Networked motorized drive roller conveyor
a motorized drive and conveyor technology, applied in the direction of conveyor control devices, conveyor parts, roller-ways, etc., can solve the problems of mdr systems lacked the ability to control the gap size between items on the conveyor system, requires significant time, labor and money to route and terminate wiring, and achieves reduced maintenance costs, noise reduction, and power consumption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
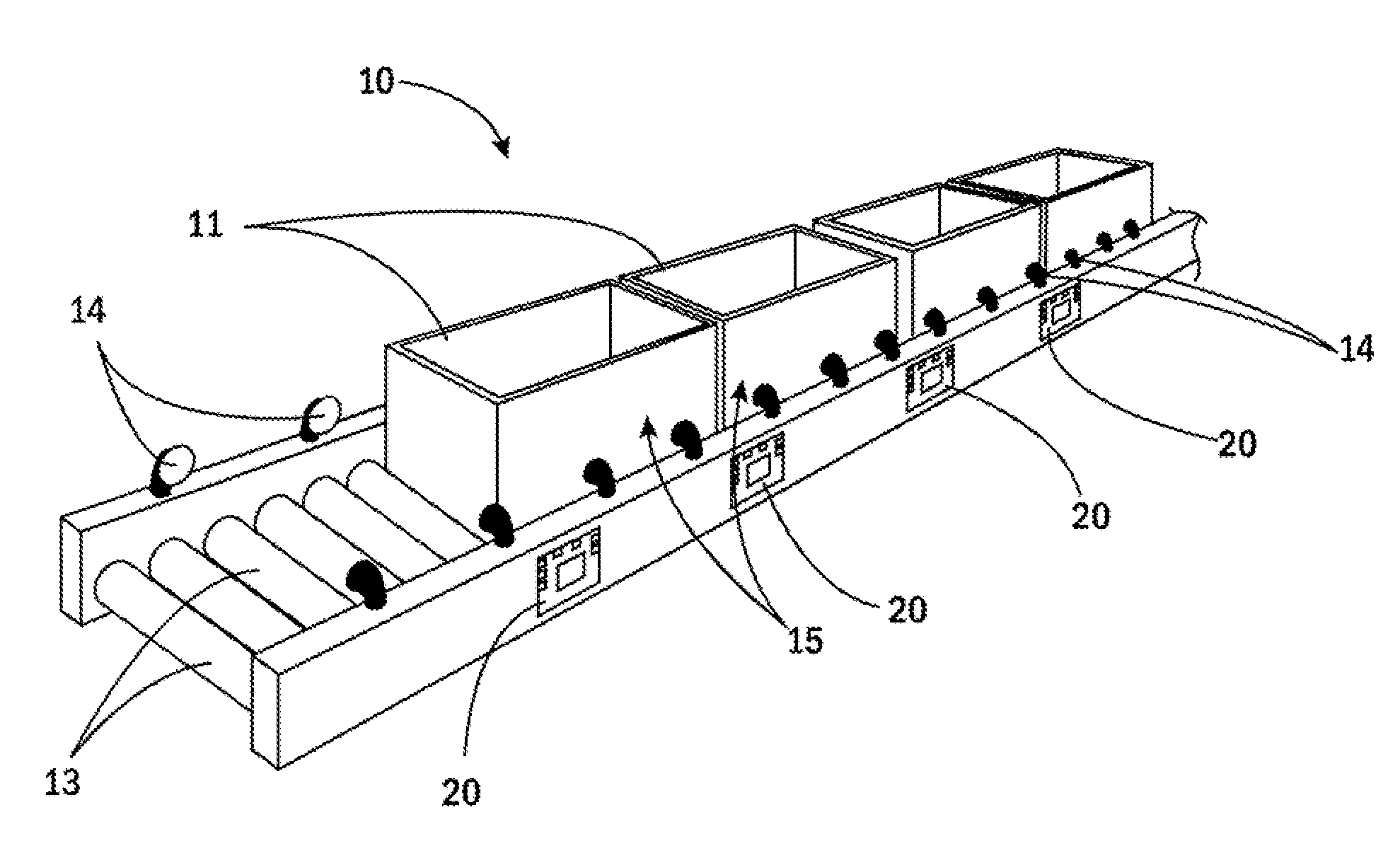
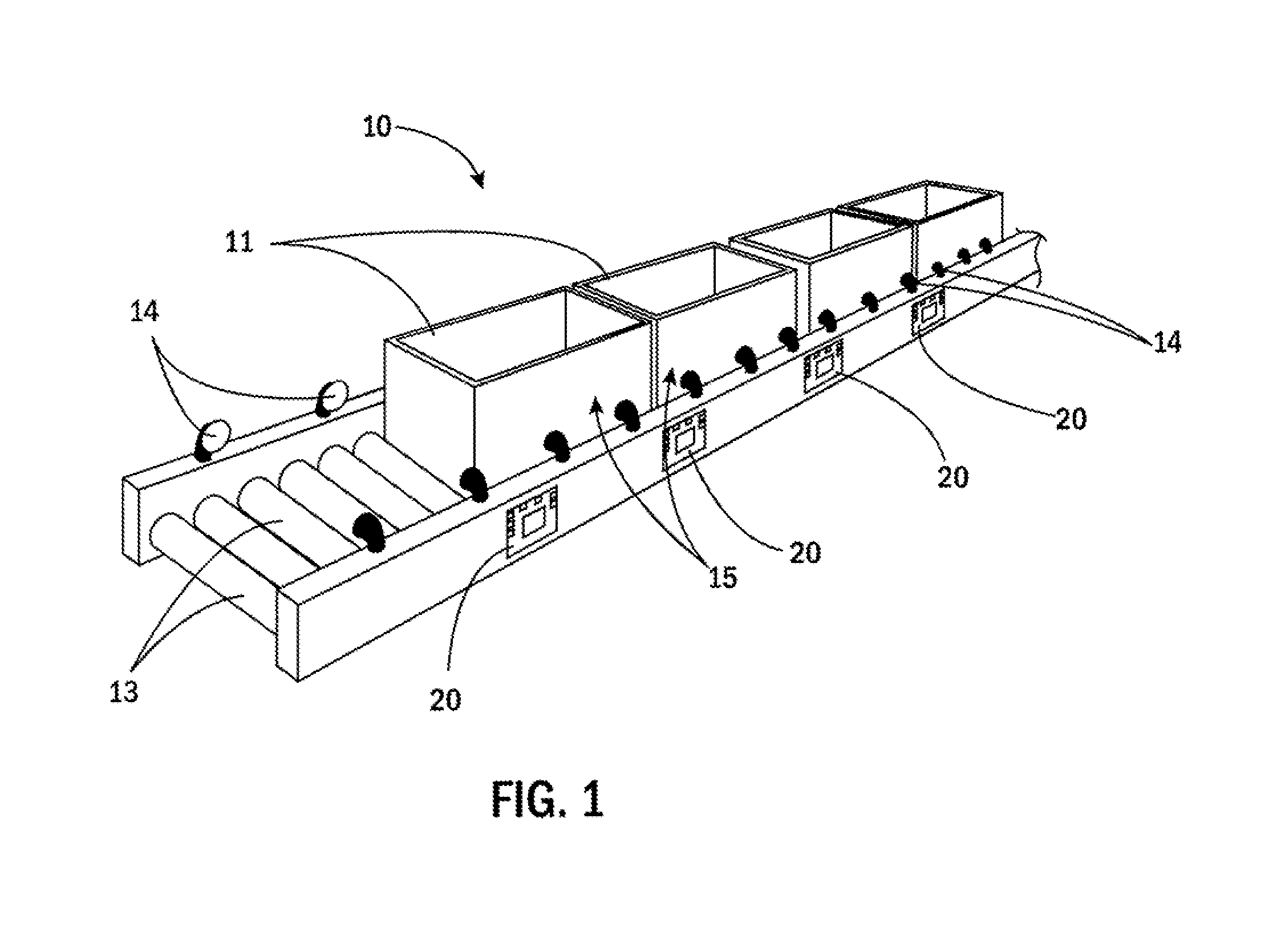
[0028]FIG. 1 shows a portion of the conveyor system 10 of the present invention that incorporates control cards 20 in accordance with the present invention. Generally speaking, a number of items 11 are supported on the conveyor 10, which includes a plurality of rollers 13, including MDRs and corresponding idler rollers. The conveyor system 10 further includes a plurality of sensors 14 that detect items 11 as the items 11 move along the conveyor system 10. The conveyor system 10 is divided into zones 15. Each zone 15 is defined between adjacent sensors 14. Additionally, each zone 15 corresponds with an MDR / idler roller assembly. In the inventive system, each zone 15 is shorter than the length of the respective items 11 being conveyed by the conveyor system 10.
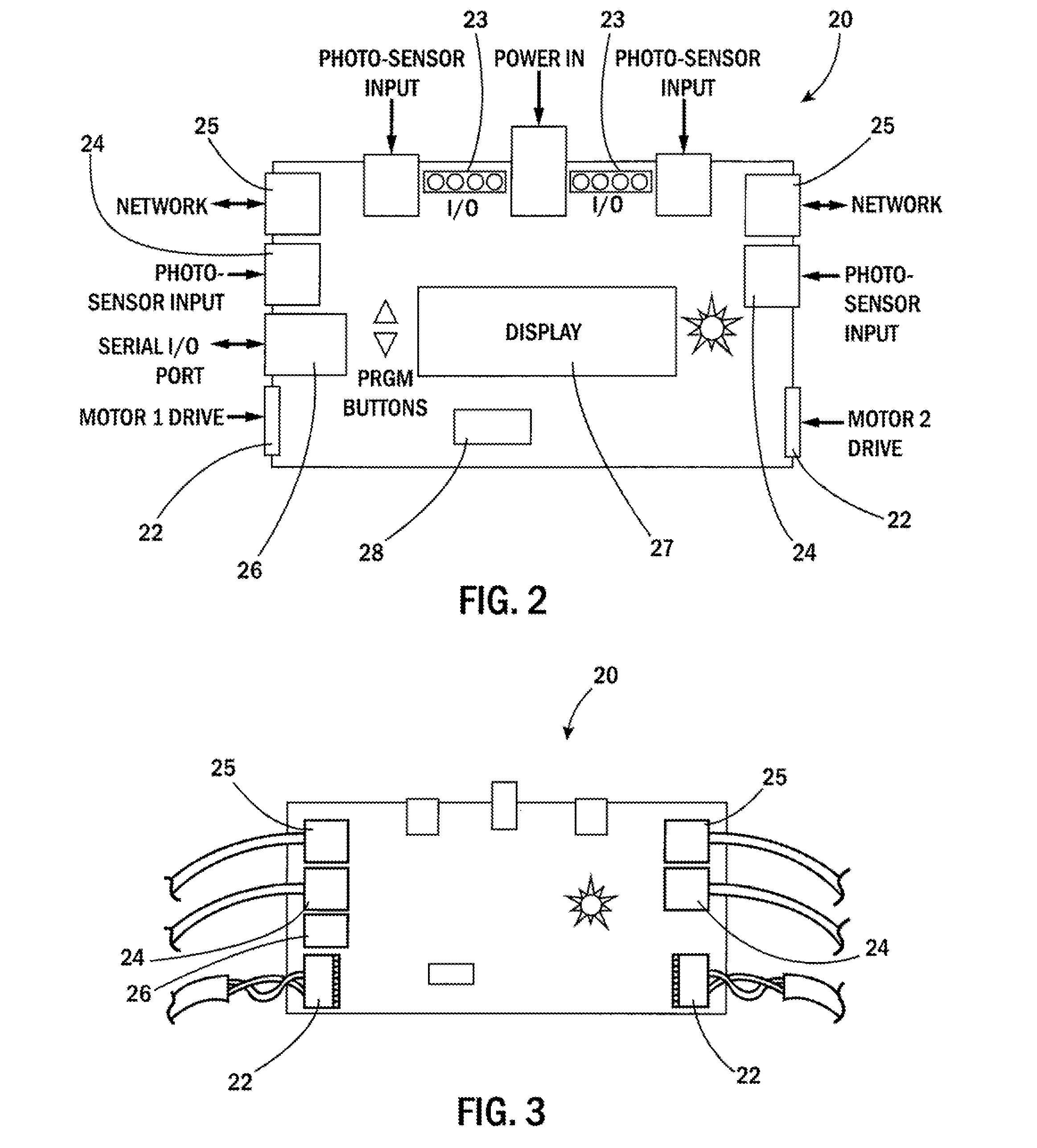
[0029]FIGS. 2 and 3 illustrate a networked, distributed MDR control card 20 with local control capabilities. Accordingly, the inventive card 20 eliminates the need for a central PLC and reduces and / or eliminates the need for wir...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com