Cover glass for display device, and manufacturing method for same
a technology for display devices and glass, applied in glass/slag layered products, chemistry apparatuses and processes, layered products, etc., can solve the problems of less likely to provide compressive stress layers at the surface portion of glass plates, failure to provide desired high strength, and easy cracking, etc., to achieve excellent mechanical strength, excellent cutting processability, and high strength.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
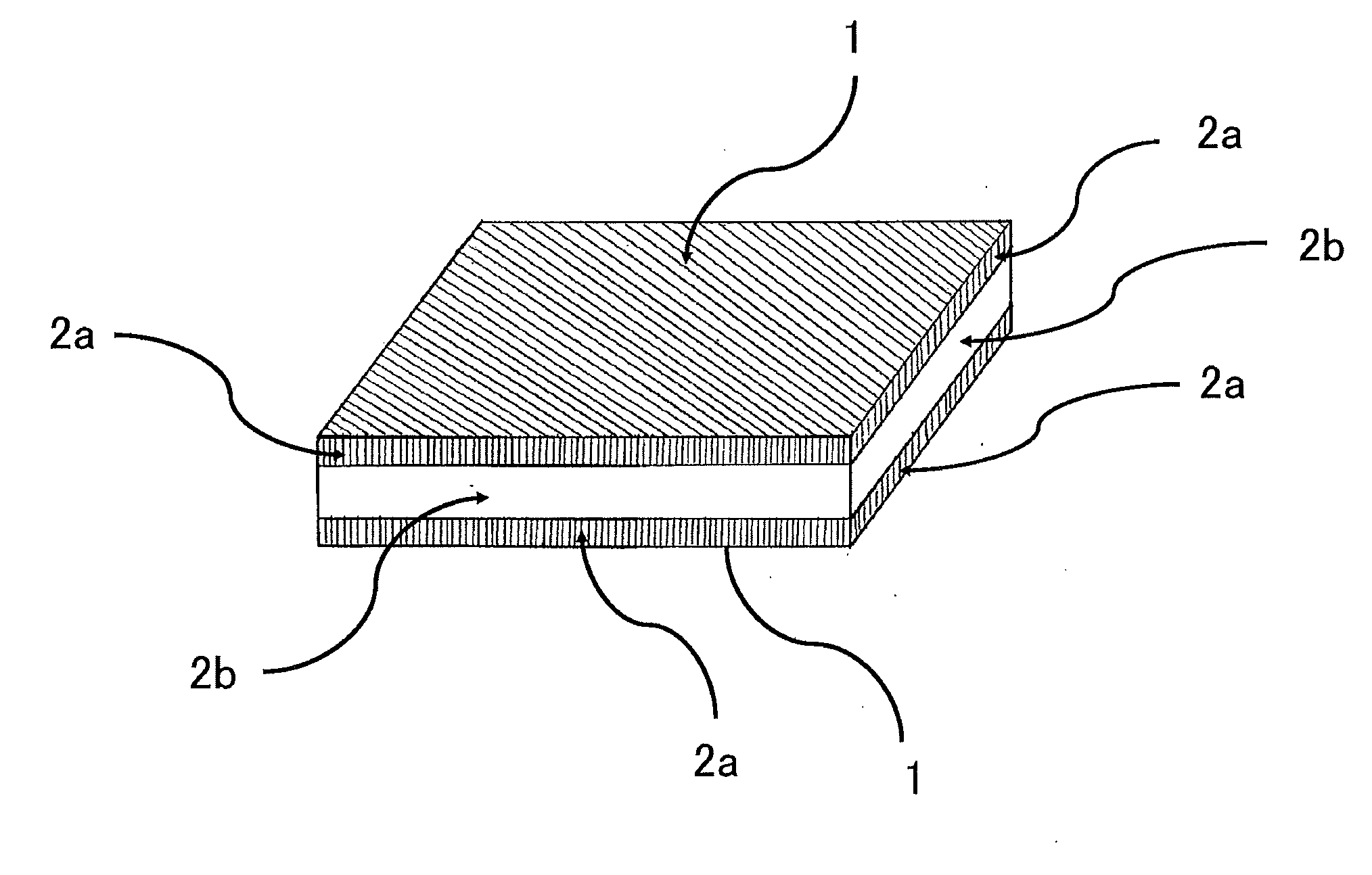
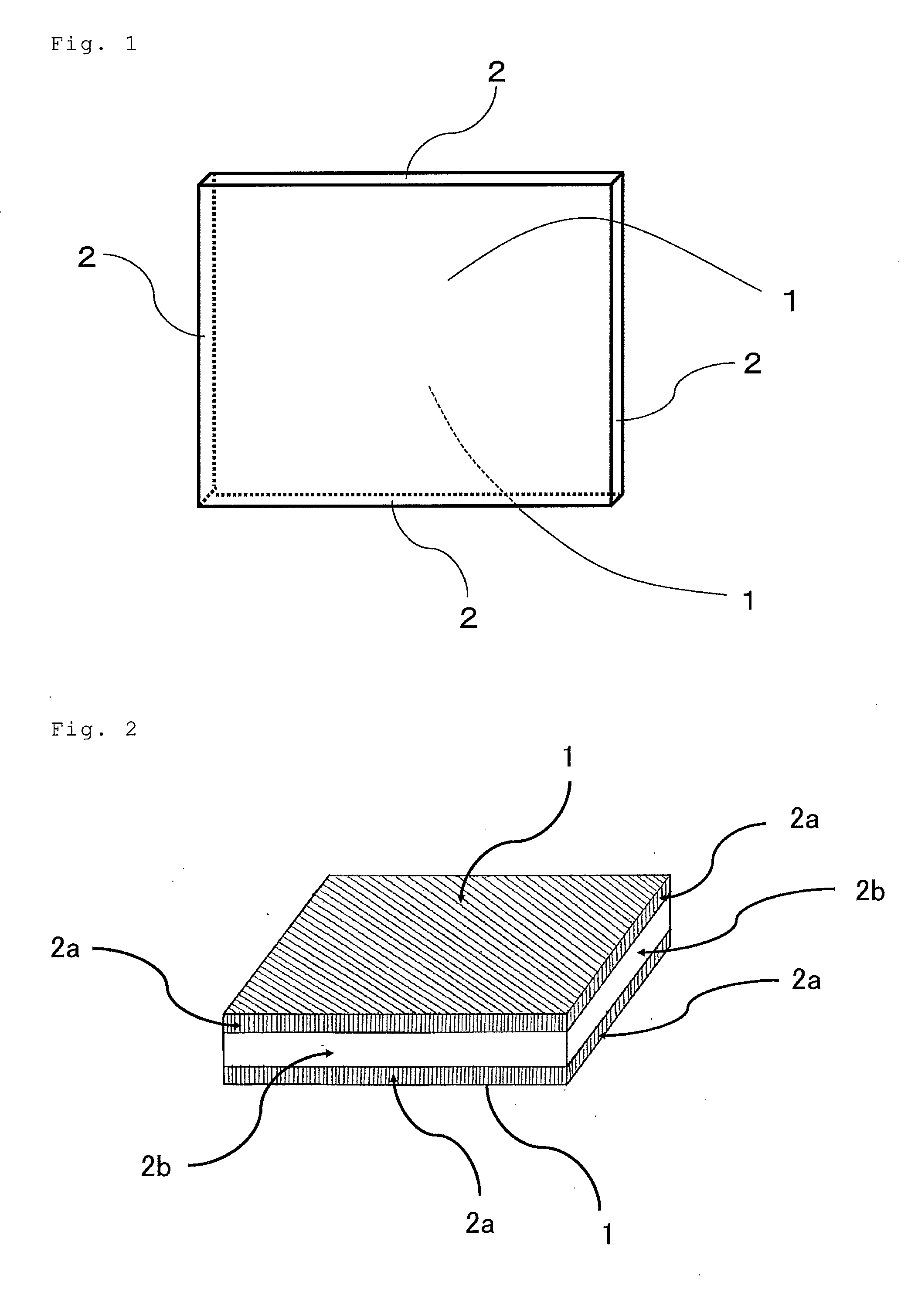
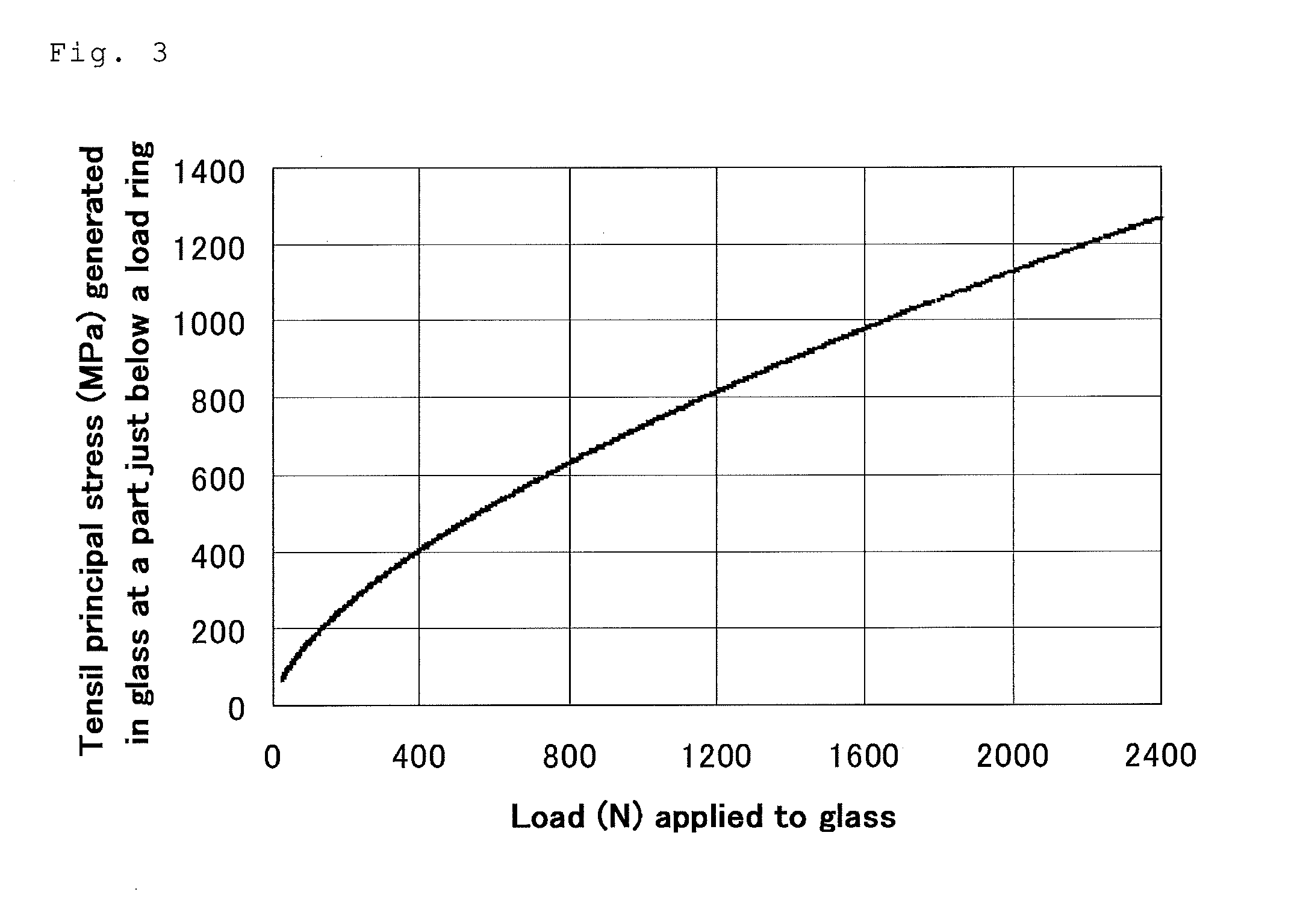
Image
Examples
example 1
(1) Preparation of Chemically Strengthened Glass and Evaluation of Surface Compressive Stress and Depth of Compressive Stress Layer
[0125]As a glass plate before ion exchange (chemical strengthening), a 0.7-mm thick soda-lime glass plate with 400 mm×500 mm sizes (SiO2: 71.6%, Na2O: 12.5%, K2O: 1.3%, CaO: 8.5%, MgO: 3.6%, Al2O3: 2.1%, Fe2O3: 0.10%, SO3: 0.3% (on a mass basis) the strain point of the plate glass was 503° C.) (hereinafter, referred to as glass base plate) was produced by a float process.
[0126]The glass base plate prepared above was submerged in a molten salt (first salt, proportion P: 34.7 mol %) bath composed of a mixture of 65.3 mol % of potassium nitrate and 34.7 mol % of sodium nitrate at a constant temperature of 475° C. for 120 minutes, as a first step. The glass base plate was then taken out from the bath and gradually cooled, and the surface of the glass base plate was washed and dried.
[0127]In a subsequent second step, the dried glass base plate was submerged i...
example 2
[0135]Chemically strengthened cut glasses were prepared as in Example 1 except that the thickness of the glass base plate was changed and the temperature of the first salt was set at 470° C., and evaluated. The depth of the compressive stress layer formed through the first step, the surface compressive stress, and the depth of the compressive stress layer of each glass were measured as in Example 1 to be 12 μm, 683 MPa, and 10 μm, respectively. The shape parameter and the strength when a cumulative fracture probability was 1% determined as in Example 1 were 8.07 and 512 MPa, respectively.
example 3
[0136]Chemically strengthened cut glasses were prepared as in Example 2 except that the thickness of the glass base plate was changed, and evaluated. The depth of the compressive stress layer formed through the first step, the surface compressive stress, and the depth of the compressive stress layer of each glass were measured as in Example 1 to be 12 μm, 677 MPa, and 11 μm, respectively. The shape parameter and the strength when a cumulative fracture probability was 1% determined as in Example 1 were 11.5 and 578 MPa, respectively.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface compressive stress | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com