Detection and quantification of donor cell-free DNA in the circulation of organ transplant recipients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
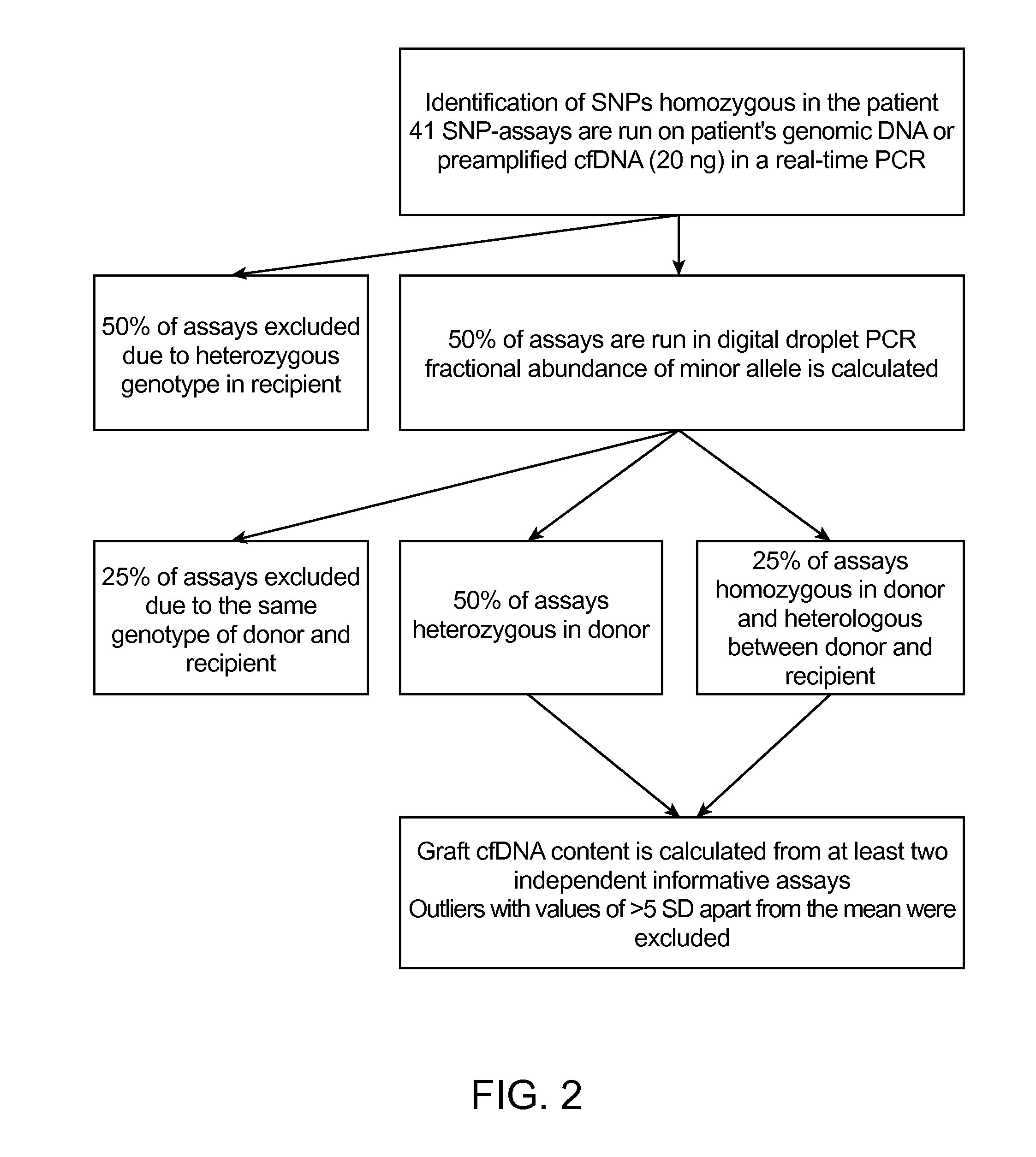
Quantification of Donor Cell-Free DNA
Methods
SNP Assays
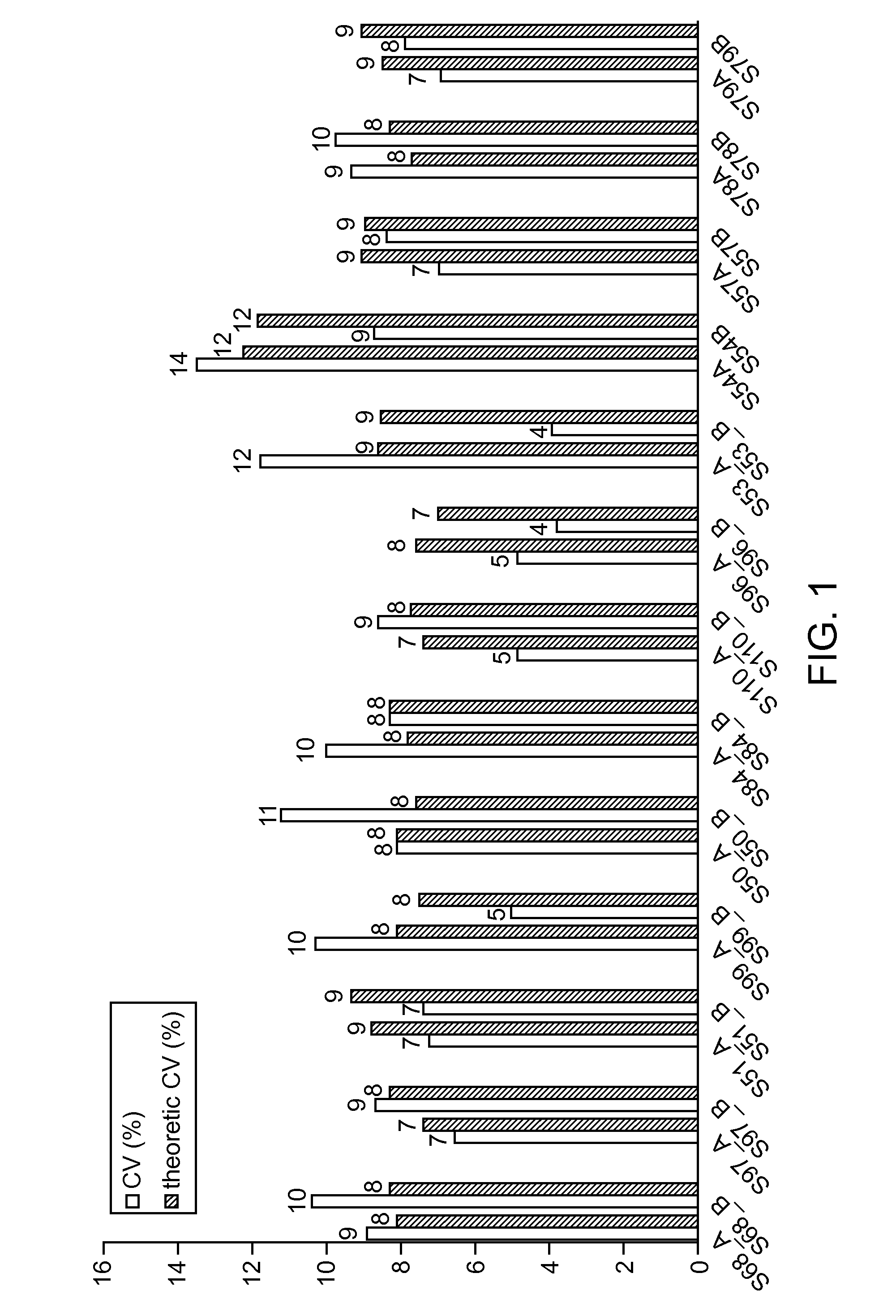
[0072]SNPs were selected from public databases considering those which show a known and validated minor allelic frequency of >40% in Caucasians and >45% over all reported ethnicities. As a next step, SNP that are in or directly adjacent to a repetitive element were eliminated. The remaining SNPs were then investigated for their usefulness in a probe hydrolysis assay. This was done in silico by using thermodynamic calculations (Schlitz & von Ahsen, Biotechniques 27:1218-1222, 1224, 1999) to optimize the binding differences for the two probes that hybridize to the two alleles at the desired temperature of 65° C. at standard PCR buffer conditions (e.g. 0.18 mol / L salt and 0.5 μmol / L DNA / primer). Because the slope of a dsDNA probe melting curve is mainly dependent on the enthalpy of the probes (Marky & Breslauer, Biopolymers 26:1601-1620, 1987), the latter dominates the selection for a maximized difference of free Gibbs energy betwee...
example 2
Further Analysis of cfDNA-Quantification of GcfDNA as Copies / mL
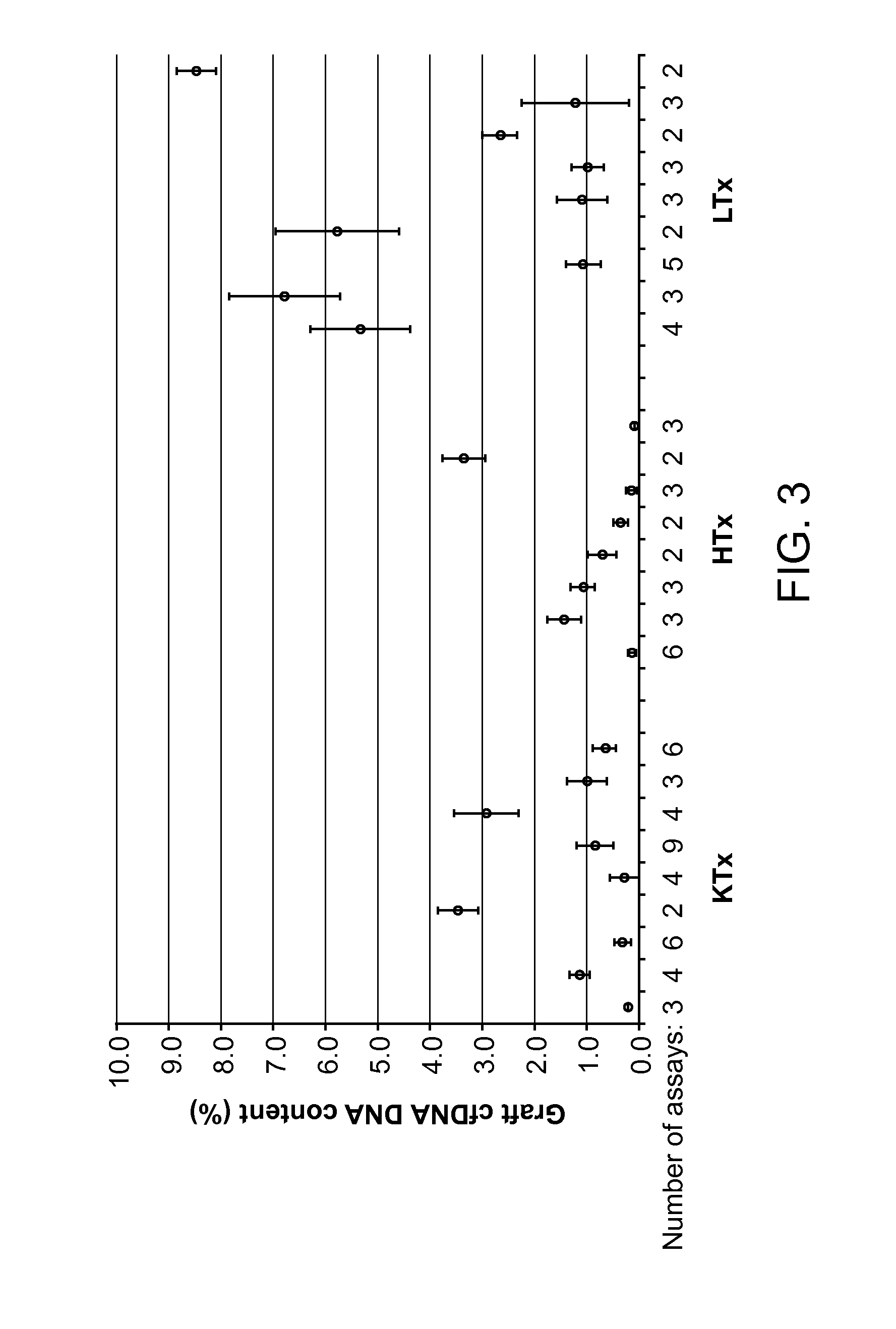
[0085]Where the ratio of graft to host cfDNA has analytical advantages by eliminating disturbing variables, such as DNA extraction efficiency, variablities in host cfDNA may obfuscate the view on the engrafted organ. The early phase after transplant was used as model to compare the percentage or absolute plasma concentration of GcfDNA is a more valuable graft integrity measure.
Materials and Methods
[0086]Blood samples from patients after liver (LTx), heart (HTx) and kidney (KTx) were drawn according to IRB approved protocols. Samples (288) from 23 LTx were included for evaluation of the potency to measure copy numbers of GcfDNA in the initial post-operative phase. For the cfDNA extraction investigations, pools from normal volunteers were used.
[0087]EDTA-whole blood was drawn and processed within 4 hours. For LTx patients, cfDNA tubes (9 mL) Streck Inc. were used for a subset of samples. Extraction of cfDNA from 1-2.5 ml o...
example 4
Use of GcfDNA SNP Analysis to Optimize Immunosuppressive Therapy
[0092]Immunosuppression minimization requires tools to assess the minimal necessary exposure in individual patients. Drug concentrations and conventional markers are not precise predictors for this purpose. Therefore, in the present study a new practical and cost-effective method for determination of graft-derived cell-free DNA (GcfDNA) was investigated as a sensitive marker of graft injury after liver transplantation (LTx).
[0093]Methods: GcfDNA was quantified (n=171) using droplet digital PCR assay in N=12 adult patients predominantly during the early phase (days 8-30) after LTx to determine the amount of graft DNA. Values obtained in patients with various causes of graft dysfunction (i.e. hepatitis C infection [HCV+], cholestasis, low tacrolimus concentrations, and rejection) were compared to a published cut-off (10%) from a historical control group (N=10) of stable adult LTx patients without any clinical or laborator...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com