Metallic compositions useful for brazing, and related processes and devices
a technology of metal compositions and brazing, applied in the field of brazing compositions, can solve the problems of difficult metal-to-ceramic bonding, difficult use of metal-to-ceramic bonding, and the inability of most seals to withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments, and achieve the effect of less complicated processing and less cos
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0065]The example provided herein is merely illustrative, and should not be construed to be any sort of limitation on the scope of the claimed invention. Unless specified otherwise, all ingredients may be commercially available from such common chemical suppliers as Alpha Aesar, Inc. (Ward Hill, Mass.), Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, Mo.), Spectrum Chemical Mfg. Corp. (Gardena, Calif.), and the like.
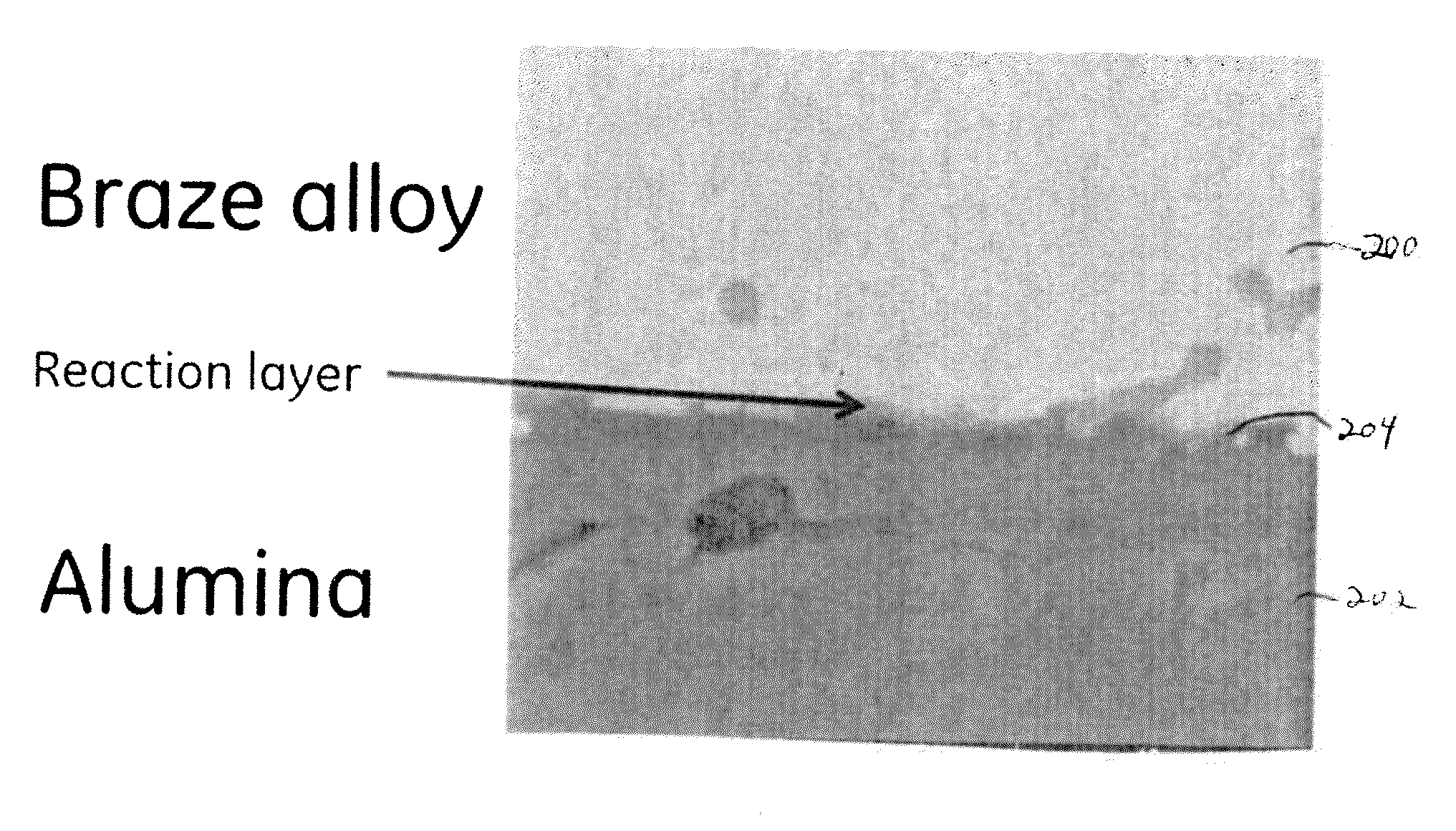
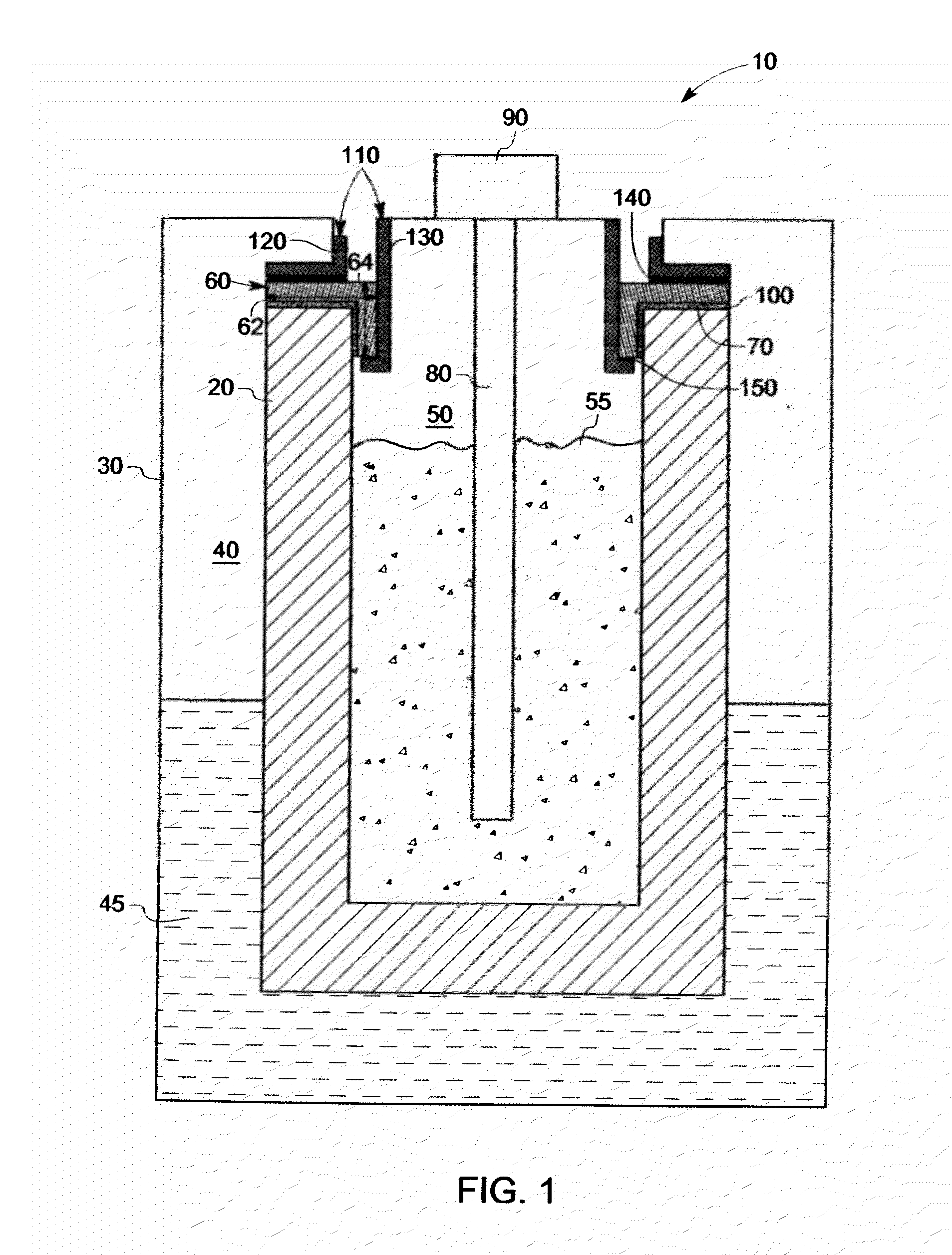
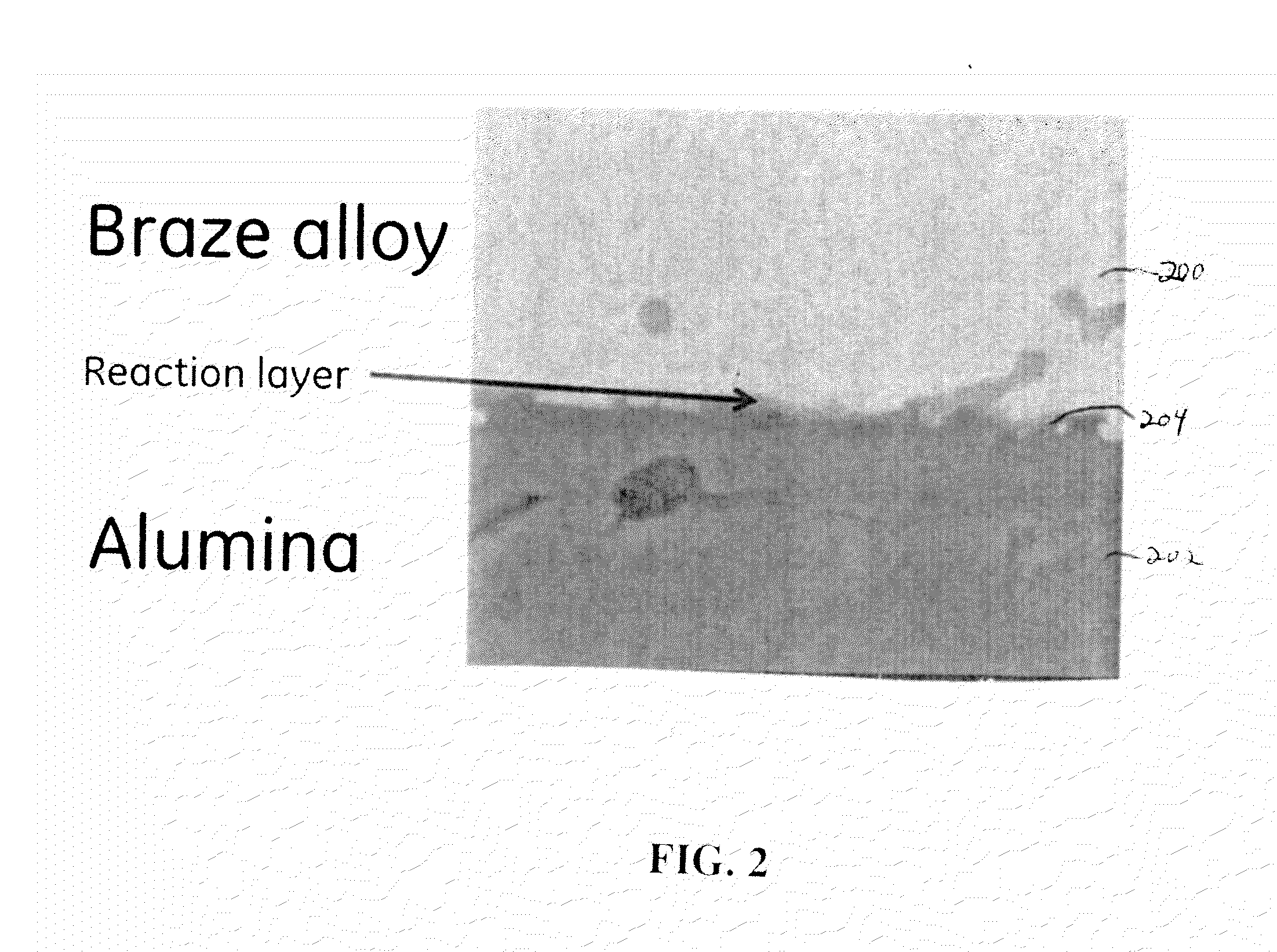
[0066]A braze alloy composition of nickel, chromium, niobium, and titanium was prepared, having the nominal composition Ni-27.2Cr-14.1Nb-4Ti (weight percent). In the preparation of the alloy, the individual elements were weighed according to the desired proportions, and then arc-melted to provide an ingot of the material. To ensure homogeneity of the composition, the ingot was triple-melted. The liquidus temperature of the sample was determined to be 1203° C., using a Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC).
[0067]The ingot was formed into approximately a 75 micron-thick sheet, and cooled. The...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| liquidus temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| liquidus temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com