Porous solid phase for rapidly isolating biological molecules for nucleic acid amplification reaction from biological sample, and use thereof
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Adsorption of a Genetic Material Using a Porous Ceramic Cube and its Use as a Template for RT-PCR / PCR
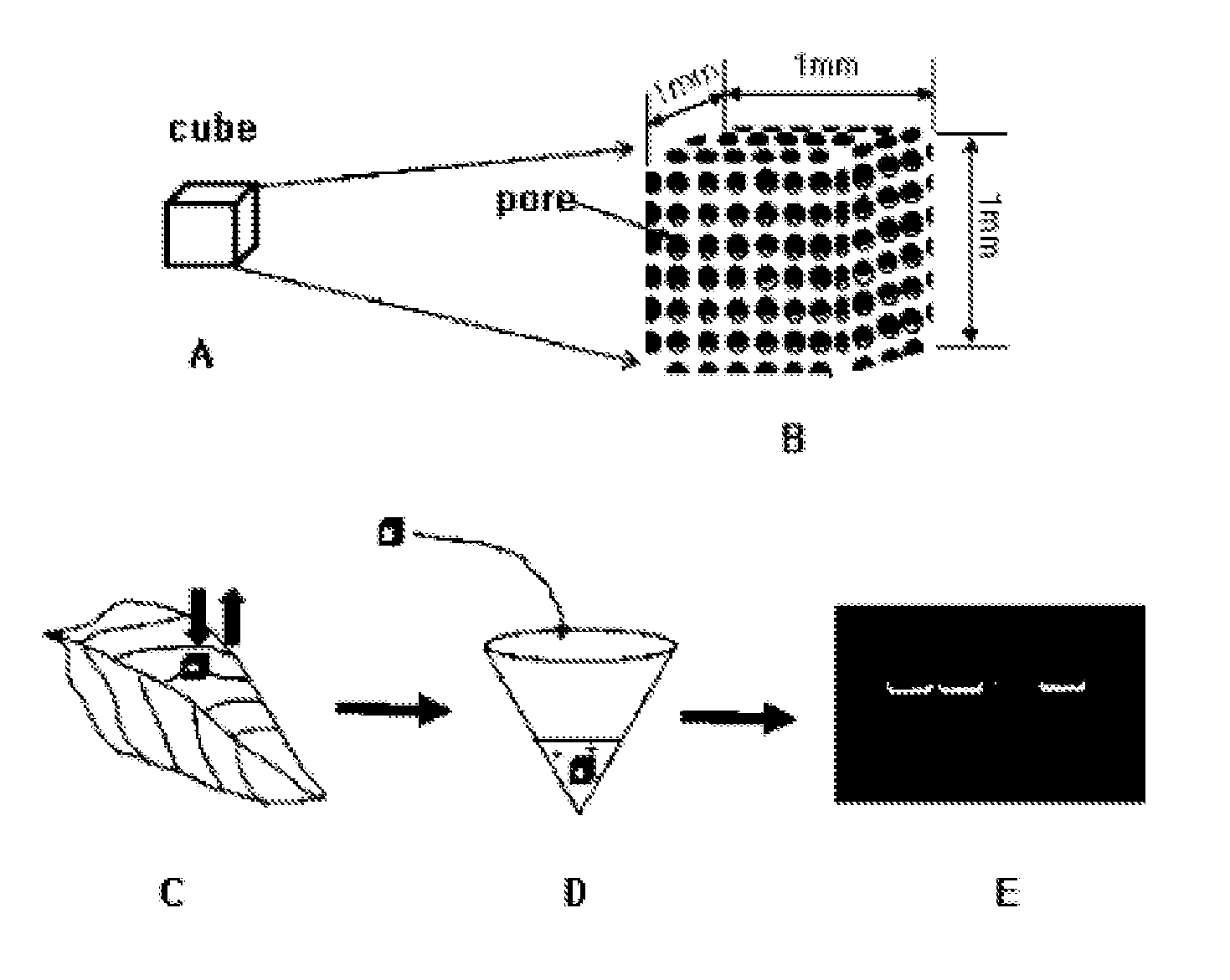
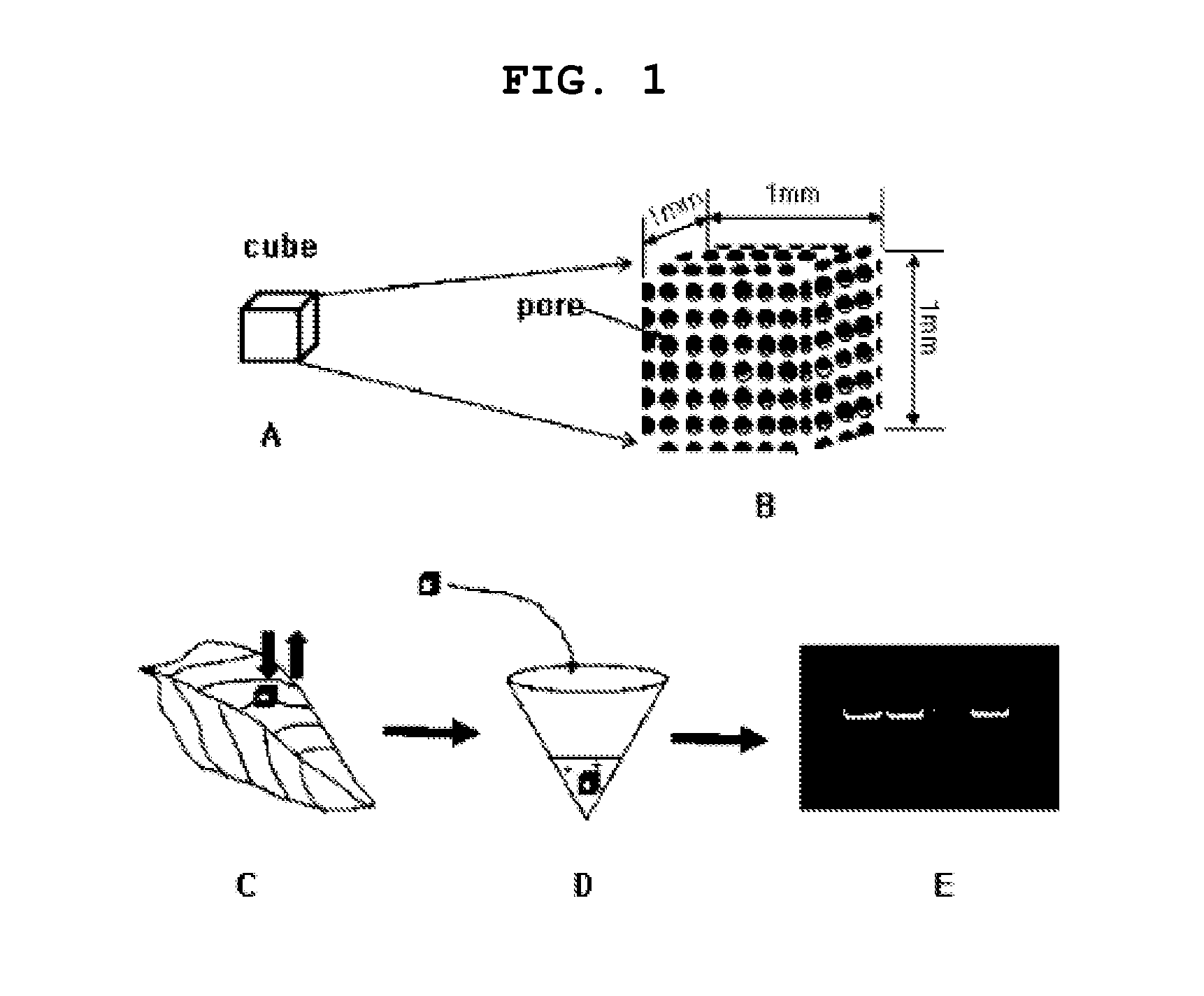
[0068]The adsorption of a genetic material using a porous ceramic cube of the present invention and a diagram illustrating its use as a template for RT-PCR / PCR is shown in FIG. 1. In the present invention, 14 kinds of cubes were manufactured by varying the manufacturing temperature using the main components described in Table 1 so that the size of pores on the surface of the 1 mm3 cube can vary, and the enlarged view of the porous ceramic cube is shown in FIG. 1B. Since cubes are porous smaller substances than the pores can be sucked. The present invention aims at selectively absorbing the desirable ones among various substances generated during rupture of tissues by varying the size of pores (In general, when ceramics are manufactured at high temperature the pore size becomes smaller), that is, providing a cube with an ultrafiltration function to be capable of maximally excluding PC...
example 2
Isolation of a DNA / RNA Template for Nucleic Acid Amplification from a Biological Sample Using a Cut-Out Ceramic Fragment
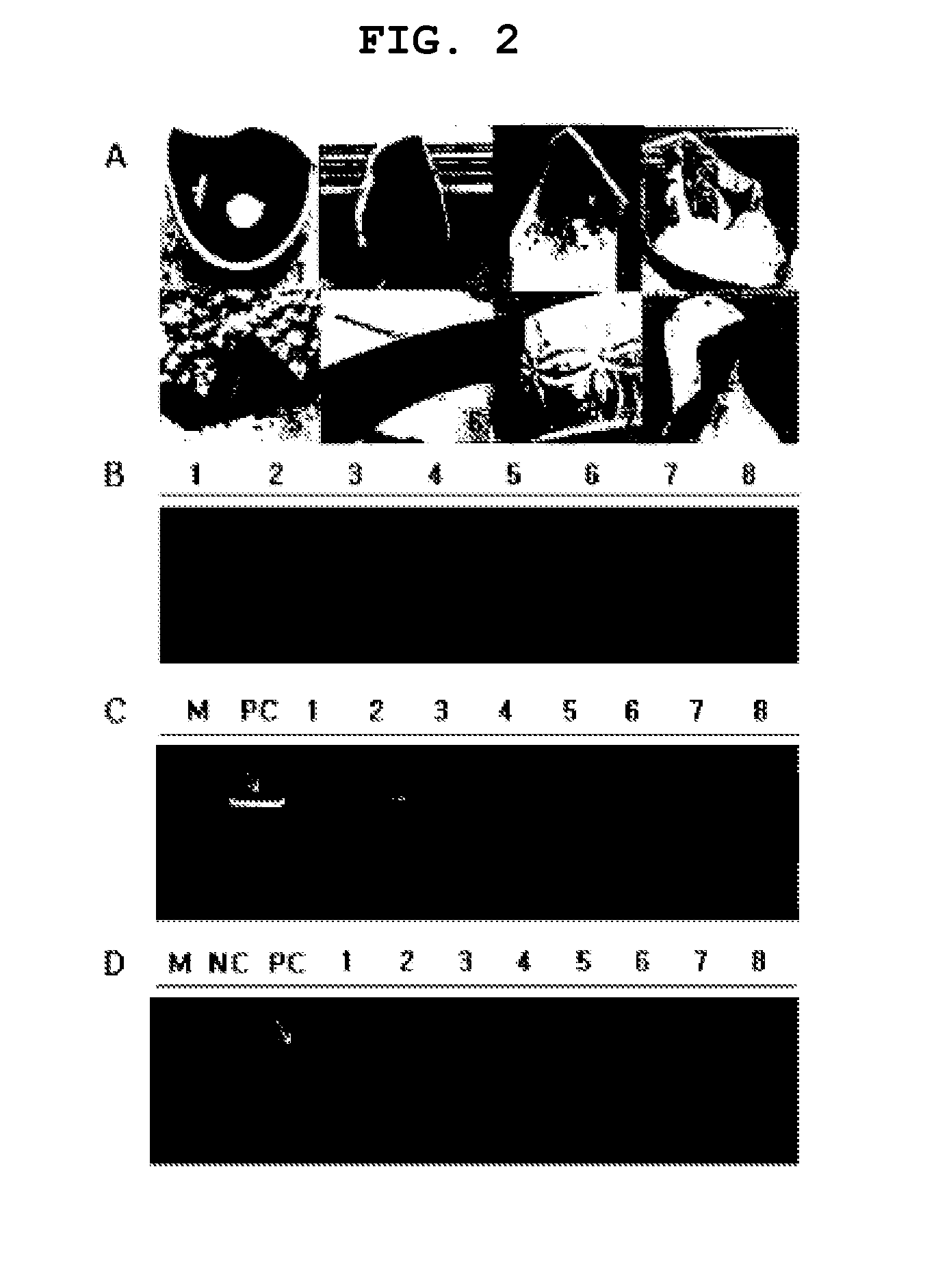
[0070]Seven kinds of cut-out ceramic fragments including blue and white porcelain was broken into small pieces using a nipper, and the fragments with a volume of about 1 mm3 selected from the unglazed area were used as an absorptive material for a genetic material. For the 5th ceramic fragment in FIG. 2A, it was divided into yellow and grey according to the area coated with glaze, and the yellow fragments and the grey fragments obtained respectively therefrom were indicated as 5 and 6, respectively. Each ceramic fragment was placed on top of Capsicum annuum CM334 pepper leaves, lightly pressed with a flat portion on the rear side of metal tweezers to obtain gDNA. One ceramic fragment keeping gDNA was added into each PCR tube, which was already added with a primer premix capable of verifying molecular markers related to the trichomes of pepper. The PCR premix consis...
example 3
Examination of an Absorption Rate of Biological Molecules According to the Types of Porous Ceramic Cubes of Oxide Material
[0073]The picture of the surfaces of the respective porous ceramic cube manufactured using the oxide described in Table as a main component enlarged under scanning electron microscope (SEM) is shown in FIG. 3. Since the surface and pore size vary according to the main components of ceramics and their manufacturing temperature, they should be manufactured to obtain the optimum pore size and number of the ceramic cubes in order to improve the absorption rate of the target biological molecules.
TABLE 1SignMain ComponentManufacturing Temperature (° C.)1Al2O314502Al2O315503Fe2O38004Fe2O38505Fe2O39006LTCC6507LTCC7508LTCC8509PbO100010PbO115011PbO125012ZnO80013ZnO90014ZnO1000
[0074]① Regarding Total RNA Isolated from CMV-Infected Capsicum annuum CM334 Pepper Leaves and Genomic DNA Isolated from CM334 Pepper
[0075]In order to examine the absorption efficiency of biological m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com