Nickel-based alloy, method and use
a technology of nickel-based alloys and alloys, applied in the field of nickel-based alloys, methods and use, can solve the problems of increasing the depth of oil and affecting the chemical homogeneity of products, and achieve the effects of reducing chemical irregularities, and reducing the number of alloys
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Implementing the Method
[0049]The metal mass which the invention relates to is preferably melted in an electric arc furnace, refined in A.O.D. (Argon Oxygen Decarburization) so as to obtain an intense desulphurisation, thorough deoxidisation and a very restricted analytical range of compositions to ensure repeatability of the mechanical and corrosion properties.
[0050]The refining process could be completed by at least one of the following operations:
[0051]further elaboration of liquid steel at V.I.D.P. (Induction Vacuum Degassing and Pouring);
[0052]source casting in moulds suitable for subsequent forging;
[0053]source casting of ingots intended for subsequent remelting V.A.R. / E.S.R. (Vacuum Arch Remelting / Electro Slag Remelting).
[0054]According to a variant, the ingots obtained after V.A.R. or E.S.R. remelting may be subjected to appropriate homogenisation heat treatment and then transformed into blooms through use of a forging press, for example having two integrated, fully automated...
example 2
n of the Nickel-Based Alloy of the Invention with Traditional Alloys Currently Used
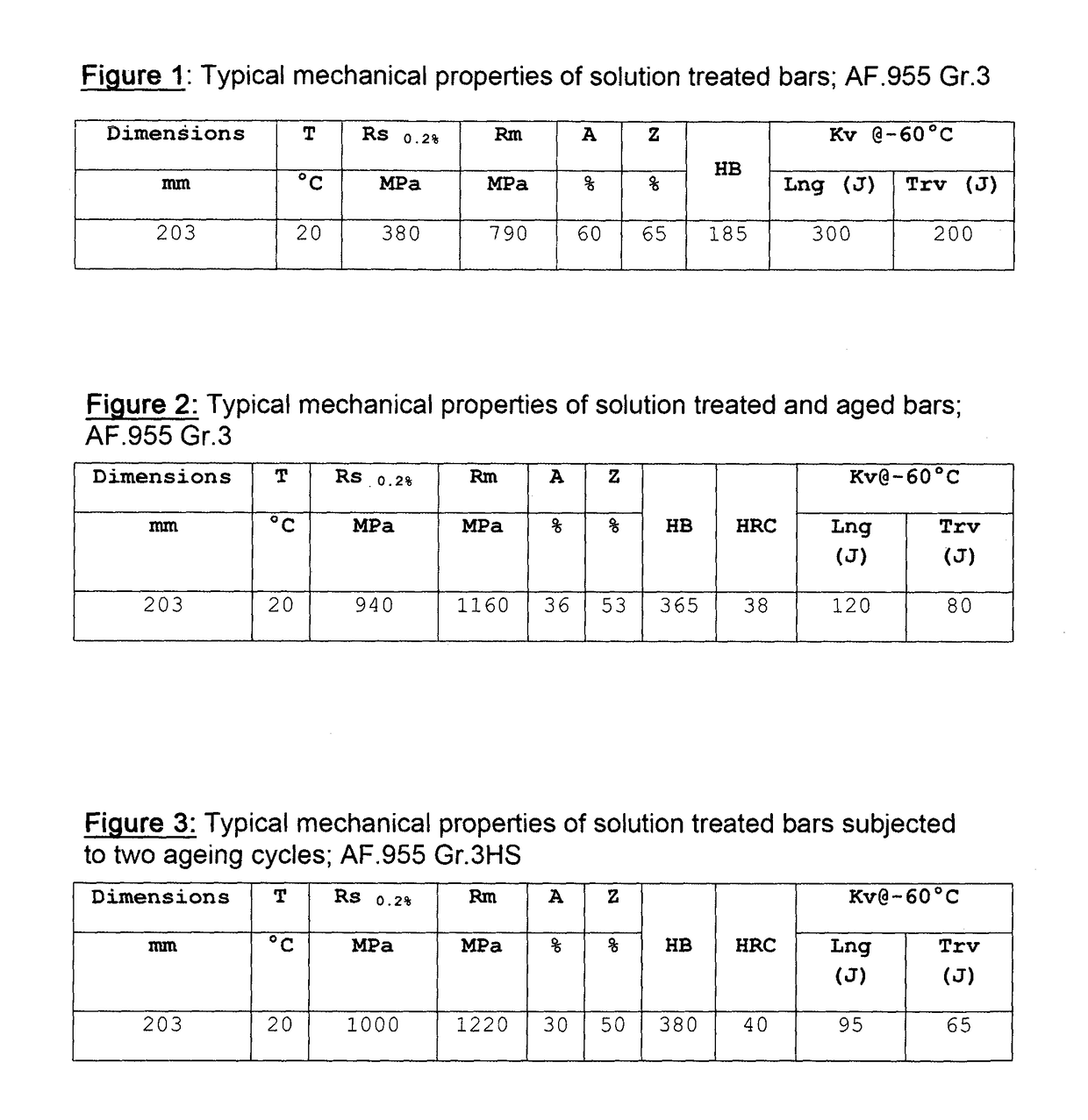
[0058]The nickel-based alloy of the present invention, after heat transformation in the temperature range 1000-1160° C. and solution treatment in the range 1030-1080° C., typically has the mechanical features shown in FIG. 1.
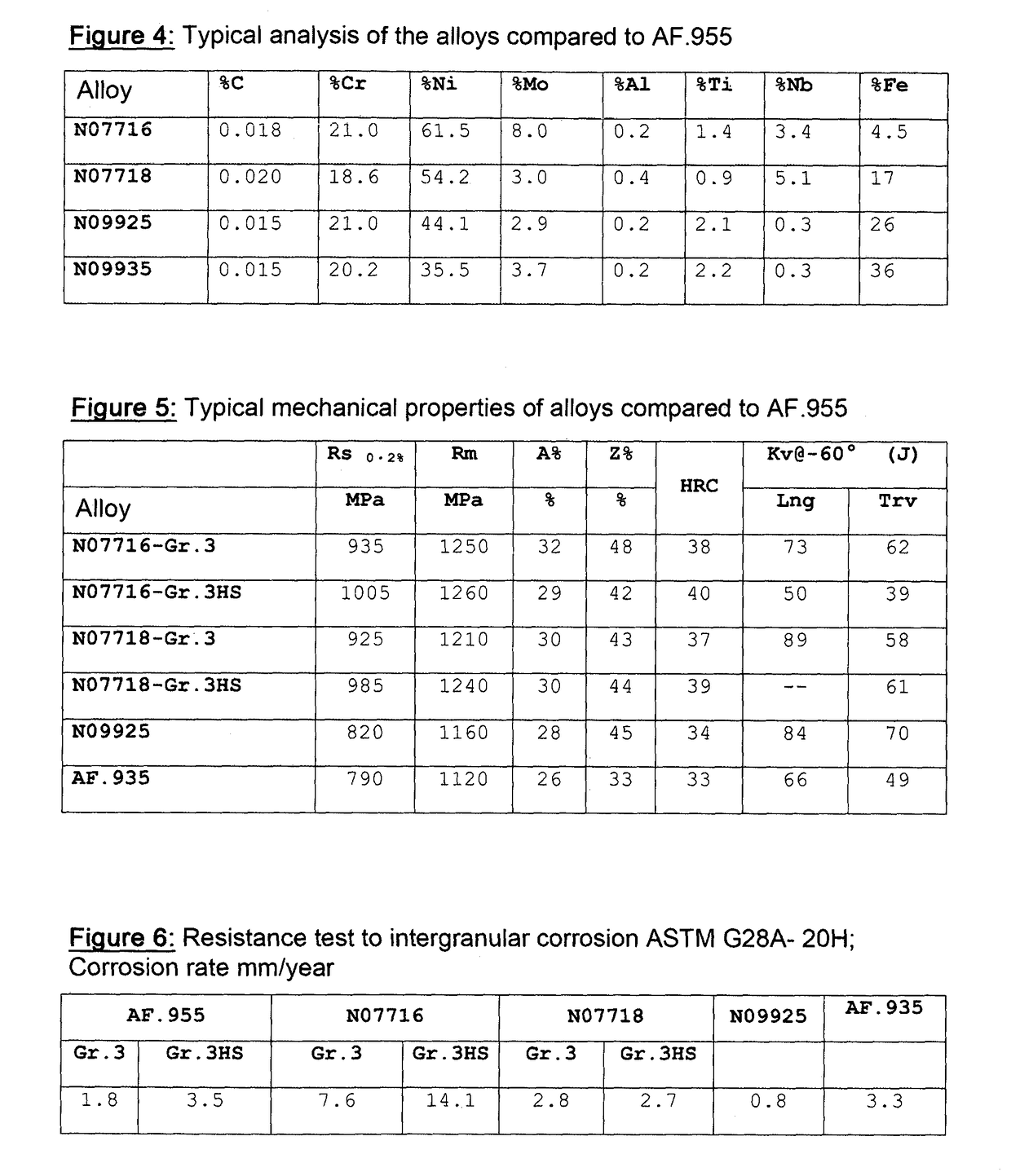
[0059]The nickel-based alloy of the present invention (called “AF.955”), after solution treatment as in the above paragraph, if aged in the temperature range 720-780° C. for 3-8 hours and air cooled (or equivalent cooling, or in case of faster cooling) typically has the mechanical features specified in FIG. 2 and the resistance data to intergranular corrosion and pitting referred to in FIGS. 6-7-8.
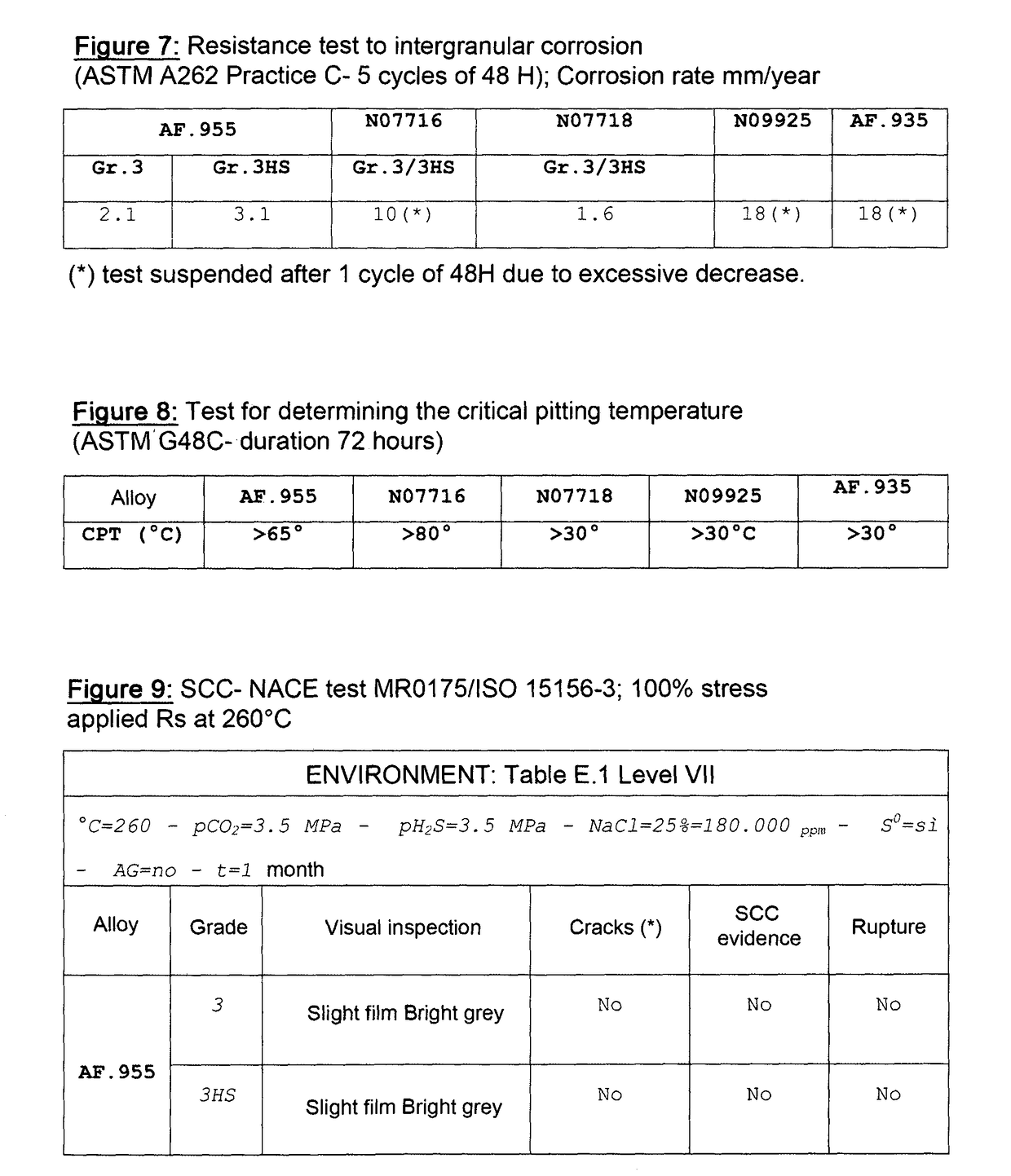
[0060]The alloy, after a second ageing at 600°-640° C. for a time ranging from 4-10 hours, followed by air cooling, presents the mechanical characteristics specified in FIG. 3, and the resistance to intergranular corrosion and pitting referred to FIGS. 6-7-8.
[0061]The results of the SCC ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com