System of anchoring and mooring of floating wind turbine towers and corresponding methods for towing and erecting thereof
a technology of floating wind turbines and anchoring systems, which is applied in the direction of floating buildings, vessel safety, and vessel movement reduction by mass displacement, can solve the problems of high energy consumption, high efficiency of wind turbines with two or three blades and horizontal axles, and inability to improve due to the laws of physics, so as to achieve the effect of less expensive and efficient erection and maintenance of towers on si
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
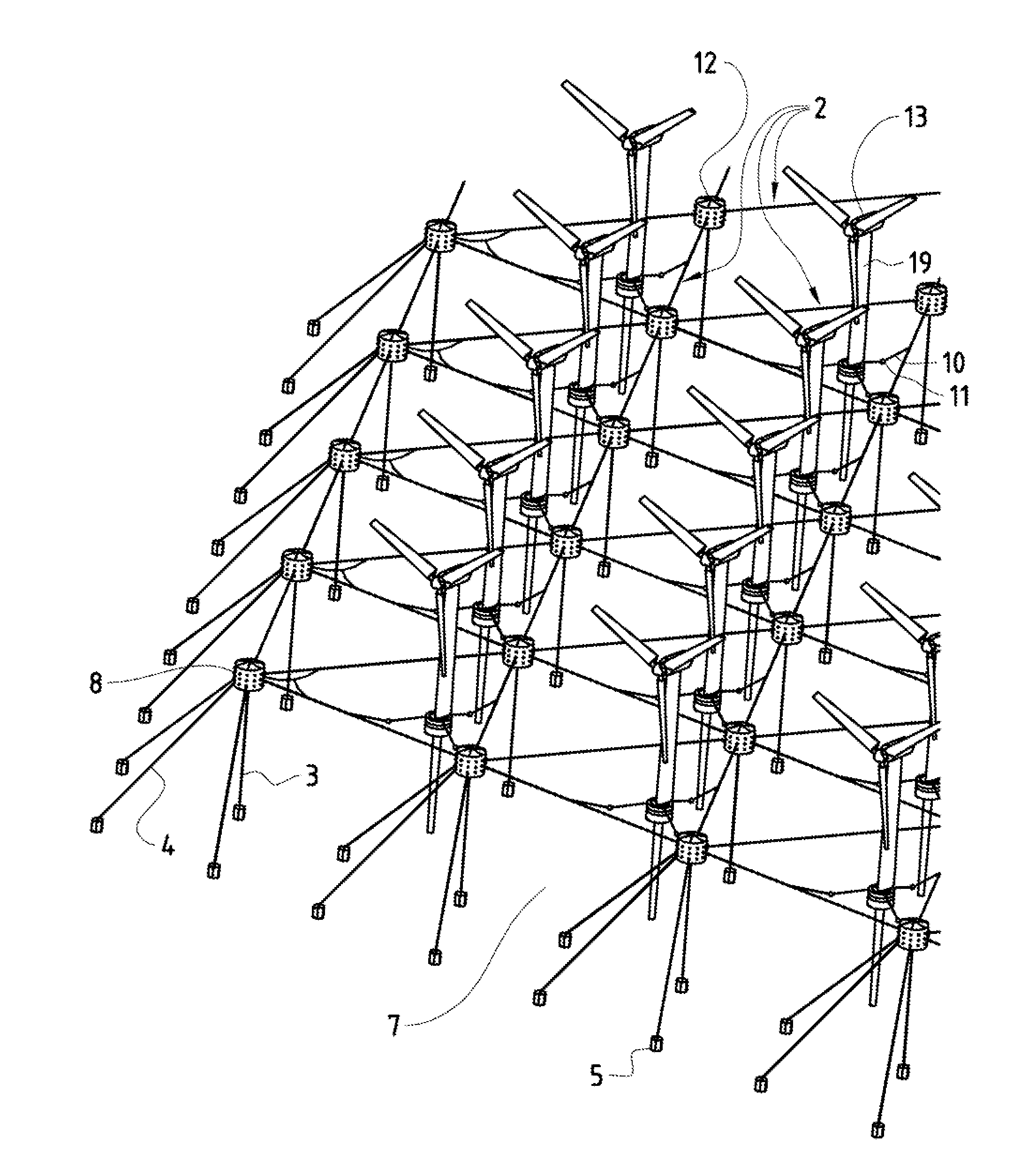
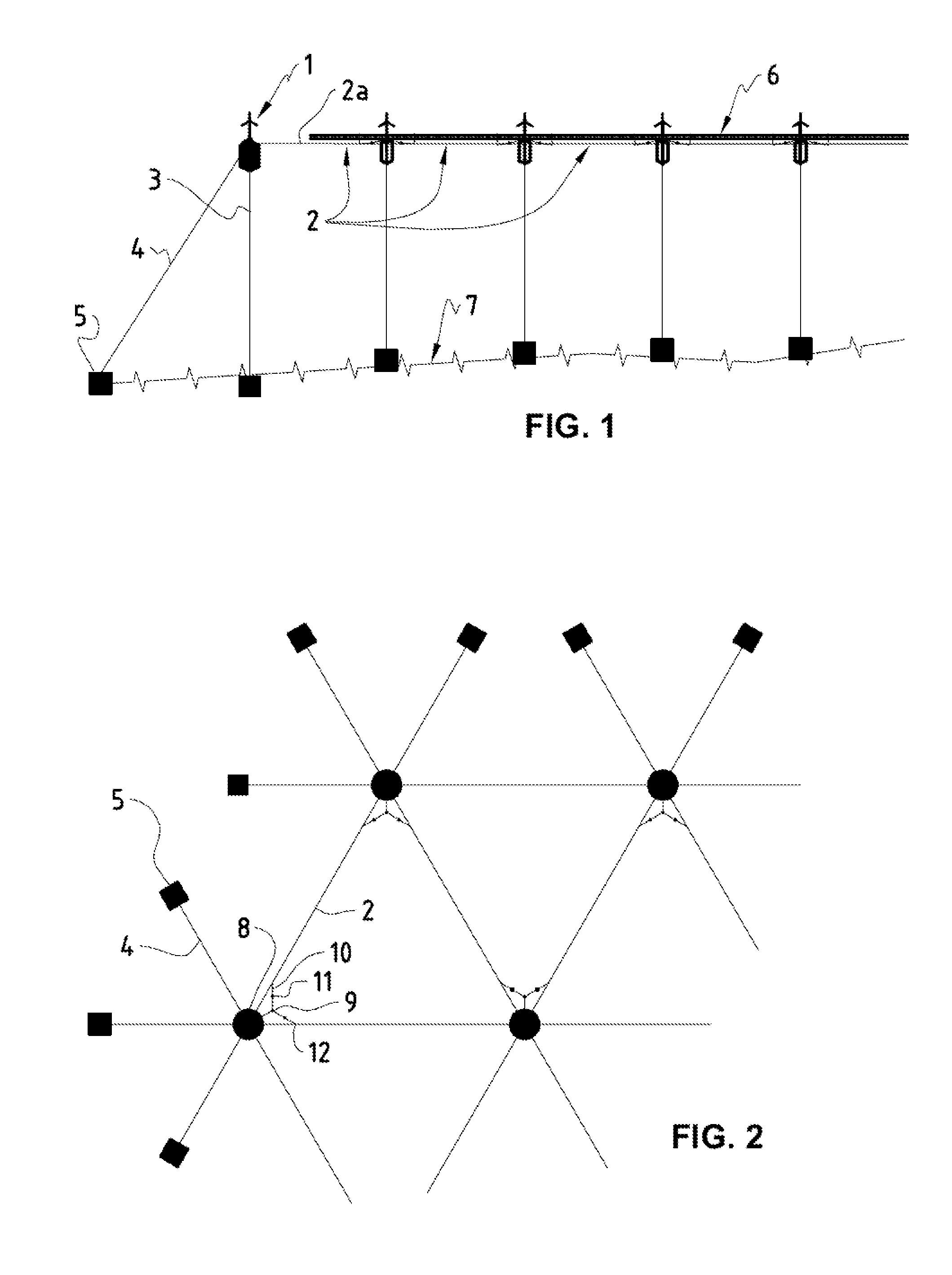
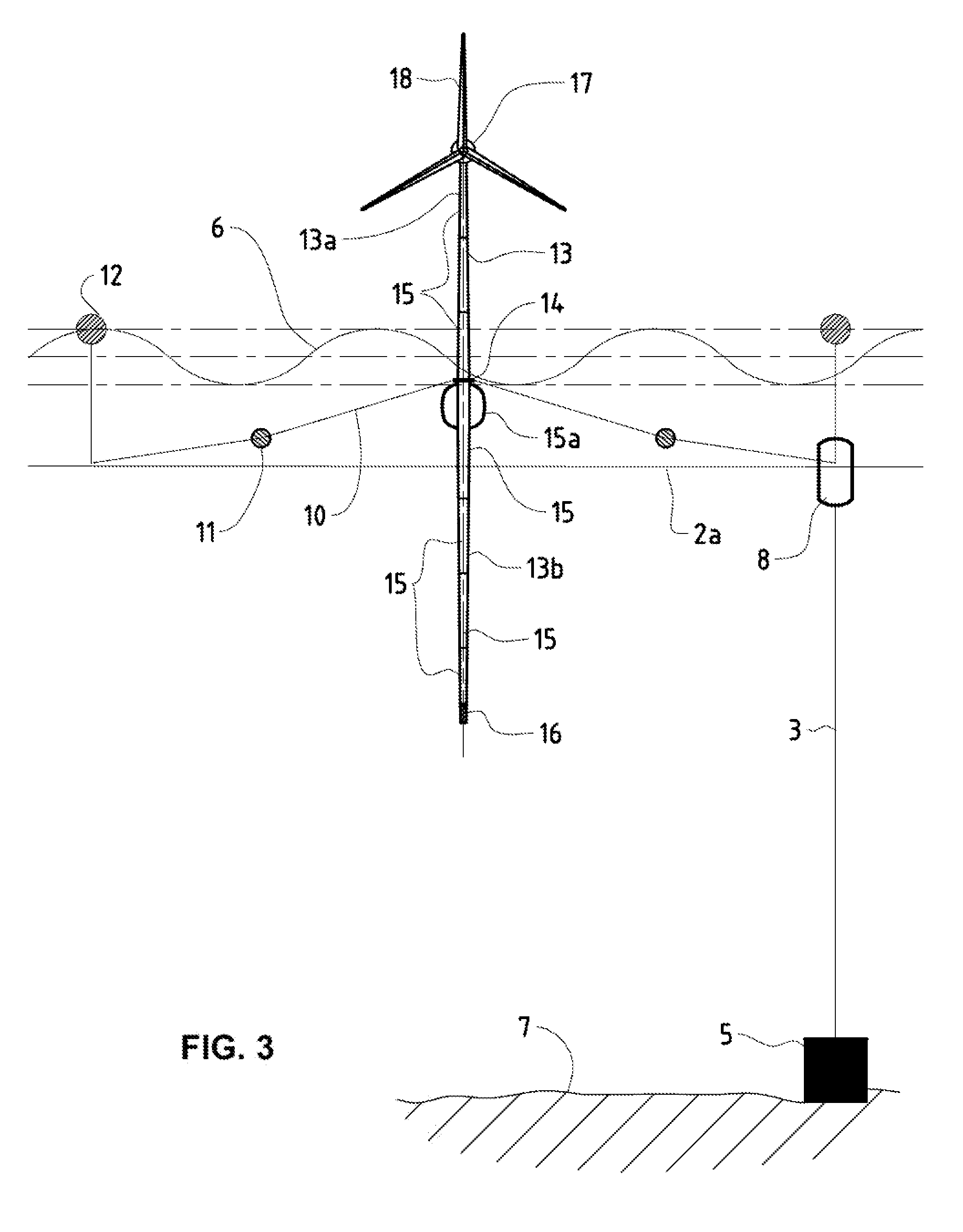
[0031]FIG. 1 is a schematic side view of the floating off-shore windpark system of the present invention. The reference number 1 is a floating wind turbine unit comprising a wind turbine tower 13 (cf. FIG. 3) moored to a semi-submersible major buoy 8 and the adjacent semisubmersible, horizontally floating cables, chains or lines 2a (in the following only called horizontal lines 2a) of the floating meshwork 2. The reference number 3 is a vertical mooring chain, cable or line (in the following only called vertical mooring lines 3) connected typically to a weight-anchor 5 on the seabed 7. At the edges of the windpark the major buoys 8 and with it the entire floating meshwork 2 would typically be transversely braced by border mooring lines 4 to achieve an optimal reduction of side drift of the windpark system. The reference number 6 depicts the water surface and maximal swell amplitude.
[0032]FIG. 2 is the schematic bird's view of the same windpark system. The reference number 9 is a sin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com