Collagen producing plants and methods of generating and using same
a technology of collagen and plants, applied in the field of collagen producing plants and methods of generating, can solve the problems of poor proline hydroxylation of collagen, limited extensibility of collagen fibers, and great tensile strength of collagen fibers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Constructs and Transformation Schemes
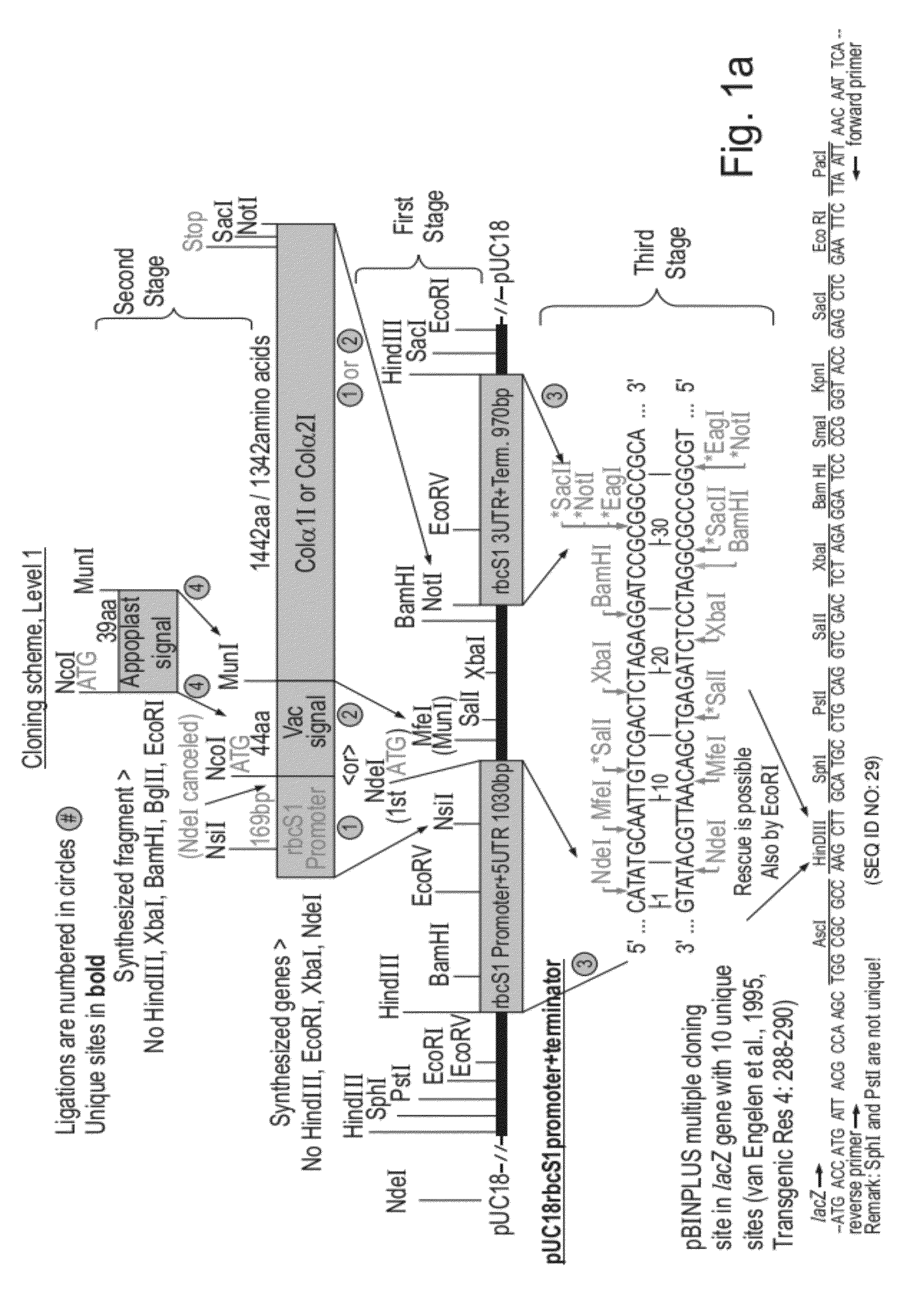
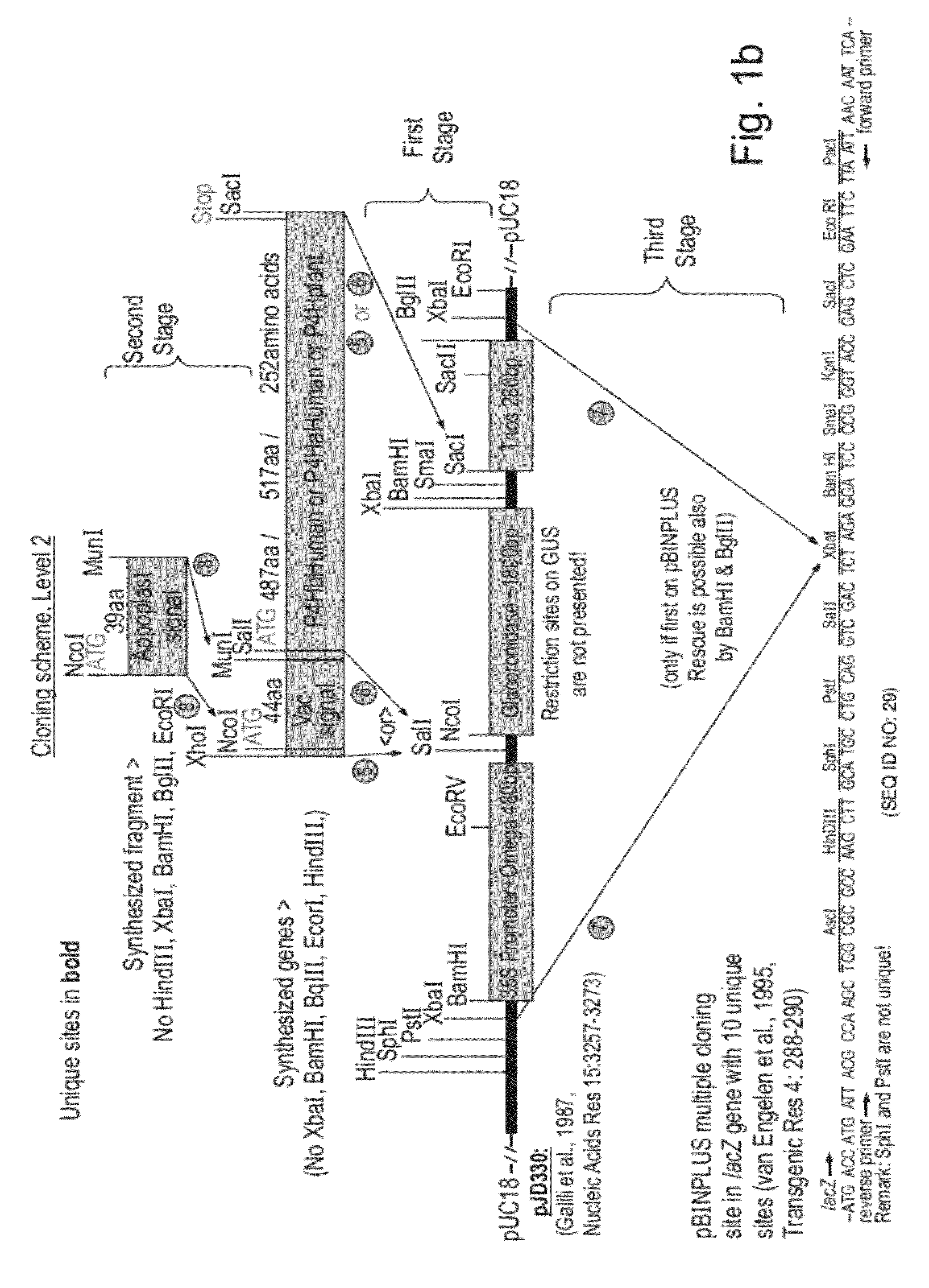
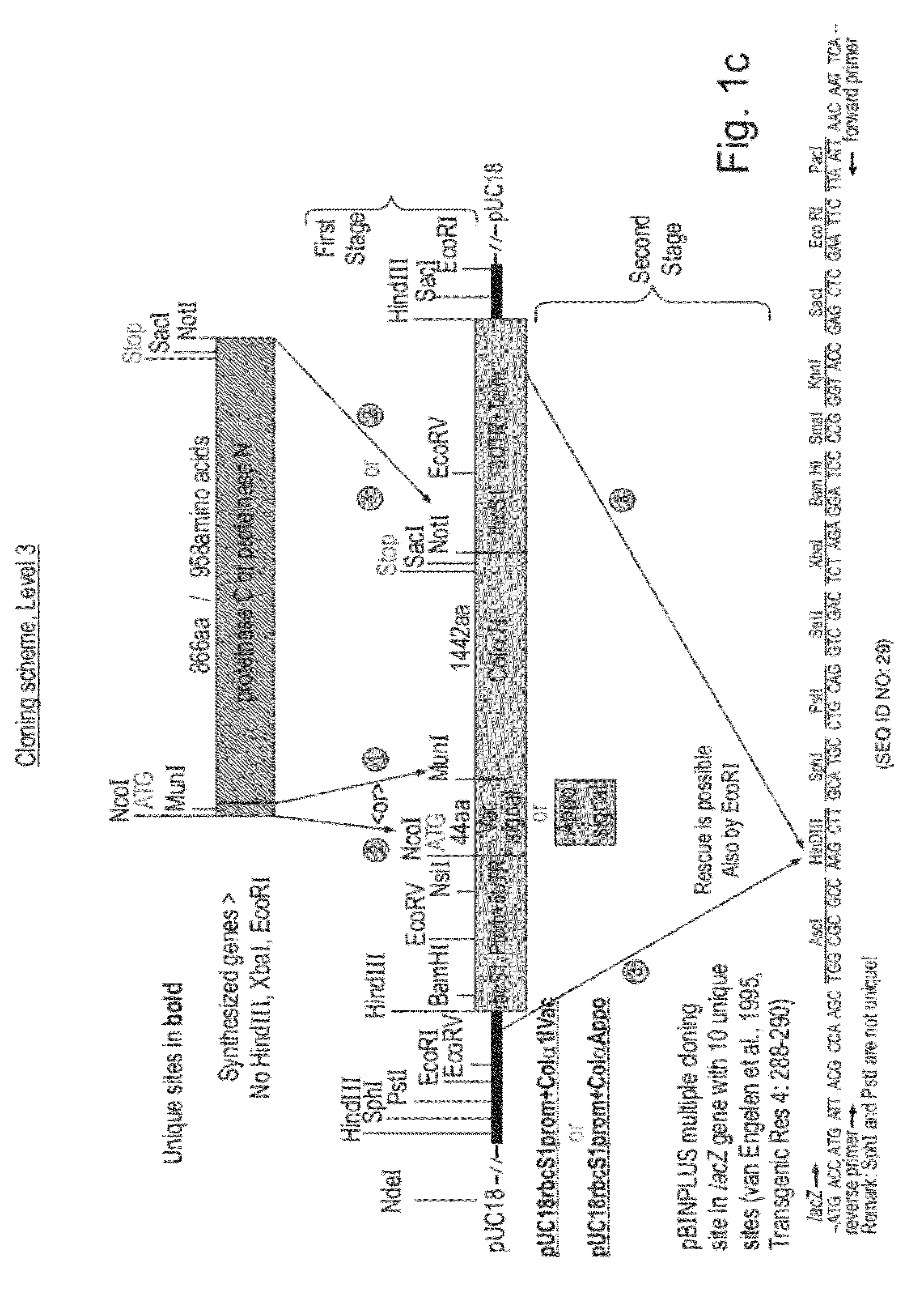
[0163]Constructions of expression cassettes and vectors used in this work are illustrated in FIG. 1a-d. All of the coding sequences in this work were optimized for expression in tobacco and chemically synthesized with desired flanking regions (SEQ ID NOs: 1, 4, 7, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22). FIG. 1a—the synthetic genes coding for Col1 and Col2 (SEQ ID's 1, 4) fused either to the vacuolar signal or to the apoplast signal (encoded by SEQ ID NO: 7) or without signals were cloned in expression cassettes composed of a Chrysanthemum rbcS1 promoter and 5′ UTR (SEQ ID NO: 10) and a Chrysanthemum rbcS1 3′UTR and terminator (SEQ ID NO: 11). The complete expression cassettes were cloned in the multiple cloning site of the pBINPLUS plant transformation vector (van Engelen et al., 1995, Transgenic Res 4: 288-290). FIG. 1b—The synthetic genes coding for P4H beta-human, P4H alpha-human and P4H-plant (SEQ ID NOs: 12, 14 and 16) fused either to the vacuolar signal o...
example 2
Plant Collagen Expression
[0165]Synthetic polynucleotide sequences encoding the proteins listed in Table 1 below were designed and optimized for expression in tobacco plants.
TABLE 1List of expressed proteinsIncludedEncodedSwissProtAminoSplicingin SEQby SEQName:accessionacidsisoformDeletionsnameID NO.ID NO.Collagenp024521442OneER signalCol131alpha 1(I)versionchain[Precursor]Collagenp081231342OneER signalCol264alpha 2(I)Two changesversionchaindone in[Precursor]p08123:D549A andN249IProlyl 4-p07237487OneER signal,P4H1312hydroxylaseversionKDELbetaHumanbeta subunitProlyl 4-p13674517P13674-1ER signalP4H1514hydroxylasealphaHumanalpha-1subunitProlyl 4-No entry in252OneMitochon-P4Hplant1716hydroxylaseSwissprot.versiondrial signalPlantNCBIpredictedaccession:as: aa1-39gi:15227885Procollagenp13497866P13497-1ER signal,Proteinase1918C-proteinaseBMP1-3propeptideCProcollagen Io95450958O95450-1ER signal,Proteinase2120N-proteinaseLpNPIpropeptideNLysylo60568714OneER signalLH32322hydroxylase 3version
[016...
example 3
Detection of Human Collagen in Transgenic Tobacco Plants
[0183]Total soluble proteins were extracted from tobacco transformants 2, 3 and 4 by grinding 500 mg of leaves in 0.5 ml 50 mM Tris-HCl pH=7.5 with a “Complete” protease inhibitor cocktail (product #1836145 from Roche Diagnostics GmbH, 1 tablet per 50 ml buffer). The crude extract was mixed with 250 μl 4× Sample application buffer containing 10% beta-mercapto-ethanol and 8% SDS, the samples were boiled for 7 minutes and centrifuged for 8 minutes in 13000 rpm. 20 μl of the supernatant were loaded in a 10% polyacrylamide gel and tested with anti-Collagen I (denatured) antibody ((#AB745 from Chemicon Inc.) in a standard Western blot procedure (FIG. 4). W.T. is a wild type tobacco. Positive collagen bands are visible in plants that are PCR positive for collagen typeI alpha 1 or alpha 2 or both. Positive control band of 500 ng collagen type I from human placenta (#CC050 from Chemicon Inc.) represents about 0.3% of the total soluble ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com