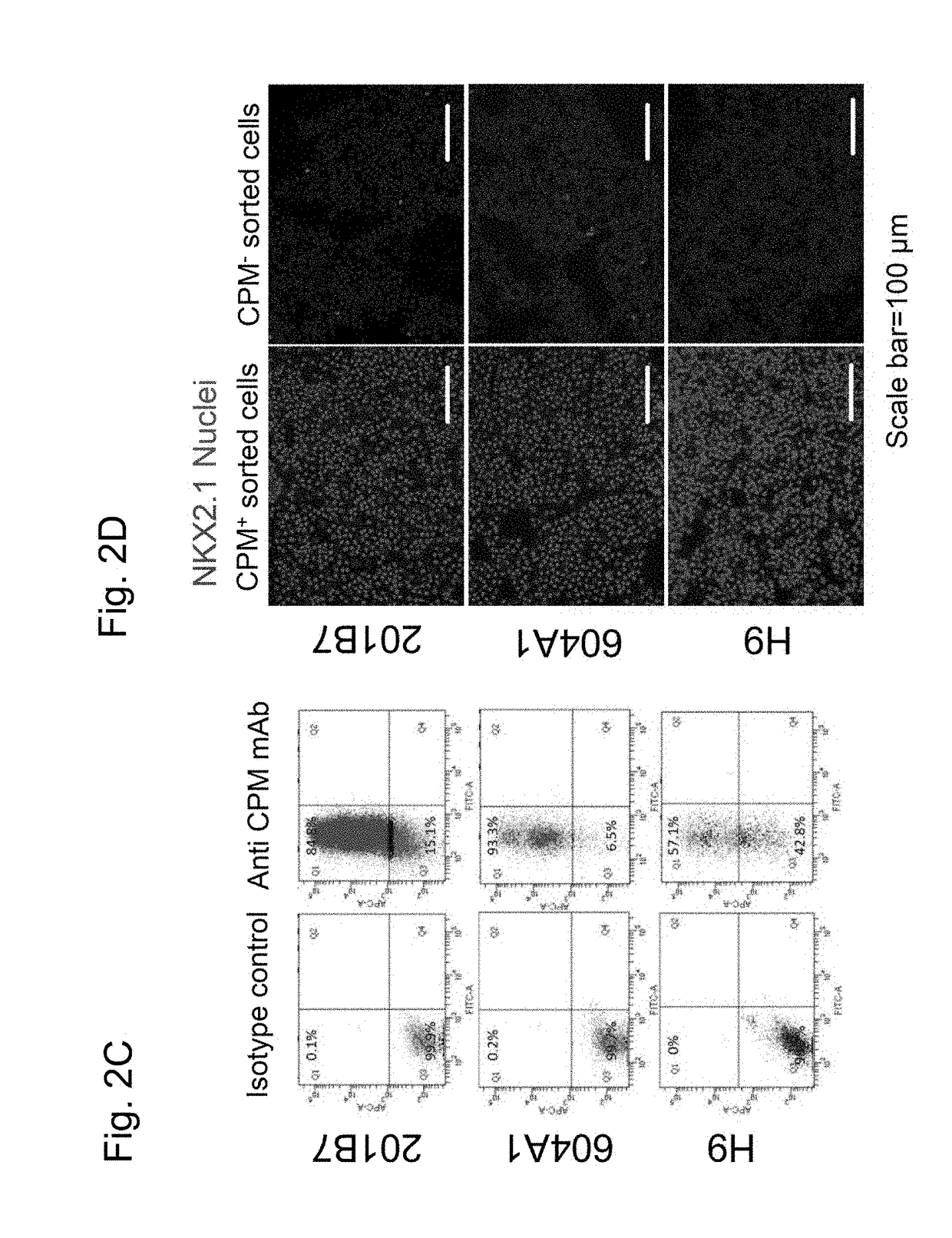
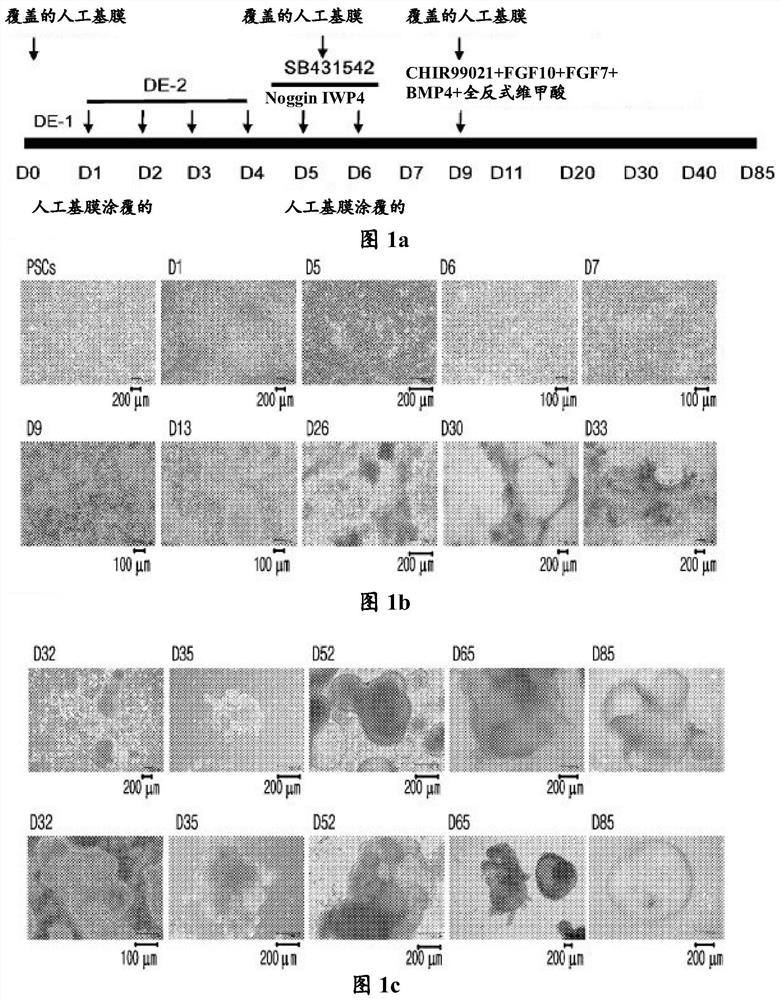
Method for inducing differentiation of alveolar epithelial cells
ActiveUS20180051256A1Artificial cell constructsCell culture active agentsPluripotential stem cellProgenitor
This invention provides a method for stably producing type II alveolar epithelial cells from pluripotent stem cells. Specifically, the invention relates to a method for producing type II alveolar epithelial cells from pluripotent stem cells comprising steps of: (1) culturing pluripotent stem cells in a medium containing activin A and a GSK3β inhibitor; (2) culturing the cells obtained in Step (1) in a medium containing a BMP inhibitor and a TGFβ inhibitor; (3) culturing the cells obtained in Step (2) in a medium containing BMP4, retinoic acid, and a GSK3β inhibitor; (4) culturing the ventral anterior foregut cells obtained in Step (3) in a medium containing a GSK3β inhibitor, FGF10, KGF, and a NOTCH signal inhibitor; and (5) subjecting the alveolar epithelial progenitor cells obtained in Step (4) to three-dimensional culture in a medium containing a steroid drug, a cAMP derivative, a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, and KGF.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
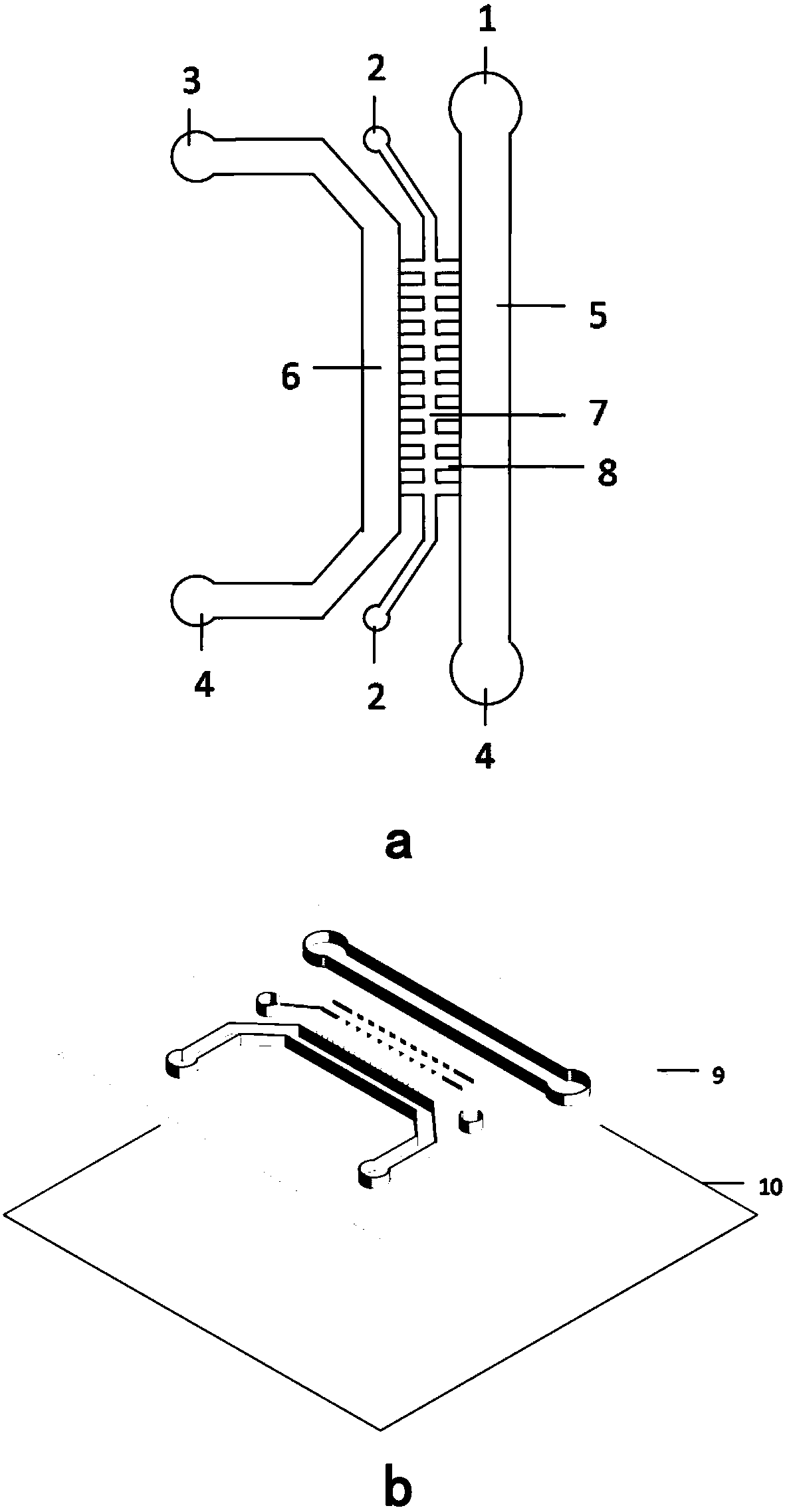
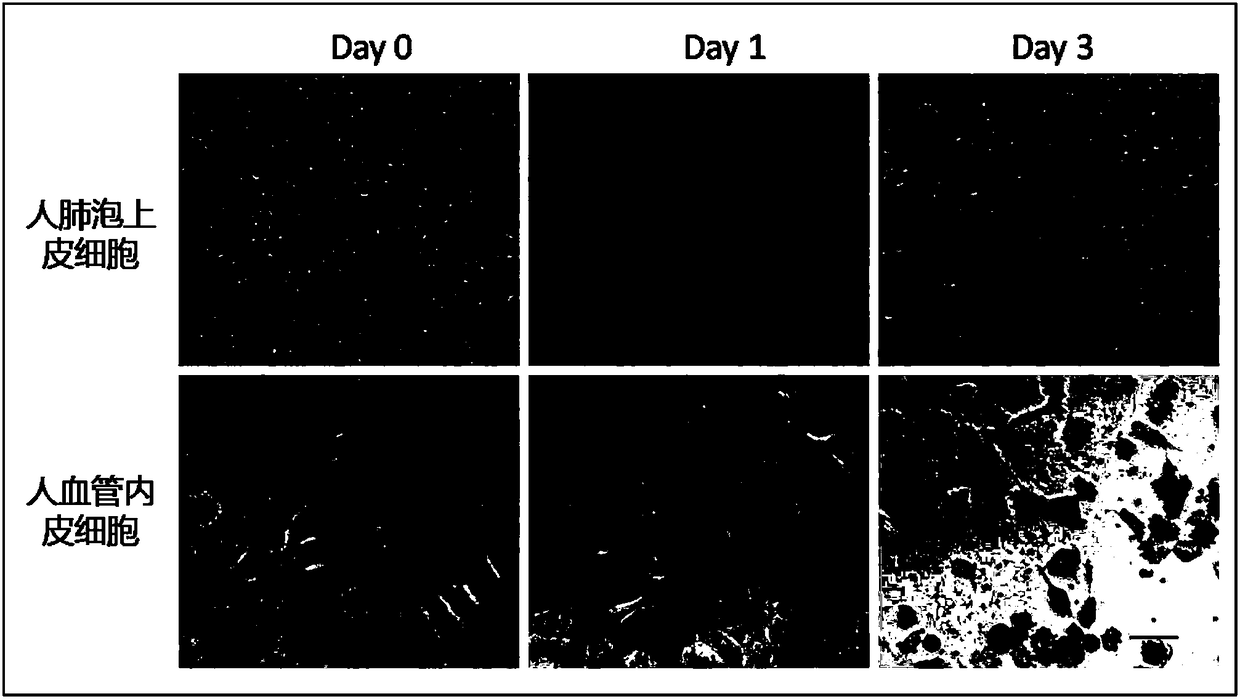
Method for evaluating lung injury caused by nanoparticles based on organ-on-a-chip technology
ActiveCN108117989AEasy to moveSimulate mobileMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue screeningEndothelial cell cultureVascular endothelium
The invention provides a method for evaluating lung injury caused by nanoparticles based on organ-on-a-chip technology. A chip is mainly prepared by bonding and sealing an upper PDMS layer and a lowerPDMS layer and comprises a matrix inlet pool, two cell inlet pools, a waste liquid pool, a cell culture chamber and a matrix chamber. The chip is vertically inoculated with vascular endothelial cellsand alveolar epithelial cells separately, and culture is carried out for a certain period of time so as to form a lung air-blood barrier. Nanometers are added into an alveolar epithelial cell culturechamber, and monocytes are added into a vascular endothelial cell culture chamber in the manner of perfusion to simulate monocytes in the circulating blood of people, so an in-vitro nanoparticle lunginjury evaluation model is established. The nanoparticle lung injury evaluation model based on the chip can simulate the injury of the nanoparticles to the lung air-blood barrier, monitors destroy tothe integrity of the barrier in real time, realizes observation of the responses of two types of cells of the air-blood barrier, and traces the motion of the monocytes in real time.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Primary culture method for alveolar epithelial cells of Microhyla ornata
InactiveCN108774629AConducive to survivalAvoid damageCell dissociation methodsEpidermal cells/skin cellsMicrohyla ornataCell culture media
The invention discloses a primary culture method for alveolar epithelial cells of Microhyla ornata. The primary culture method comprises the following steps: subjecting adult Microhyla ornate to surface sterilization; dissecting the adult Microhyla ornate, taking out the lung and carrying out cleaning with a HBSS balanced salt solution; adding a collagenase I solution for digestion; subjecting a digested solution to refrigeration and centrifugation and adding a complete cell culture medium; blowing and beating the fragments of the lung tissue, and then carrying out filtering by using a cell filter screen with a pore diameter of 100 [mu]m so as to obtain a cell suspension; and subjecting the cell suspension to culture at a constant temperature of 27 DEG C and replacing the previous completecell culture medium with a new complete cell culture medium every 3 to 4 d. The primary culture method of the invention can rapidly and repeatedly establish primary culture of the alveolar epithelialcells of Microhyla ornate; needed cell culture equipment is simple and has good operability; and acquired cells have obviously faster growth speed than the alveolar epithelial cells of mammals. The prepared alveolar epithelial cells of the invention significantly supplement existing alveolar epithelial cells of mammals and provide a novel cell material for research on major biological and medicalproblems such as terrestrial adaptability, lung development, pulmonary fibrosis and tuberculosis.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
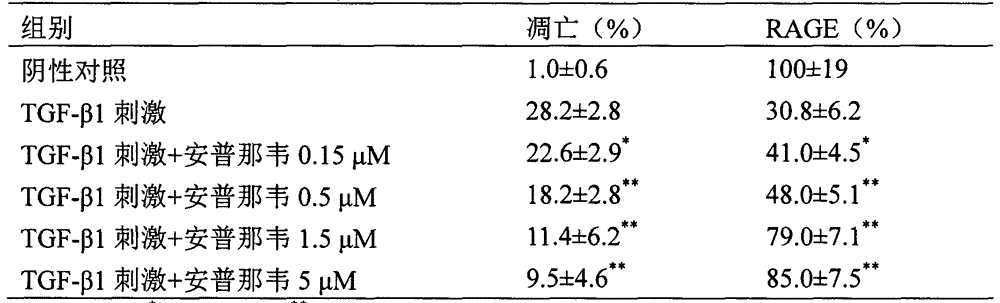
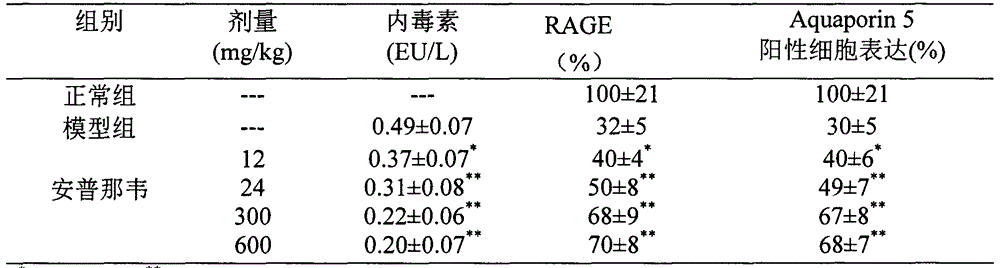
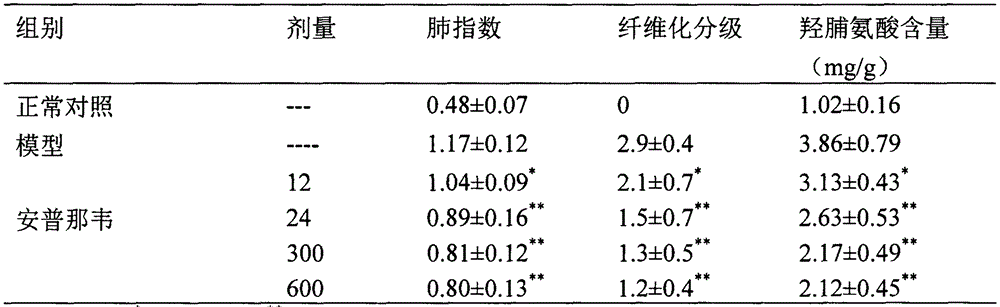
Use of amprenavir in preparation of medicines for preventing or treating acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome and pulmonary fibrosis
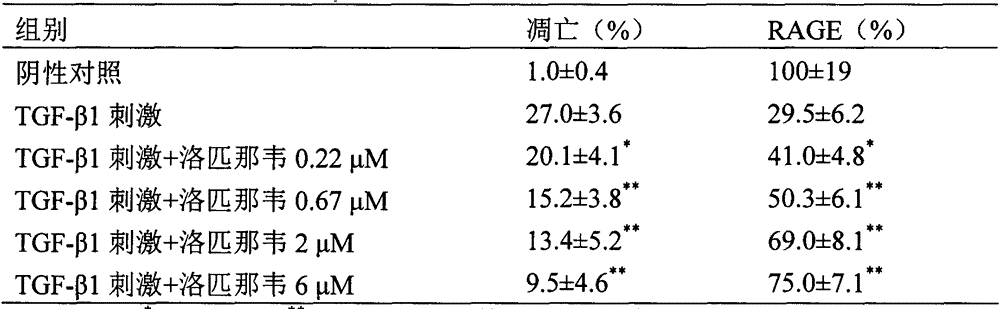
The invention provides a new medical use of amprenavir and specifically relates to a use of the amprenavir for inhibiting the apoptosis of type I alveolar epithelial cells, promoting the expression of the receptor for advanced glycation endproducts of the type I alveolar epithelial cells, further inhibiting the occurrence and development of the ALI / ARDS and the pulmonary fibrosis and finally preventing or treating acute lung injury / acute respiratory distress syndrome (ALI / ARDS) and pulmonary fibrosis. In the use, the dosage of the amprenavir ranges from 120mg to 6000mg, preferably from 240mg to 3000mg.
Owner:BINZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
Fluorescent diagnosis and treatment reagent development for diagnosing and treating non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and application of cells thereof
InactiveCN105732681AEarly and Rapid DiagnosisEarly and rapid curativeOrganic active ingredientsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsCancer cellFluorophore
The invention relates to a fluorescent probe for quickly diagnosing and accurately treating non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), particularly fluorine boron pyrrole compounds and application thereof. The fluorine boron pyrrole compounds are disclosed as General Formula I, and are used as the fluorescent probe for diagnosing and treating NSCLC. The fluorophore and lung cancer cells are used for locating the label of the ligand, and the probe can specifically select the NSCLC cells. The overexpressed glutathione in the lung cancer cells breaks the disulfide bond in the probe, the drugs can be slowly released in the cancer cells to generate the target treatment effect, and meanwhile, near-infrared fluorescence can be emitted, thereby generating the double effects of diagnosis and treatment. The fluorescent probe can trace the alveolar epithelial cells with pathological changes at high sensitivity, and can release the drugs to the cancer tissues in a more accurate mode, thereby lowering the general untoward effects of the drugs and enhancing the living quality of the patient. The research has important biomedical meanings for the diagnosis and treatment modes of NSCLC and the research of the drug-resistance mechanism of the NSCLC cell strain.
Owner:BINZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
Pulsatilla chinensis extract and application thereof to preparation of drugs for preventing and treating pulmonary fibrosis
ActiveCN104983814AIt has the effect of preventing and treating pulmonary fibrosisHas potentialRespiratory disorderPlant ingredientsFibroblastMedicine
The invention discloses a pulsatilla chinensis extract and application thereof to the preparation of drugs for preventing and treating pulmonary fibrosis. The pulsatilla chinensis extract uses pulsatilla chinensis as a raw material and is prepared through the following steps: firstly, adding ethanol for extraction, concentrating the obtained extracting solution until an extractum is obtained, and then extracting, concentrating and drying the extractum sequentially to obtain pulsatilla chinensis total saponins; adding distilled water into the residue after extraction, decocting and extracting, concentrating the extracting solution until an extractum is obtained, and then treating the extractum to obtain pulsatilla chinensis polysaccharide; mixing the pulsatilla chinensis total saponins with the pulsatilla chinensis polysaccharide uniformly to obtain the final pulsatilla chinensis extract. Through experimental verification, the pulsatilla chinensis extract can prevent the formation and development of pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the proliferation of lung fibroblast and the transformation of alveolar epithelial cells to mesenchymal cells, so that the pulsatilla chinensis extract achieves new application to the preparation of drugs for preventing and treating pulmonary fibrosis.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Reversion pulmonary fibrosis nano preparation and preparation method thereof
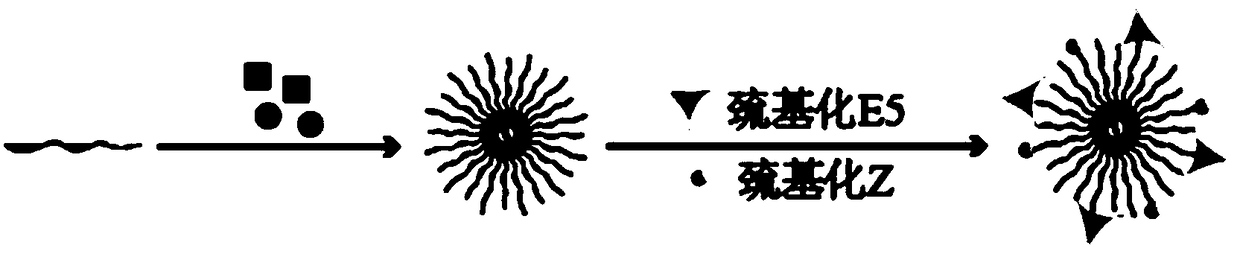
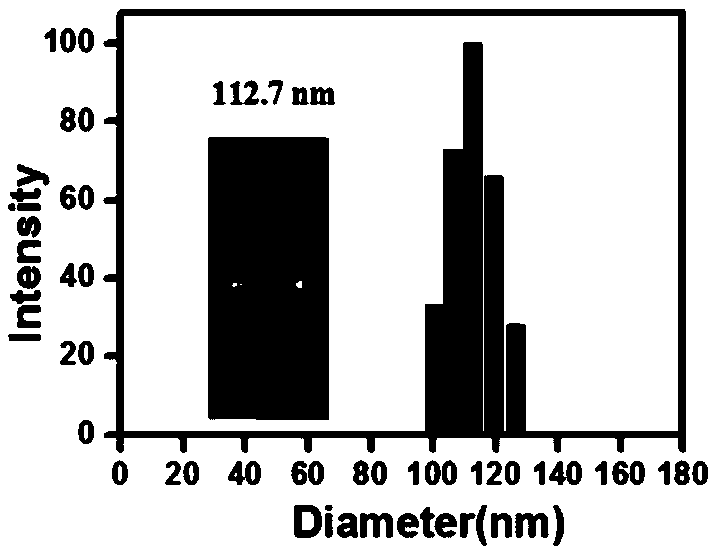
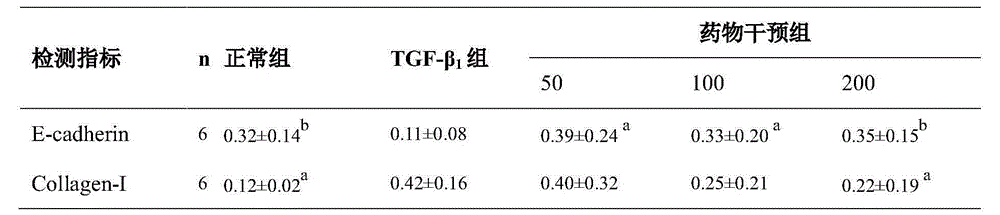
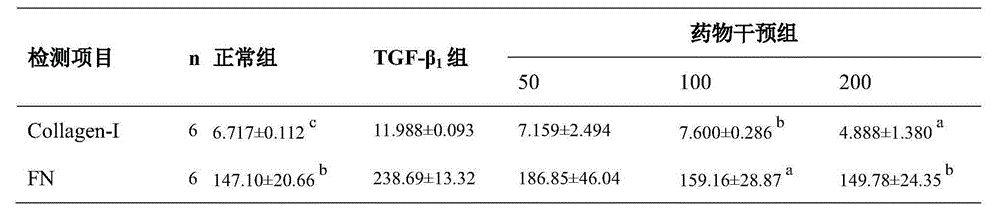
ActiveCN109432047AWrapper implementationAchieve specific targetingOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderCXCR4Oxidative stress
The invention discloses a reversion pulmonary fibrosis nano preparation and a preparation method thereof, and relates to a synthetic E5 and polypeptide Z modified nano preparation and a carrier thereof. The nano preparation is capable of, through E5 targeted circulation fibrocyte CXCR4, CCR2 and CCR7 acceptors, reaching a pulmonary fibrosis injured part in a fixed point, and avoiding from being packaged and cleared by in-vivo macrophages and proteins; and through polypeptide Z, specific-targeting alveolar epithelial cells II of a high-expression integrin acceptor AlphavBeta6, and efficiently targeting and delivering the nano preparation. The nano preparation contains an anti-oxidant and / or a fibroblast activation inhibitor. A purpose of reversing pulmonary fibrosis is achieved by controlling an alveolar epithelial cell II oxidative stress level and inhibiting fibroblast activation double-channel control.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Tree peony bark extract and application thereof to preparation of medicines for treating pulmonary fibrosis
ActiveCN104983816AIt has the effect of preventing and treating pulmonary fibrosisRespiratory disorderPlant ingredientsBiological activationAlveolar epithelial cell
The invention discloses a tree peony bark extract and application thereof to preparation of medicines for treating pulmonary fibrosis. At first, tree peony bark is extracted, and after that, pH value adjustment and heating for enzymolysis are carried out; after enzymolysis, the distillate is collected by the steam distillation method, left to stand and filtered to obtain crystal paeonol; the residual extracting solution and the leaves are filtered, and the herb residues are left for later use; the filtrate is subjected to concentration under reduced pressure and deproteinization, then ethanol is added, the mixture is left to stand, the ethanol solution is separated and collected for later use, and the sediment is washed to obtain cortex moutan polysaccharide; the stand-by ethanol solution is added into the stand-by herb residues for soaking and filtering, and the filtrate is subjected to concentration under reduced pressure and purification to obtain total glucosides of cortex moutan; the paeonol, the polysaccharide and the total glucosides are mixed to obtain the tree peony bark extract. Experimental results show that the tree peony bark extract can effectively inhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transition and lung fibroblast activation of alveolar epithelial cells so as to prevent pulmonary fibrosis from formation and development, and can be applied to preparation of medicines for treating pulmonary fibrosis.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
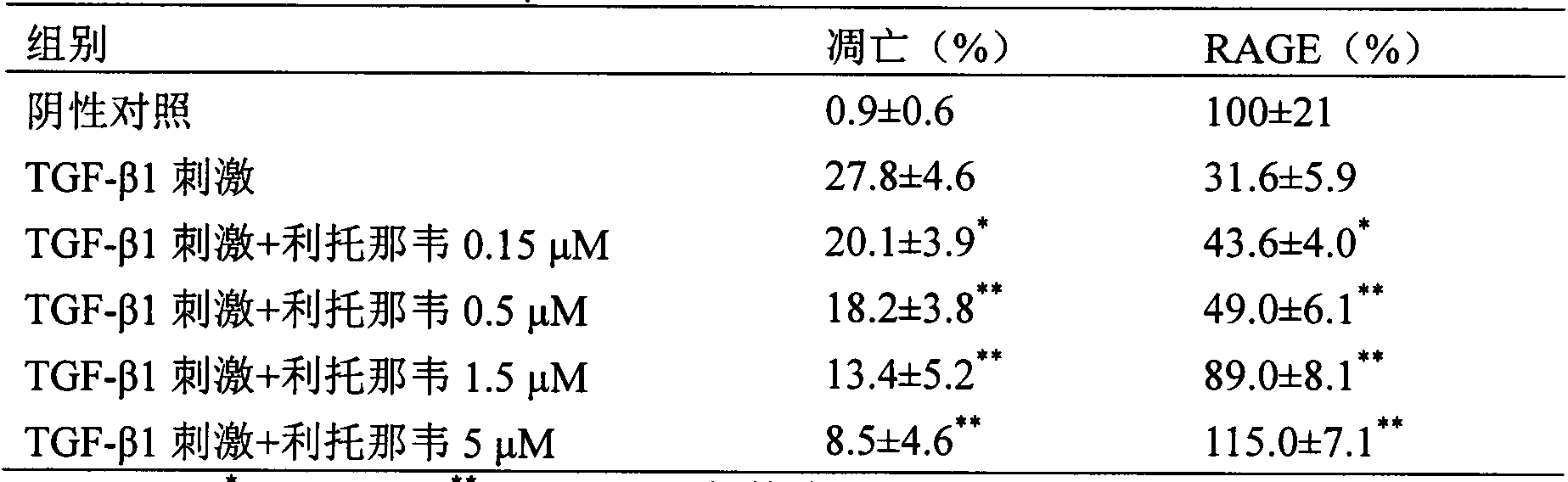
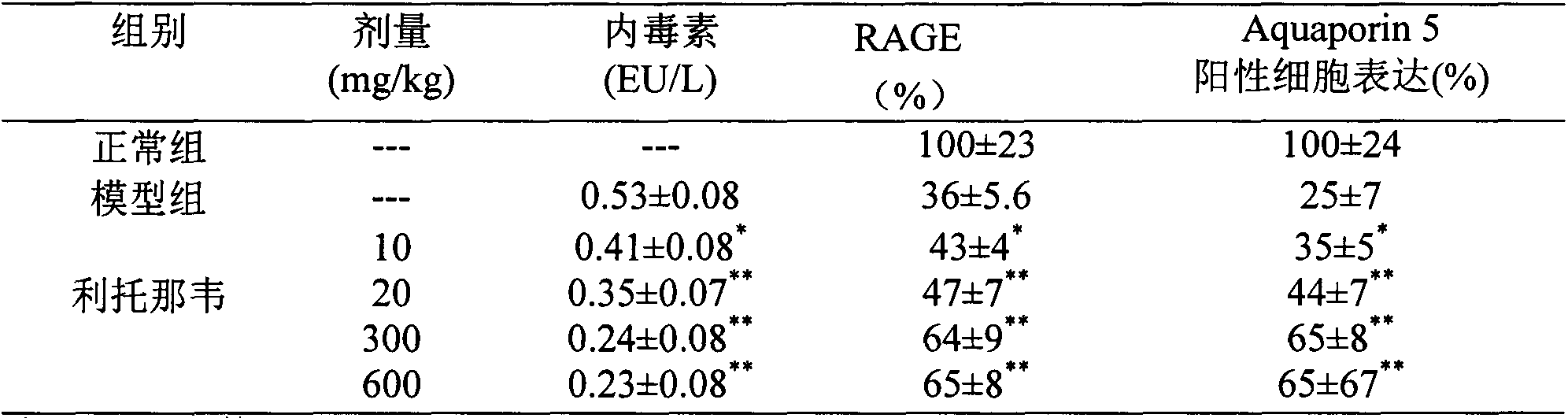
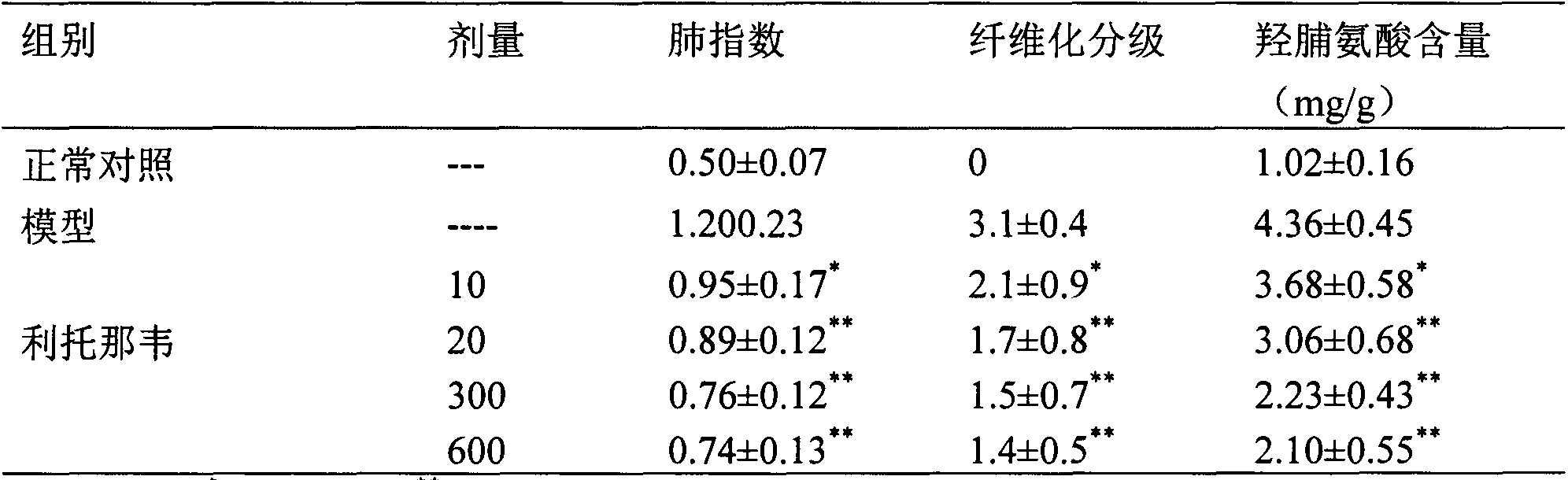
Application of ritonavir in preparing medicines for preventing or treating acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome and pulmonary fibrosis
InactiveCN104069104AOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderApoptosisARDs - Acute respiratory distress syndrome
The invention provides a new medical application of ritonavir and in particular relates to an application of the ritonavir for preventing or treating Acute Lung Injury / Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ALI / ARDS) and pulmonary fibrosis in such a manner of inhibiting the occurrence and development of the ALI / ARDS and the pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the apoptosis of type I alveolar epithelial cells and promoting the expression of the Receptor For Advanced Glycation Endproducts (RAGE) of the type I alveolar epithelial cells. When in use, the oral administration dosage of the ritonavir ranges from 100mg to 6000mg, preferably, from 200mg to 3000mg.
Owner:BINZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
Method for fabrication of three-dimensional lung organoid comprising human stem cell-derived alveolar macrophage
PendingCN112805368AEfficient developmentArtificial cell constructsCell culture supports/coatingDiseaseLung alveolus
The present invention relates to a method for fabrication of a three-dimensional lung organoid comprising human stem cell-derived alveolar macrophages. Specifically, a lung organoid is fabricated by co-culturing cells not expressing the definitive endoderm marker CRCX4 according to a fabrication method of the present disclosure. The lung organoid comprises type 1 and type 2 alveolar epithelial cells as well as alveolar macrophages and realizes infectious or inflammatory responses unlike conventional lung organoids that contain no immune cells and as such, can be advantageously used in studying mechanisms of related lung diseases, excavating biomarkers, developing therapeutic agents, and so on.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF CHEM TECH
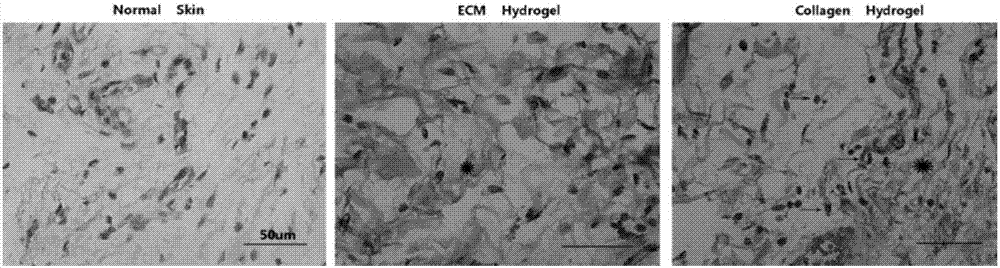
Preparation method and application of lung matrix hydrogel and medicine
InactiveCN107496459ASensitive to temperatureEasy to useAerosol deliveryDigestive systemSide effectApoptosis
The invention provides a preparation method and application of lung matrix hydrogel and a medicine, and aims to solve the problem that no effective medicine is available to adjust and control apoptosis process of alveolar epithelial cells in APALI in the existing clinical application. The preparation method and application of lung matrix hydrogel comprises the following steps: crushing acellular lung tissues of a rat; then, adding into a hydrochloric acid-pepsin solution for dissolving; adding sodium hydroxide and PBS into the solution for adjusting to a physiological state; placing at 37 DEG C until the lung matrix hydrogel is formed; the lung matrix hydrogel prepared by the preparation method of the lung matrix hydrogel is applied to treatment of lung injury following severe acute pancreatitis; a medicine for treating the lung injury following severe acute pancreatitis comprises the lung matrix hydrogel prepared by the preparation method of the lung matrix hydrogel. When the lung matrix hydrogel prepared in the invention is used for preparing the medicine for treating the lung injury following severe acute pancreatitis, the medicine has an effect of adjusting and controlling the apoptosis process of alveolar epithelial cells in APALI, has low immunogenicity and substantially has no side effects.
Owner:中国人民解放军西部战区总医院
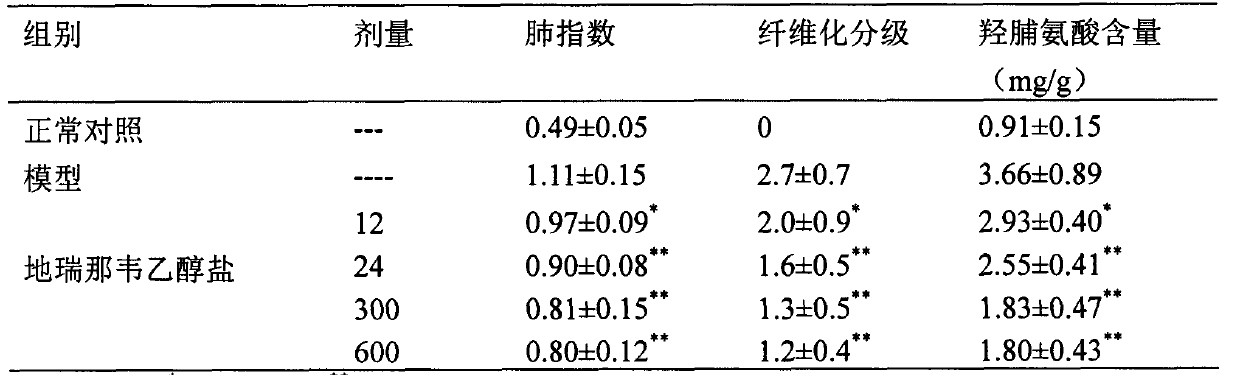
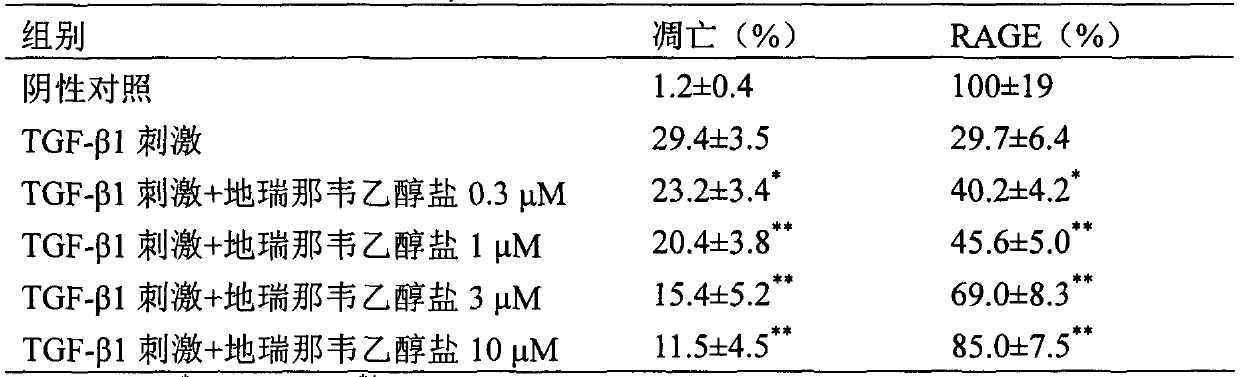
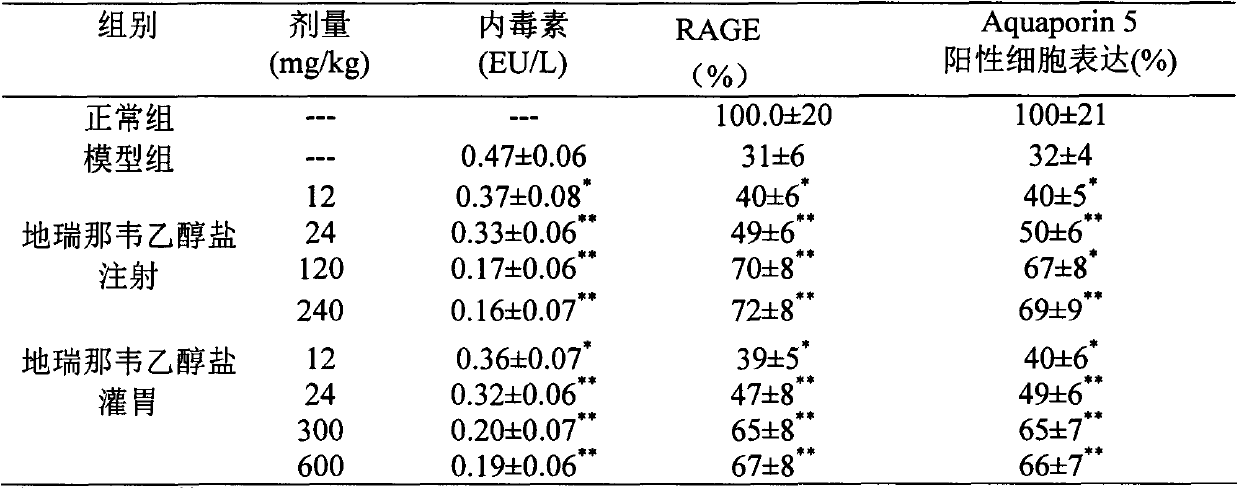
Application of darunavir ethanolate in preparing medicine for preventing or treating acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome and pulmonary fibrosis
InactiveCN103989689AOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderARDs - Acute respiratory distress syndromeAlveolar epithelial cell
The invention provides novel use of a medicine darunavir ethanolate and particularly relates to an application of darunavir ethanolate for preventing or treating genesis and development of acute lung injury / acute respiratory distress syndrome (ALI / ARDS) and pulmonary fibrosis so as to prevent or treat ALI / ARDS and pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting I type alveolar epithelial cells of alveolar epithelial cells and promoting expression of receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) of the I type alveolar epithelial cells. According to the application, the injection dosage range is 120-2400mg, preferably 240-1200mg. The oral dosage range is 120-600mg, preferably 240-3000mg.
Owner:BINZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
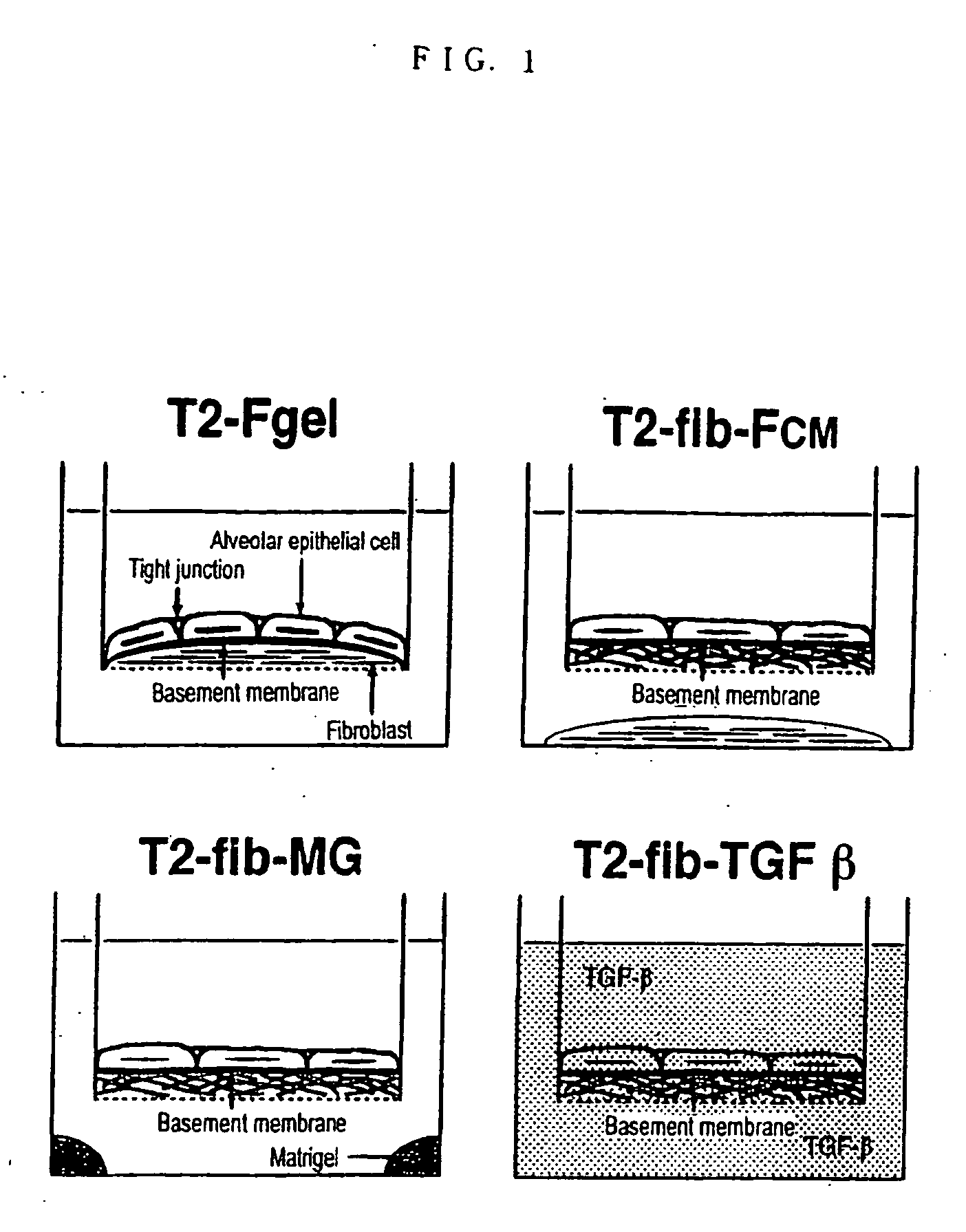
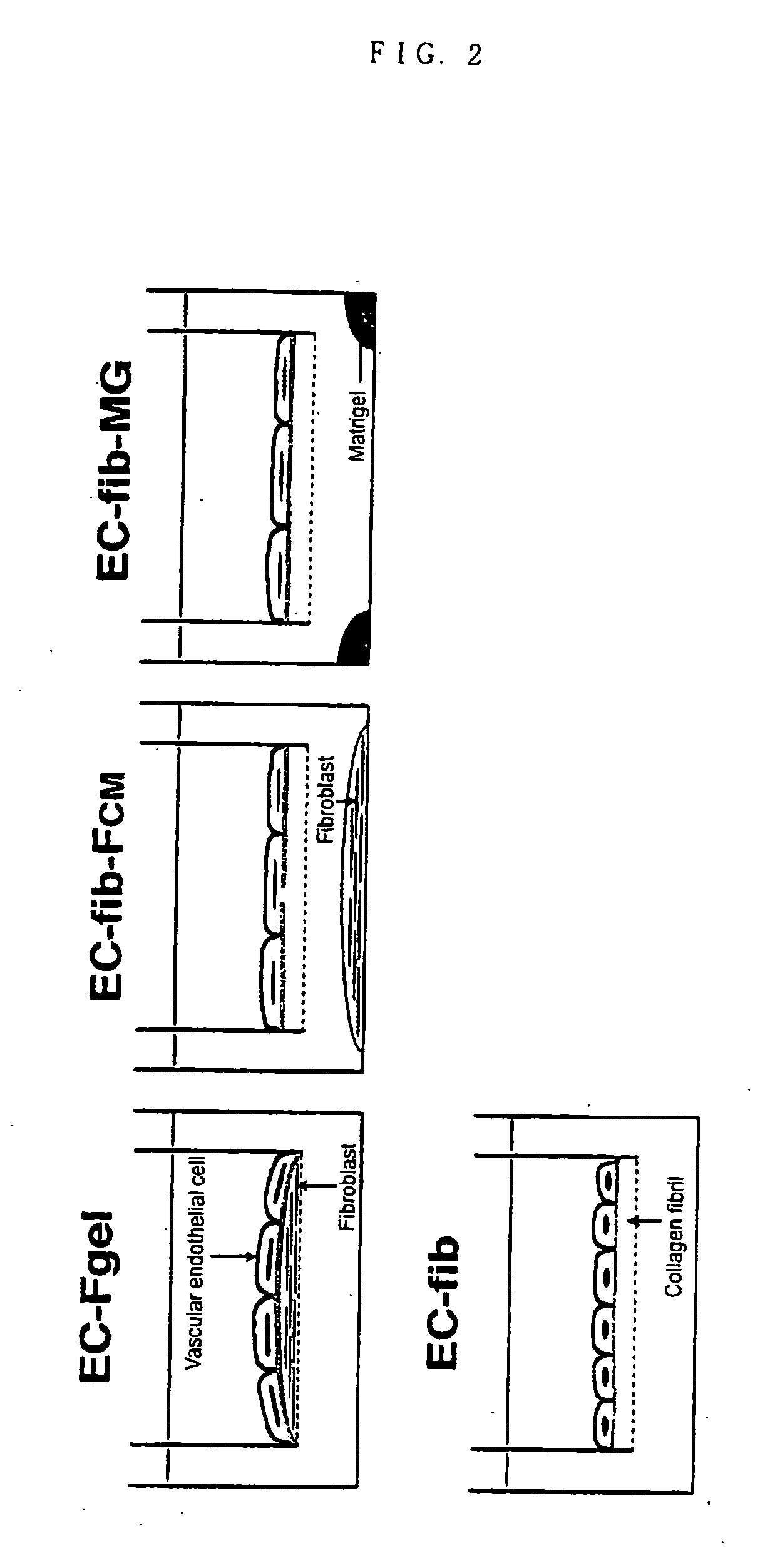
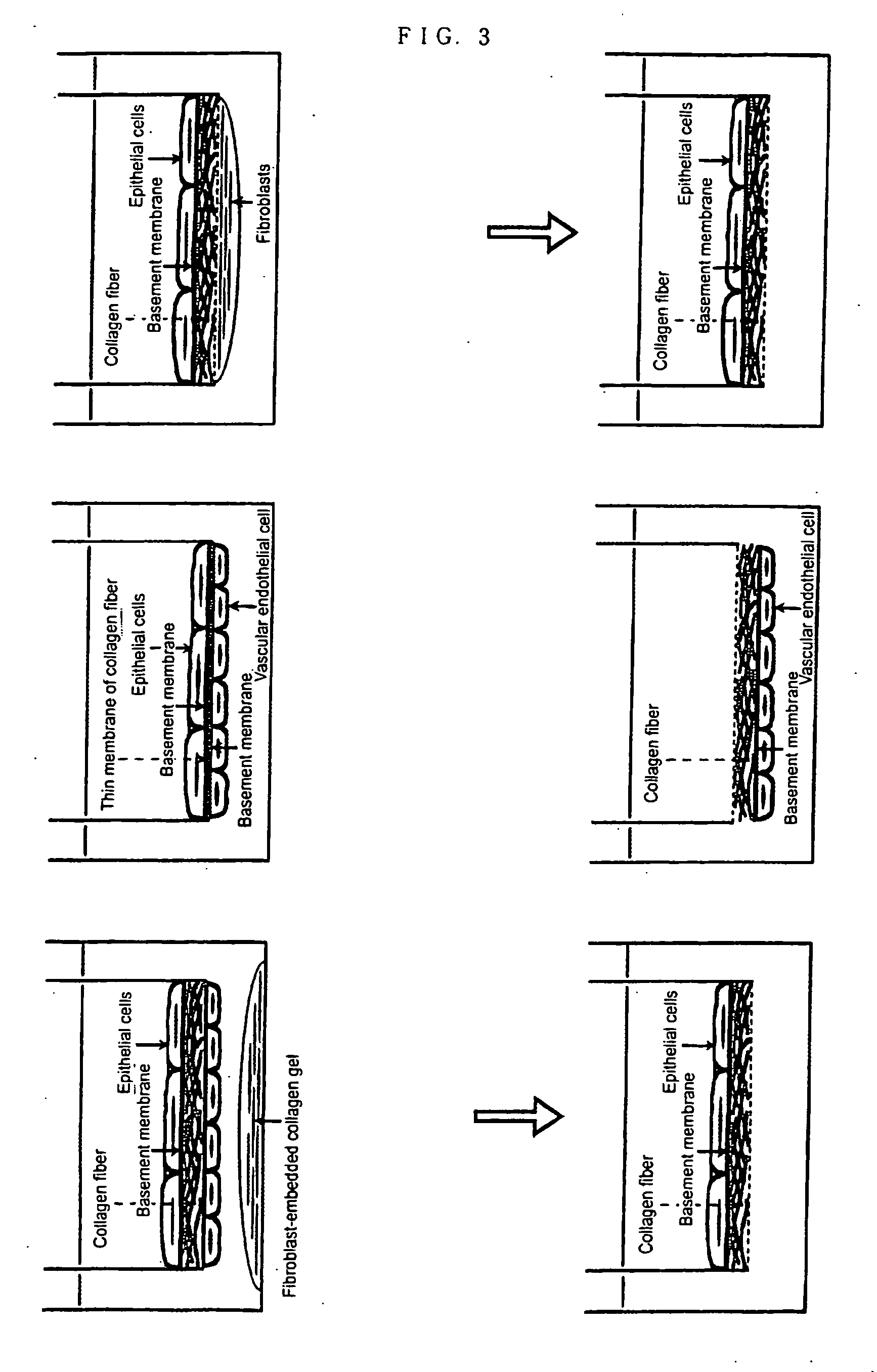
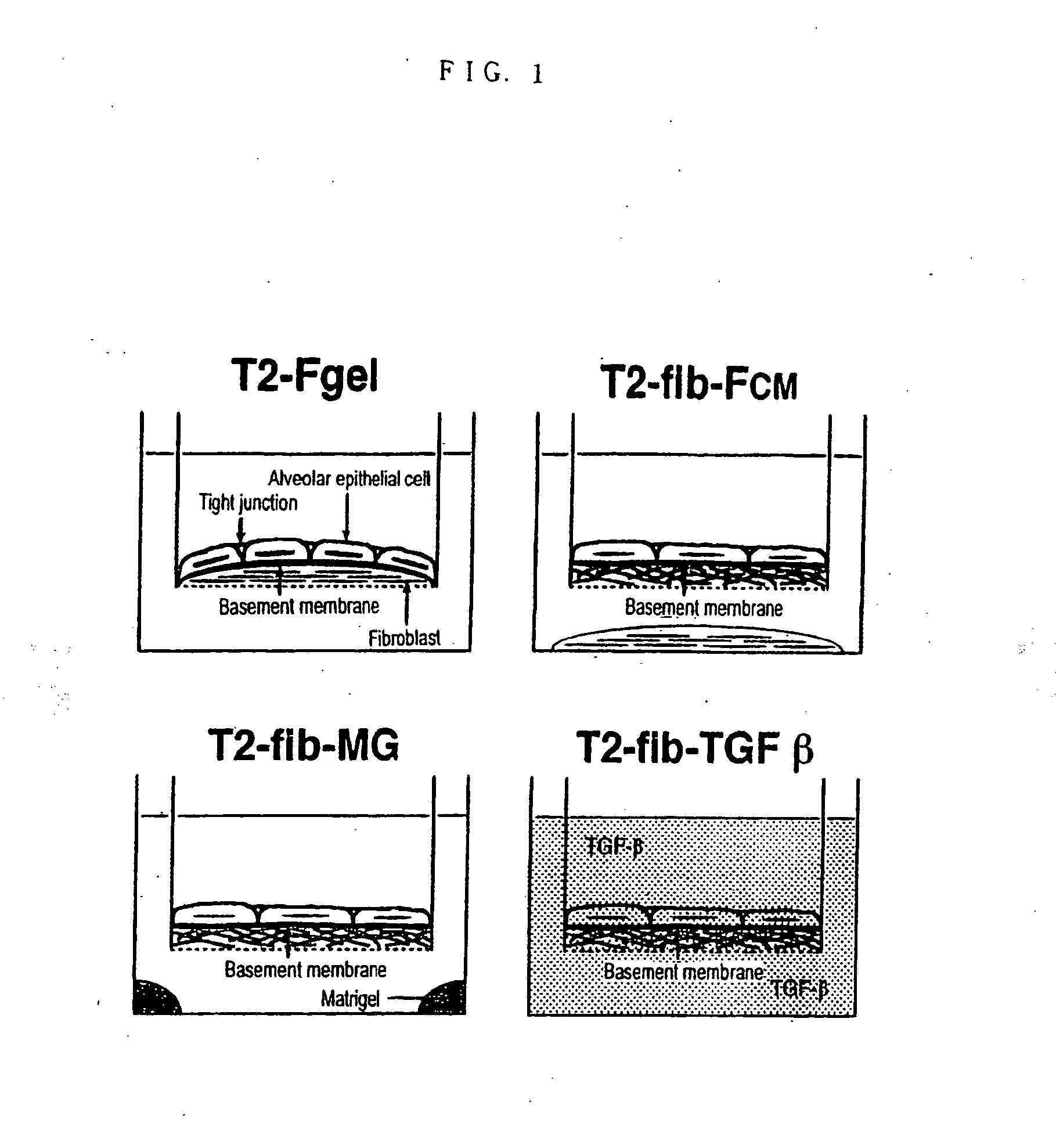
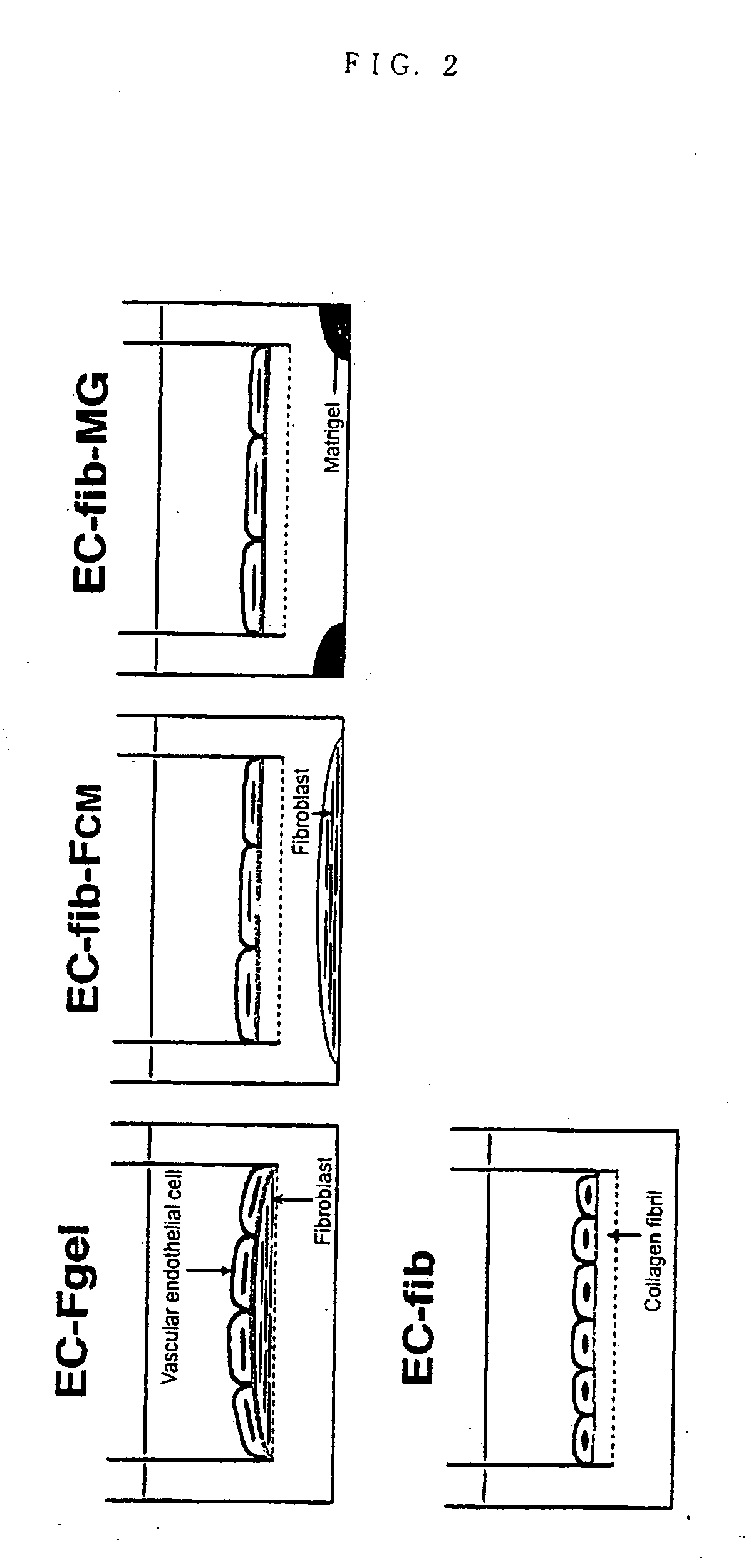
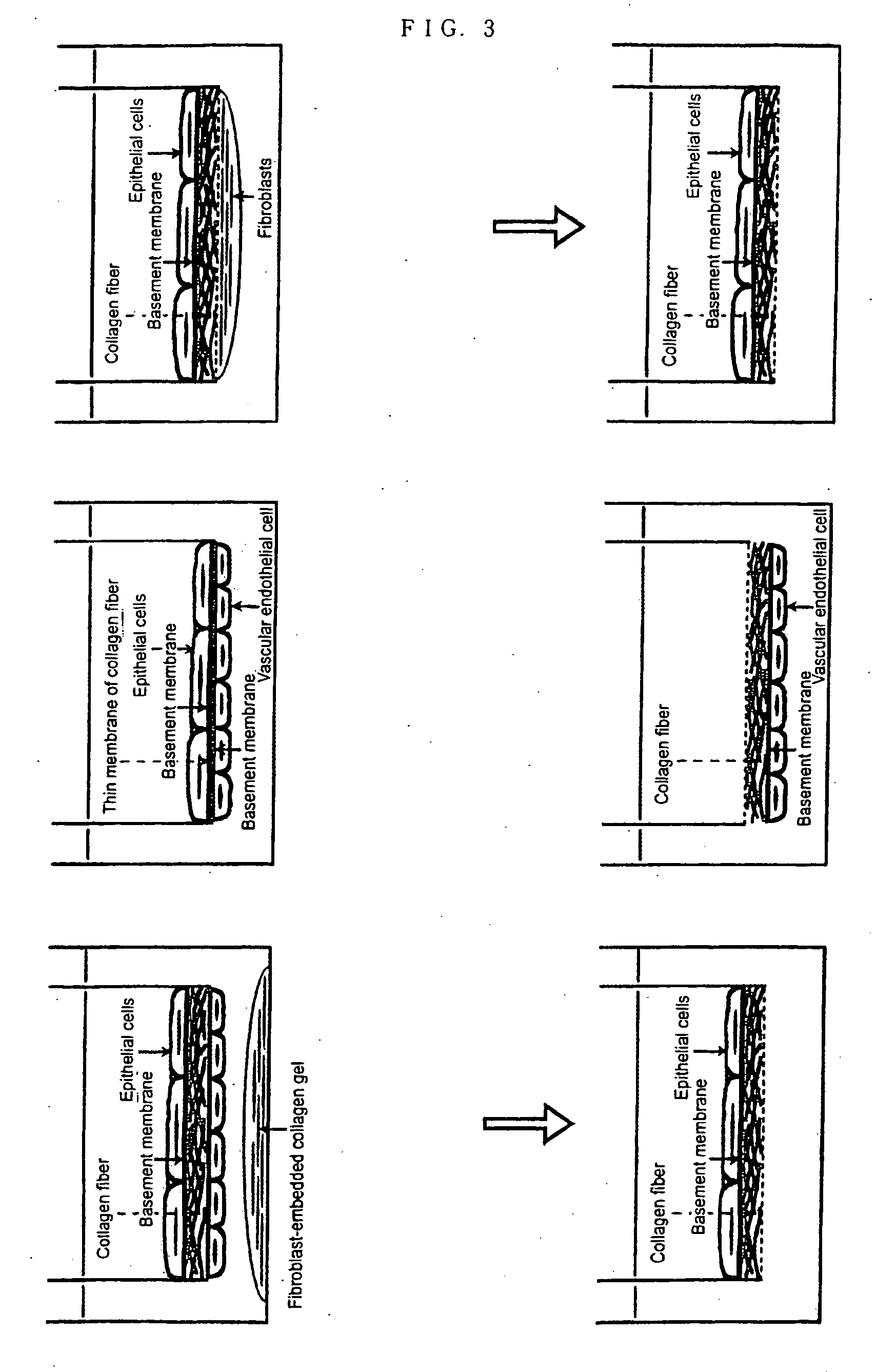
Method of preparing basement membrane, method of constructing basement membrane specimen, reconstituted artificial tissue using the basement membrane specimen and process for producing the same
The object of the present invention is to provide the following: a method for preparing a basement membrane which is extracellular matrices having a function to control morphology, differentiation, proliferation, motility, function expression and the like of cells; a method for constructing a specimen of a basement membrane; a process for producing a reconstituted artificial tissue; a basement membrane specimen or an artificial tissue which can be transplanted while maintaining the structure of a basement membrane. A basement membrane having a barrier function is formed by culturing alveolar epithelial cells or vascular endothelial cells on a fibrous collagen matrix coated with a polymer having a sugar chain which can localize a receptor having an activity to accumulate a basement membrane component on the basal surface of the cells having an ability to form a basement membrane. A reconstructed artificial tissue is obtained by seeding and culturing desired homogeneous or heterogeneous cells having an ability to form a basement membrane on the basement membrane specimen constructed by the following process: the cells having an ability to form a basement membrane adhered onto a support structure through a basement membrane are treated with a surface active agent; the lipid component of cells is lysed; the mixture of an alkaline solution and a protease inhibitor is used to lyse the protein remained on the surface of the basement membrane of the cells. A protein support structure is temporarily adhered to plastic surface through an adsorptive polymer by hydrophobic bonding, such as an alternating copolymer of methyl vinyl ether and maleic anhydride, which has a hydrophobic linear carbon skeleton and a functional group which can react with protein in a molecule and a basement membrane specimen or an artificial tissue is formed thereon, then the protein support structure supporting a basement membrane specimen or an artificial tissue is physically exfoliated from plastic surface when desired.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
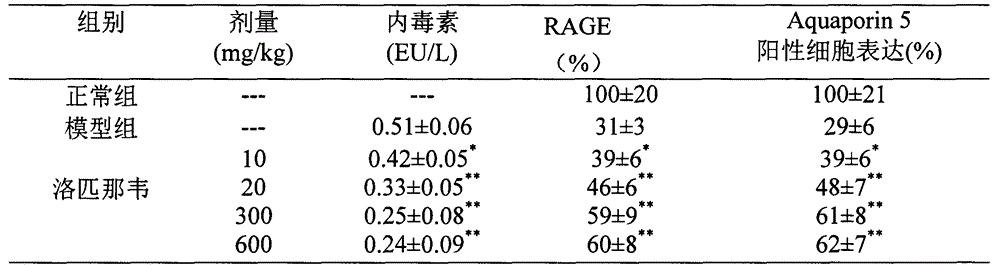
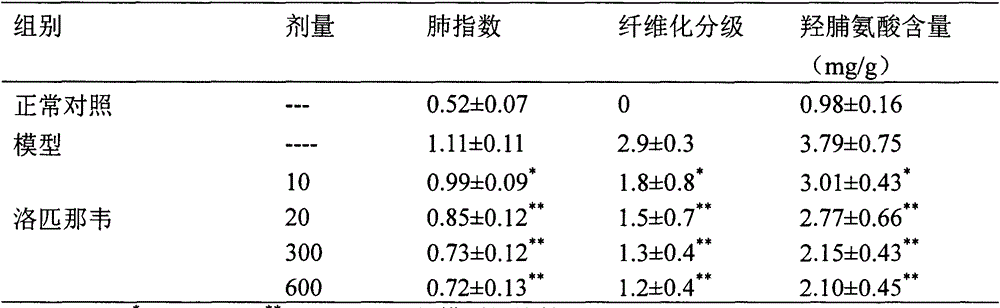
Use of lopinavir in preparation of medicines for preventing or treating acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome and pulmonary fibrosis
InactiveCN104083373AOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderApoptosisARDs - Acute respiratory distress syndrome
The invention provides a new medical use of lopinavir and specifically relates to a use of the lopinavir in preventing or treating acute lung injury / acute respiratory distress syndrome (ALI / ARDS) and pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the apoptosis of type I alveolar epithelial cells, promoting the expression of the receptor for advanced glycation endproducts of the type I alveolar epithelial cells, further inhibiting the occurrence and development of ALI / ARDS and the pulmonary fibrosis and finally preventing or treating ALI / ARDS. In the use, the dosage of the lopinavir ranges from 100mg to 6000mg, preferably from 240mg to 3000mg.
Owner:BINZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
Rat II type primary alveolar epithelial cell extraction method
InactiveCN108823147AImprove digestion efficiencyImprove digestion utilizationCell dissociation methodsArtificial cell constructsBiological cellMedicine
The invention relates to the technical field of biological cell culture, and specifically relates to a rat II type primary alveolar epithelial cell extraction method, which comprises following steps:(1) binding an intravenous infusion needle and a tracheae; (2) rapidly injecting a digestion solution; (3) putting lung tissues into a centrifuge tube; (4) absorbing the digestion solution; (5) slowlyinjecting the digestion solution; (6) reusing the digestion solution; and (7) performing cyclic operation. The primarily added digestion solution is cyclically used, the digestion solution is repeatedly absorbed and injected into a lung to carry out digestion, the amount of digestion solution that is injected into the lung is basically equal to the amount of digestion solution that exudes throughthe lung so as to ensure that the pulmonary alveoli is filled with the digestion solution; the digestion becomes stable, continuous, rapid, and more complete; the total digestion time is largely shortened, the digestion efficiency and utilization rate of the digestion solution are effectively improved; and the yield of II type primary alveolar epithelial cells is increased.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZUNYI MEDICAL COLLEGE
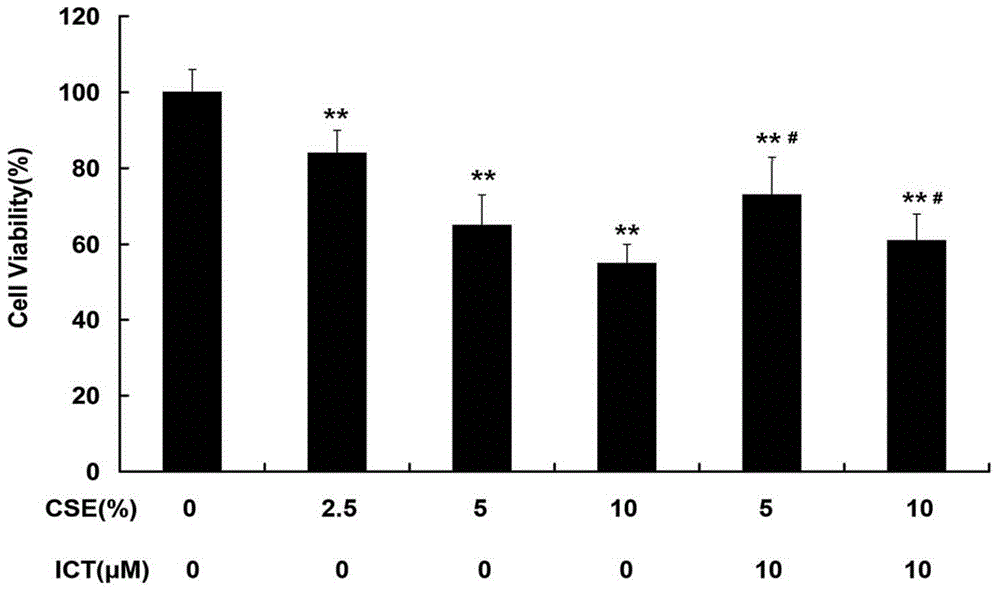
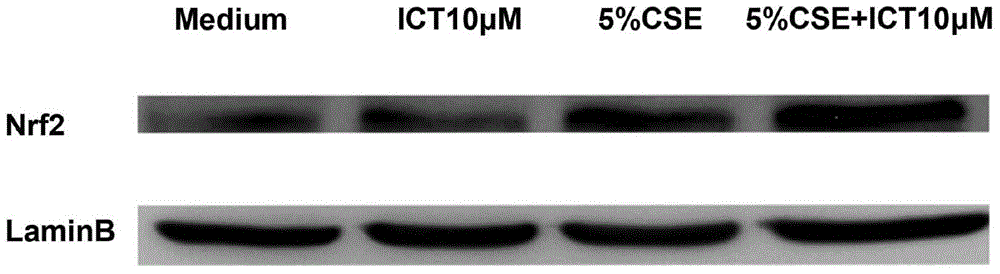
Application of icaritin in preparation of Nrf2 agonist
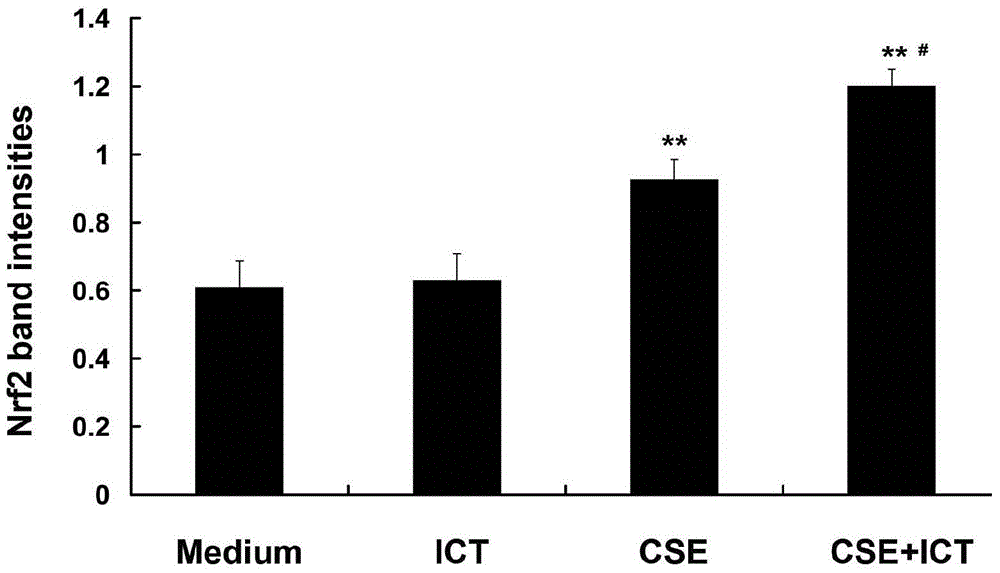
The invention belongs to the field of medicine preparation, and relates to an application of icaritin in preparation of an Nrf2 agonist. The icaritin intervention trial is carried out on an in-vitro oxidative stress model which is built by stimulation of a cigarette smoke extract. The result shows that the icaritin is capable of inducing Nrf2 phosphorylation, promoting expression of an anti-oxidative gene GCL, and increasing synthesis of an endogenous antioxidant GSH, so as to resist alveolar epithelial cell injuries induced by the cigarette smoke. Nrf2 gene is silenced by an RNA jamming technology; and the icaritin is capable of promoting the expression capacity of the anti-oxidative gene GCL to be reversed. An experiment result shows that the icaritin provided by the invention can be used for preparing the Nrf2 agonist, and further preparing medicines for resisting smoking-induced lung injuries. Furthermore, the invention provides a pharmaceutical composition for activating Nrf2. The pharmaceutical composition contains the icaritin in the formula (I) and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The formula is as shown in the specification.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
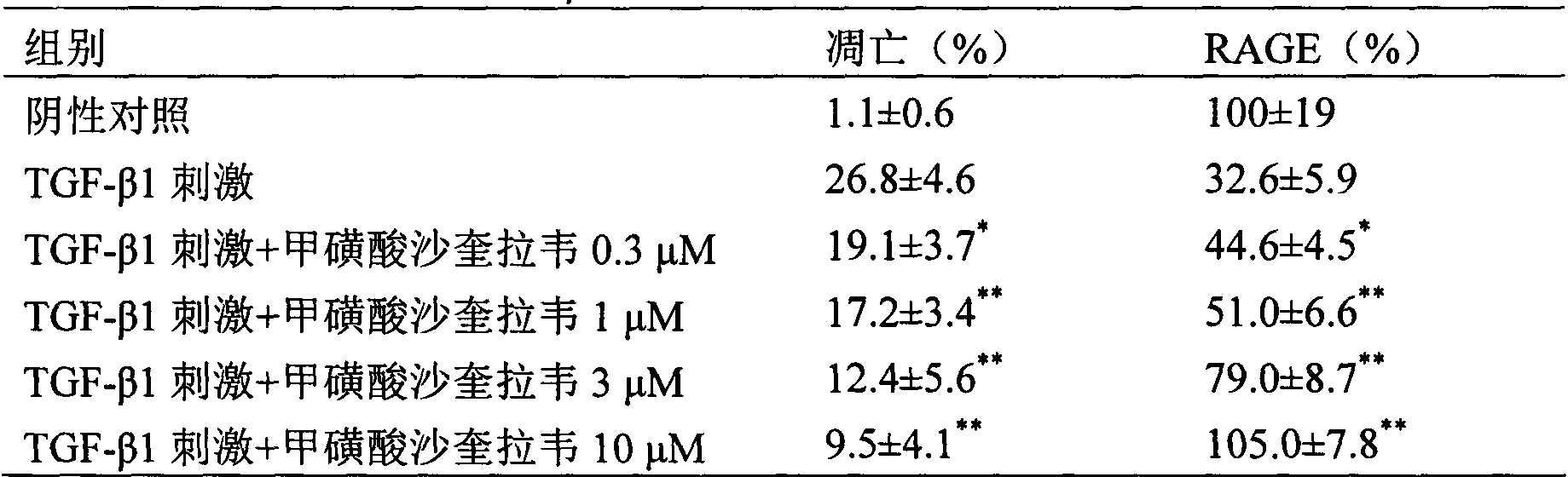
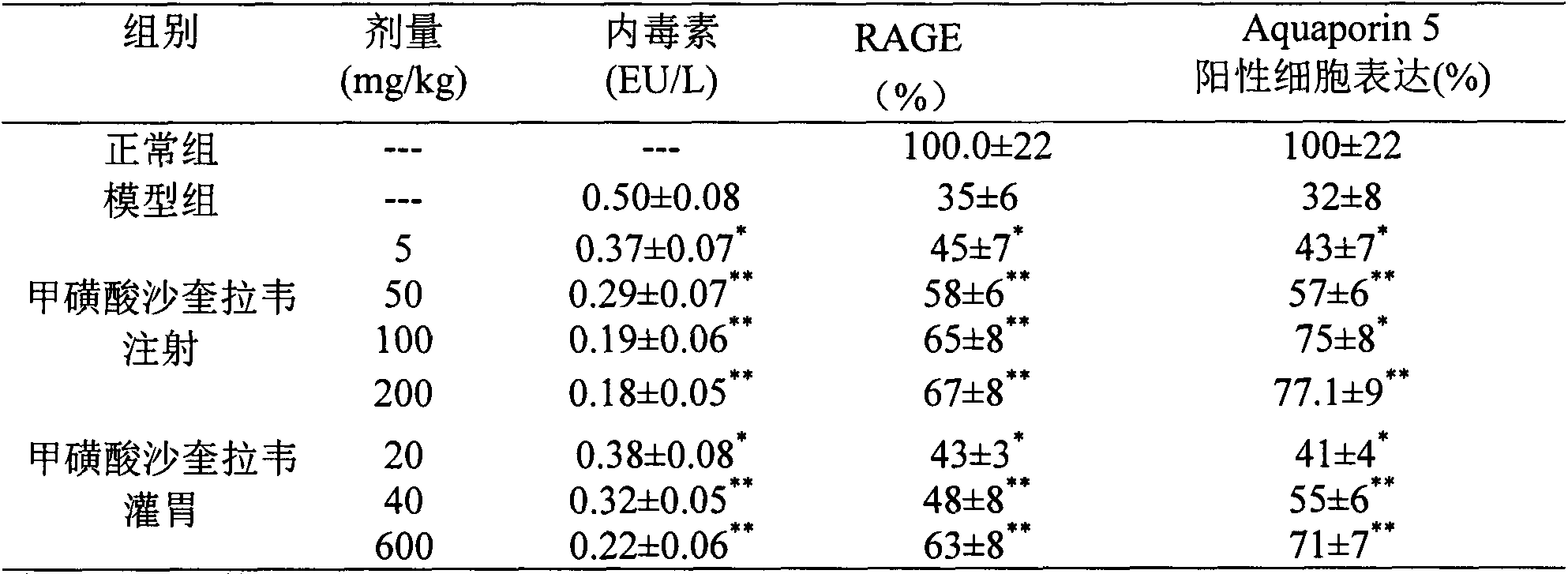
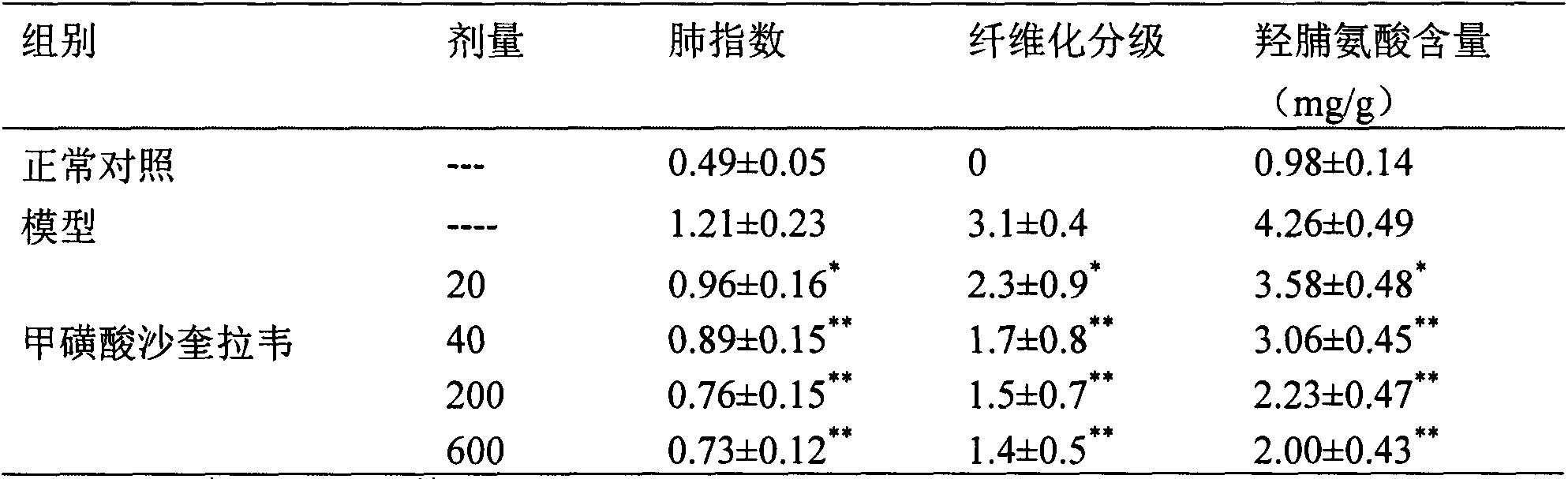
Application of saquinavir mesilate in preparation of drug for preventing or treating acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome and pulmonary fibrosis
The invention provides new use of a drug of saquinavir mesilate and particularly relates to application of saquinavir mesilate for inhibiting occurrence and development of an acute lung injury / acute respiratory distress syndrome (ALI / ARDS) and pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting I-type alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis to promote the expression of receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE), thus preventing or treating ALI / ARDS and pulmonary fibrosis. In the application, the range of the injection dosage is 50-2,000mg, preferably 50-1,000mg, and the oral dosage range is 200-6,000mg, preferably 400-6,000mg.
Owner:BINZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
Applications of thyroid hormone, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts or prodrugs of thyroid hormone in preparing drugs used for treating and/or preventing pulmonary diseases
The invention provides novel applications of thyroid hormone, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts or prodrugs of thyroid hormone. According to the invention, thyroid hormone, and the pharmaceutically acceptable salts or prodrugs of thyroid hormone can be used for treating and / or preventing pulmonary diseases; thyroid hormone and the pharmaceutically acceptable salts or prodrugs of thyroid hormone can be used for protecting alveolar epithelial cells effectively, adjusting surface protein synthesis, storage, and distribution of alveolar epithelial cells, promoting maturation, differentiation, and cell integrity of alveolar epithelial cells, promoting repairing of damaged mitochondria in alveolar epithelial cells, improving mitochondria biosynthesis, preventing and reversing pulmonary fibrosis, adjusting immunity reaction, changing cancerous environment, treating and preventing pulmonary diseases, improving pulmonary functions such as gas exchange, and achieving treatment effect, and are beneficial for cleaning of pulmonary effusion and repairing of damaged lung tissue.
Owner:深圳市润佳通科技有限公司
Uses of Ferroptosis Inhibitors
The invention relates to the technical field of medical science, in particular to new application of a ferroptosis inhibitor. The ferroptosis inhibitor is prepared from Liproxstatin-1, Ferrostatin-1,rosiglitazone, pioglitazone, troglitazone and Zileuton. The new application refers to that the inhibitor is applied to treating radiation-induced pulmonary injury diseases. The application has the advantages that (1) radioactive rays trigger radiation-induced pulmonary injury by mediating pulmonary alveoli epithelial cells to have ferroptosis, the ferroptosis specificity inhibitor can be used to prevent and treat radiation-induced pulmonary injury, and has the important meaning on development of new drug for preventing and treating radiation-induced pulmonary injury; and (2) it is found that radioactive rays can cause cell death through the mode of ferroptosis, and application of the ferroptosis inhibitor also has the significant theoretical meaning on guiding research for guiding radioactive rays to treat cancer mechanism.
Owner:JINSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Application of indinavir in preparing medicament for preventing or treating acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome and pulmonary fibrosis
InactiveCN103977005AOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderApoptosisARDs - Acute respiratory distress syndrome
The invention provides a novel medicinal application of indinavir, and particularly relates to application of indinavir in inhibiting occurrence and development of acute lung injury / acute respiratory distress syndrome (ALI / ARDS) and pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting apoptosis of alveolar epithelial cells and promoting expression of a receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (RAGE) of I-type alveolar epithelial cells to prevent and treat ALI / ARDS and pulmonary fibrosis. In the application, the injection dosage is in a range of 50-2000mg, and preferably 50-1000mg; the oral dosage is in a range of 100-5000mg, and preferably 200-5000mg.
Owner:BINZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
New application of FAR1 gene
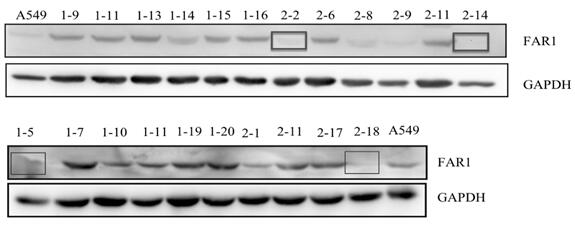
PendingCN114592007APromote proliferationImprove mobilityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCancer cellDrug target
The invention discloses a new application of an FAR1 gene, namely an application of screening a drug for treating non-small cell lung cancer aiming at inhibiting the expression of the FAR1 gene, and the new application is characterized in that an FAR1 gene knockout plasmid is constructed through a CRISPR / Cas9 technology, and an A549-KO-FAR1 stable cell line is further constructed; lipid changes among normal alveolar epithelial cells, wild type A549 and A549-KO-FAR1 cell strains are compared and analyzed through lipid metabonomics, it is found that lipid metabolism in the A549 is disordered, after the FAR1 gene is knocked out, part of PC and TG can recover to the level of the normal alveolar cells, FAR1 protein inhibits proliferation and migration of non-small cell lung cancer by adjusting lipid metabolism of cancer cells, and the non-small cell lung cancer can be effectively inhibited. Therefore, the purpose of treating the non-small cell lung cancer can be achieved, the FAR1 gene can be used as a target spot for treating the non-small cell lung cancer, and a wide prospect is provided for development of non-small cell lung cancer treatment drugs targeting the FAR1 gene in the future.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method of preparing basement membrane, method of constructing basement membrane specimen, reconstituted artificial tissue using the basement membrane specimen and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20070122796A1Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsLipid formationFiber
A basement membrane having a barrier function is formed by culturing alveolar epithelial cells or vascular endothelial cells on a fibrous collagen matrix coated with a polymer having a sugar chain that can localize a receptor that has an activity to accumulate a basement membrane component on the basal surface of the cells having an ability to form a basement membrane. A reconstructed artificial tissue is obtained by seeding and culturing desired homogeneous or heterogeneous cells on the basement membrane specimen constructed by the following process: (i) the cells having an ability to form a basement membrane adhered onto a support structure through a basement membrane are treated with a surface active agent, (ii) the lipid component of cells is lysed; (iii) the mixture of an alkaline solution and a protease inhibitor is used to lyse the protein remained on the surface of the basement membrane of the cells.
Owner:MOCHITATE KATSUMI
Lentivirus vectors for gene transfer to alveolar epithelial cells
InactiveUS20080081365A1High transduction efficiencyImprove concentrationBiocideVectorsTransfer geneLentivirus
The present invention demonstrates that VSV-G-pseudotyped lentivirus vectors efficiently transduce AEC in primary culture and in vivo with transduction favored by virus application from the apical side. Transduction efficiency in AEC increased with increasing MOI and greatly exceeded that achieved with a similarly pseudotyped MLV retrovirus vector. The present invention also demonstrates the successful in vivo transfer of genes through lentivirus vector transduction. Mammals injected with lentivirus vector via the trachea expressed the reporter protein in alveolar epithelial cells within 48 to 72 hours after infection.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com