Aluminum deposition devices and their use in spot electroplating of aluminum
a technology of aluminum deposition device and spot electroplating, which is applied in the direction of contact device, electrolysis component, electrolysis process, etc., can solve the problems of inefficiency of aqueous electroplating, voc emissions, and inability to electrodepose aluminum nor its alloys from aqueous solutions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
Introduction
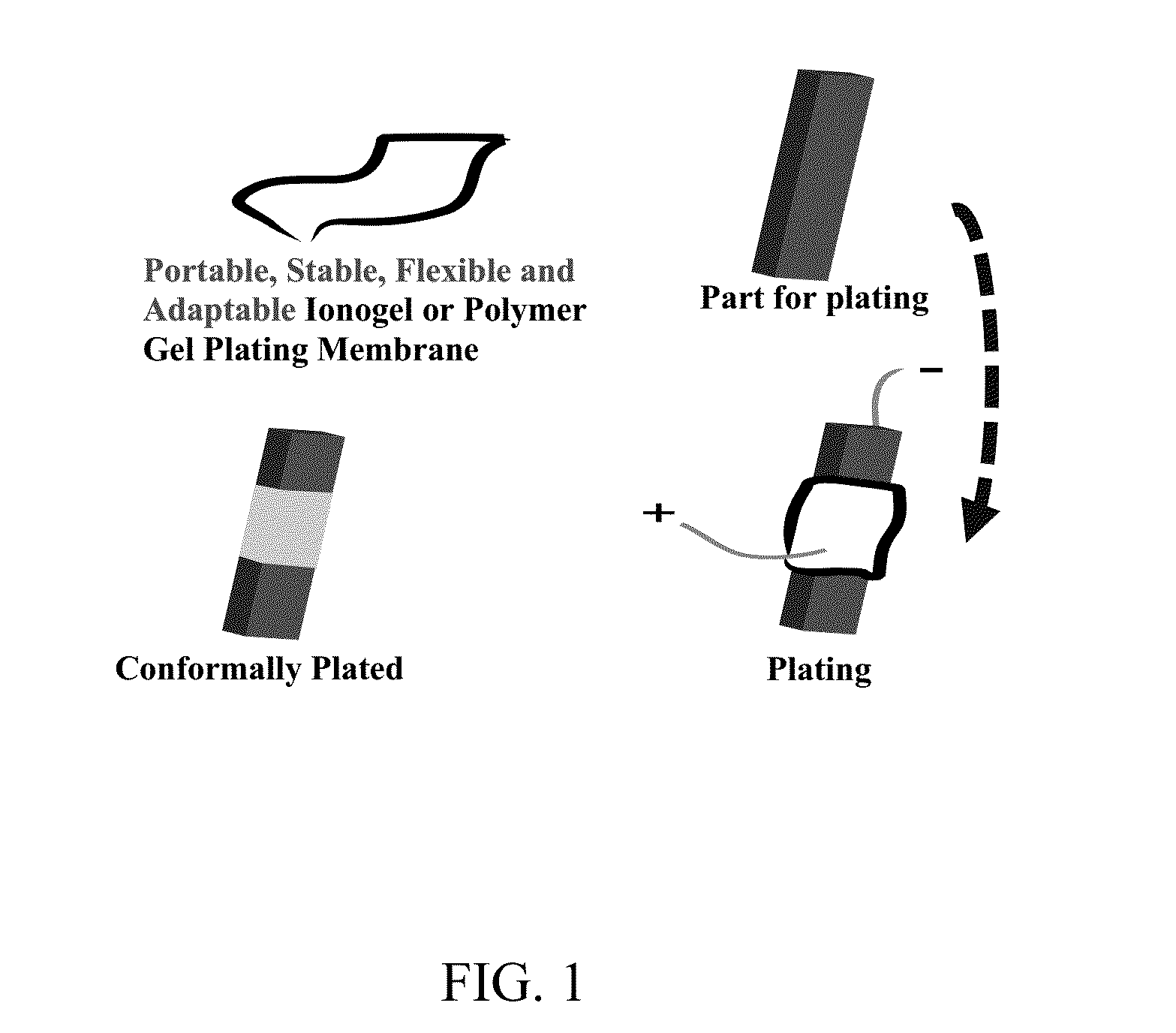
[0060]By one methodology, the moisture sensitivity of chloroaluminate-based ionic liquids was significantly reduced by forming polymer gel electrolytes (polymer membranes), either by impregnating liquid electrolytes into preformed membranes, or by co-casting polymer and liquid electrolytes, or by copolymerization of monomers in the presence of plasticizers. For more practical applications, the polymer gel membranes can be cast directly onto aluminum foil, and the resulting layered composite wrapped around a substrate to perform the plating. In this configuration, the aluminum foil serves as the anode and the substrate as the cathode during the electroplating process. A general depiction of the process using a polymer gel electrolyte is provided in FIG. 1.
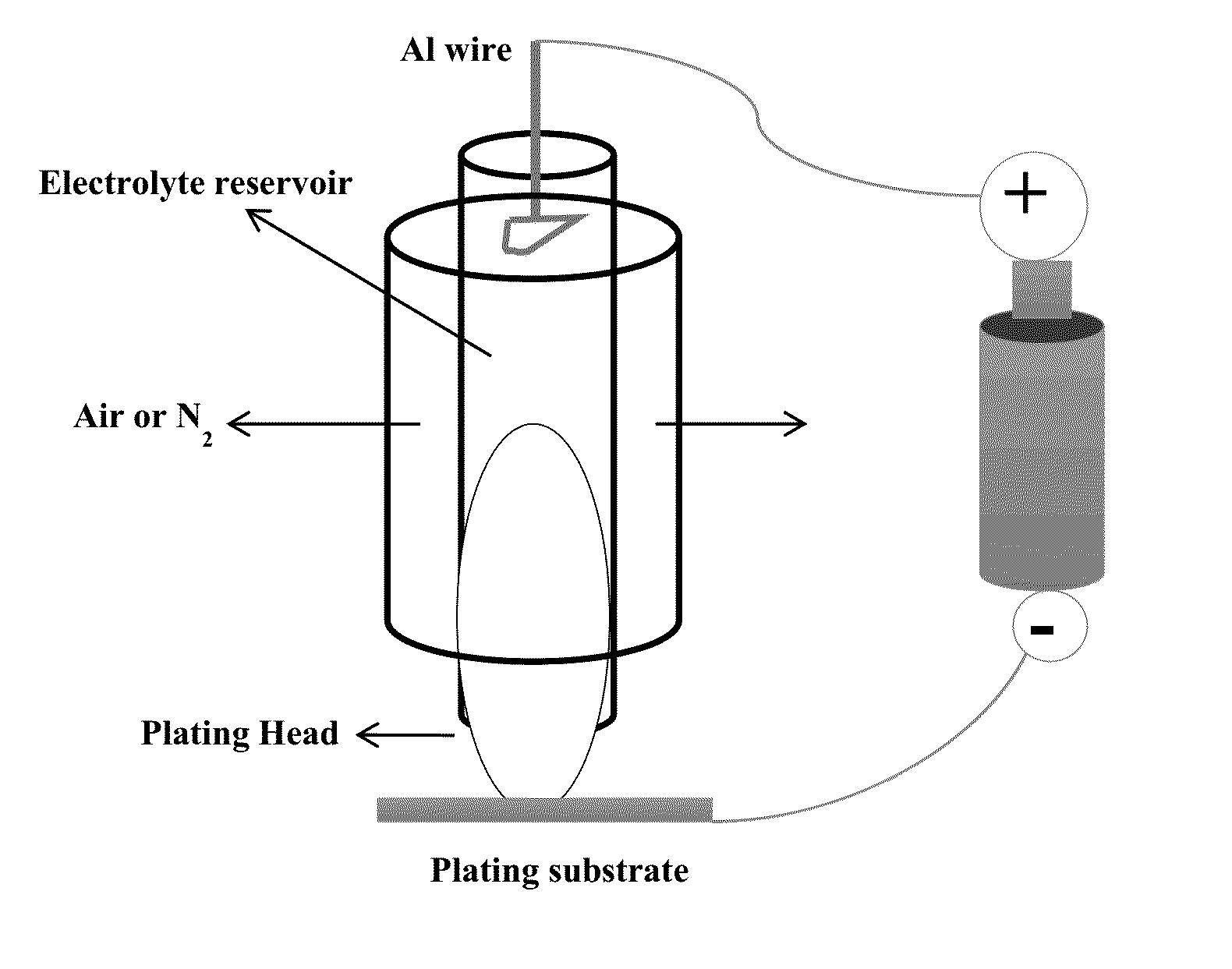
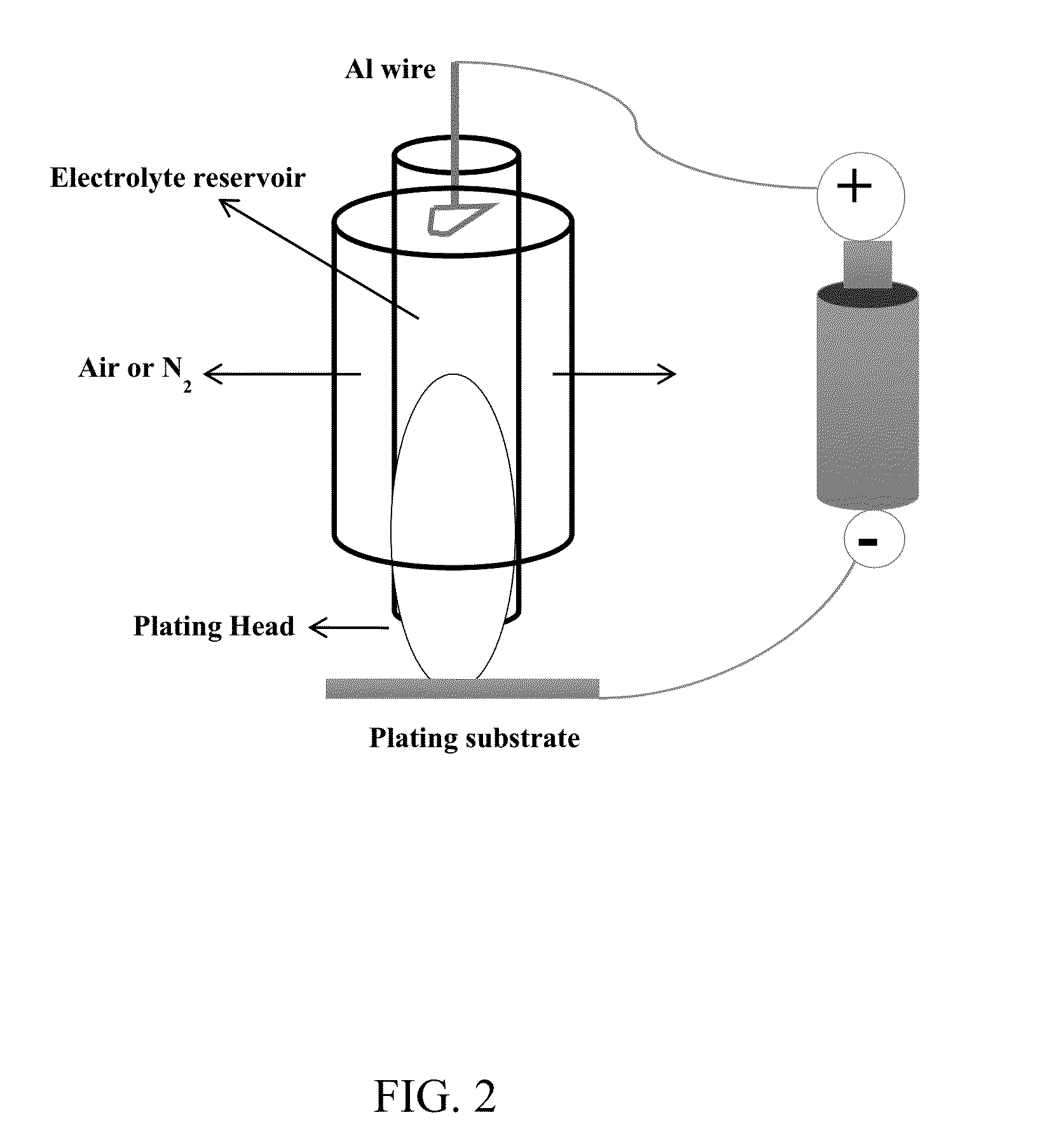
[0061]By another methodology, the moisture sensitivity of the chloroaluminate-based ionic liquids was significantly reduced by sealing the ionic liquid electrolyte inside the reservoir of a portable plating brush. The de...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com