Manufacturing method of organic light emitting device, organic light emitting device and electronic apparatus
a technology of organic light and organic light, which is applied in thermoelectric devices, instruments, optical elements, etc., can solve the problems of weak adhesion of color filters that correspond to predetermined subpixels, weak adhesion of color filters, and small pixels area, so as to enhance the adhesion and improve the wettability and affinity (ease of attachment). the effect of the second color filter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
Summary of Organic EL Device
[0053]An organic EL device 100 according to Embodiment 1 is an example of “an organic light emitting device” in the present invention, and is a self-light emitting microdisplay that is suitable for use in a display unit of a head-mounted display that will be described later.
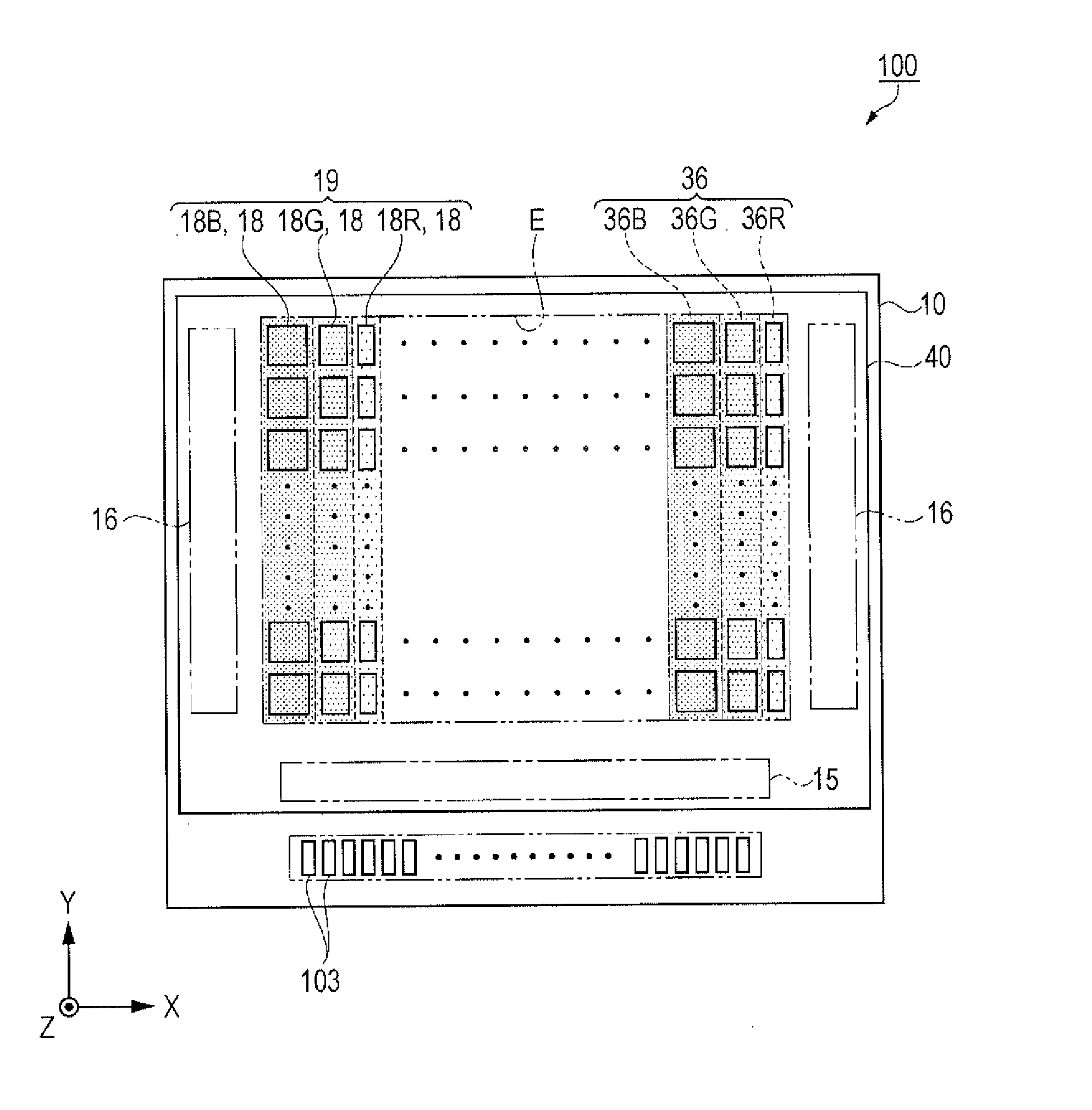
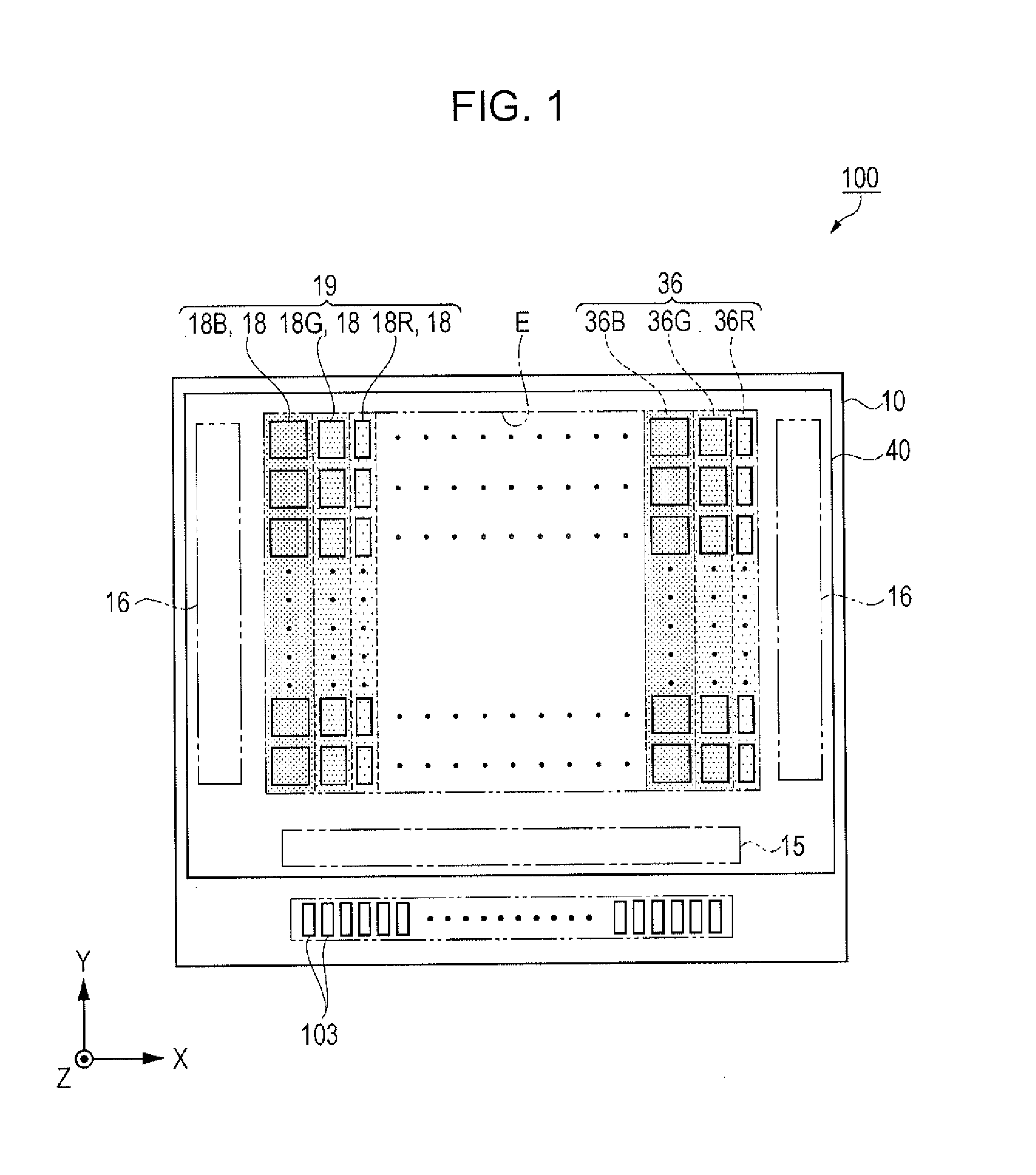
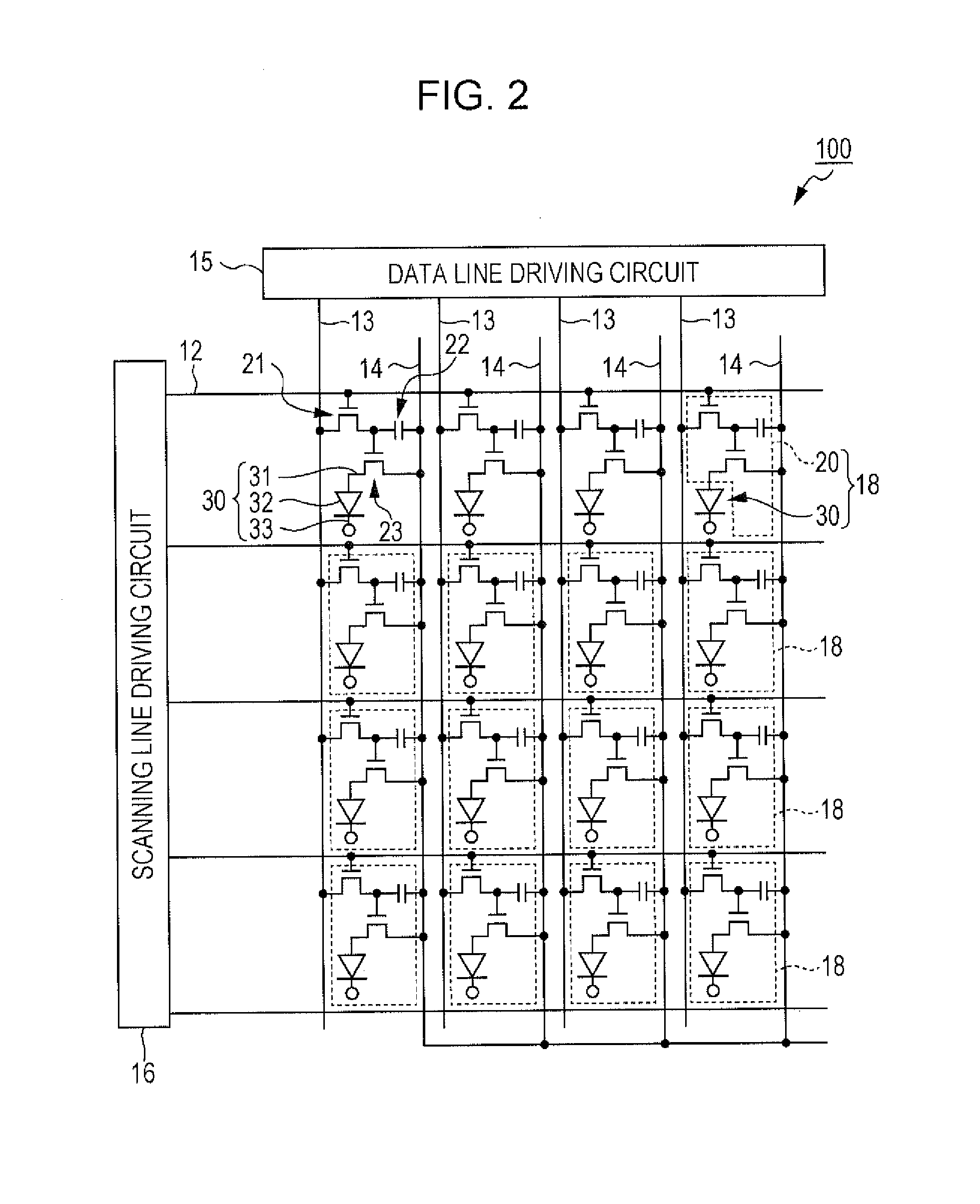
[0054]FIG. 1 is a schematic plan view that shows a summary of an organic EL device according to the present embodiment. FIG. 2 is an equivalent circuit diagram that shows an electrical configuration of the organic EL device according to the present embodiment.
[0055]Firstly, a summary of the organic EL device 100 according to the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIG. 1 and FIG. 2.
[0056]As shown in FIG. 1, the organic EL device 100 according to the present embodiment includes an element substrate 10 and a protective substrate 40. Both substrates are bonded to each other using a resin layer 42 (refer to FIG. 4) that will be described later.
[0057]The element substrate...
embodiment 2
[0135]FIG. 7 is a drawing that corresponds to FIG. 4, and is a schematic cross-sectional view that shows a summary of an organic EL device according to Embodiment 2. FIG. 8 is a process flow that shows a manufacturing method of a color filter layer. FIGS. 9A, 9B, 9C and 9D are drawings that correspond to FIG. 7, and are schematic cross-sectional views that show states after passing each process of the process flow that is shown in FIG. 8.
[0136]In an organic EL device 200 of the present embodiment, convex units 37 are provided between the second sealing layer 34c and the color filter layer 36. This feature is the main point of difference between the organic EL device 200 of the present embodiment and the organic EL device 100 of Embodiment 1.
[0137]Hereinafter, a summary of the organic EL device 200 according to the present embodiment will be described focusing on the points of difference with Embodiment 1 with reference to FIGS. 7 to 9D. Additionally, constituent elements that are th...
embodiment 3
Electronic Apparatus
[0159]FIG. 10 is a schematic view of a head-mounted display as an example of an electronic apparatus.
[0160]As shown in FIG. 10, a head-mounted display 1000 includes two display units 1001 which are provided to correspond to the left and right eyes. By mounting the head-mounted display 1000 on a head part in a manner similar to glasses, it is possible for an observer M to view characters, images and the like which are displayed on the display units 1001. For example, if an image in which a parallax in the left and right display units 1001 is taken into account is displayed, it is possible for the observer M to enjoy a stereoscopic image.
[0161]The display units 1001 are equipped with either the organic EL device 100 or the organic EL device 200 according to the abovementioned embodiments. In the abovementioned embodiments, a defect of the red coloring layers 36R, the bonding strength of which is weakest, peeling away is suppressed, and it is possible to stably manu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com